Genovesa
Animals/Wildlife





Landscape/Views




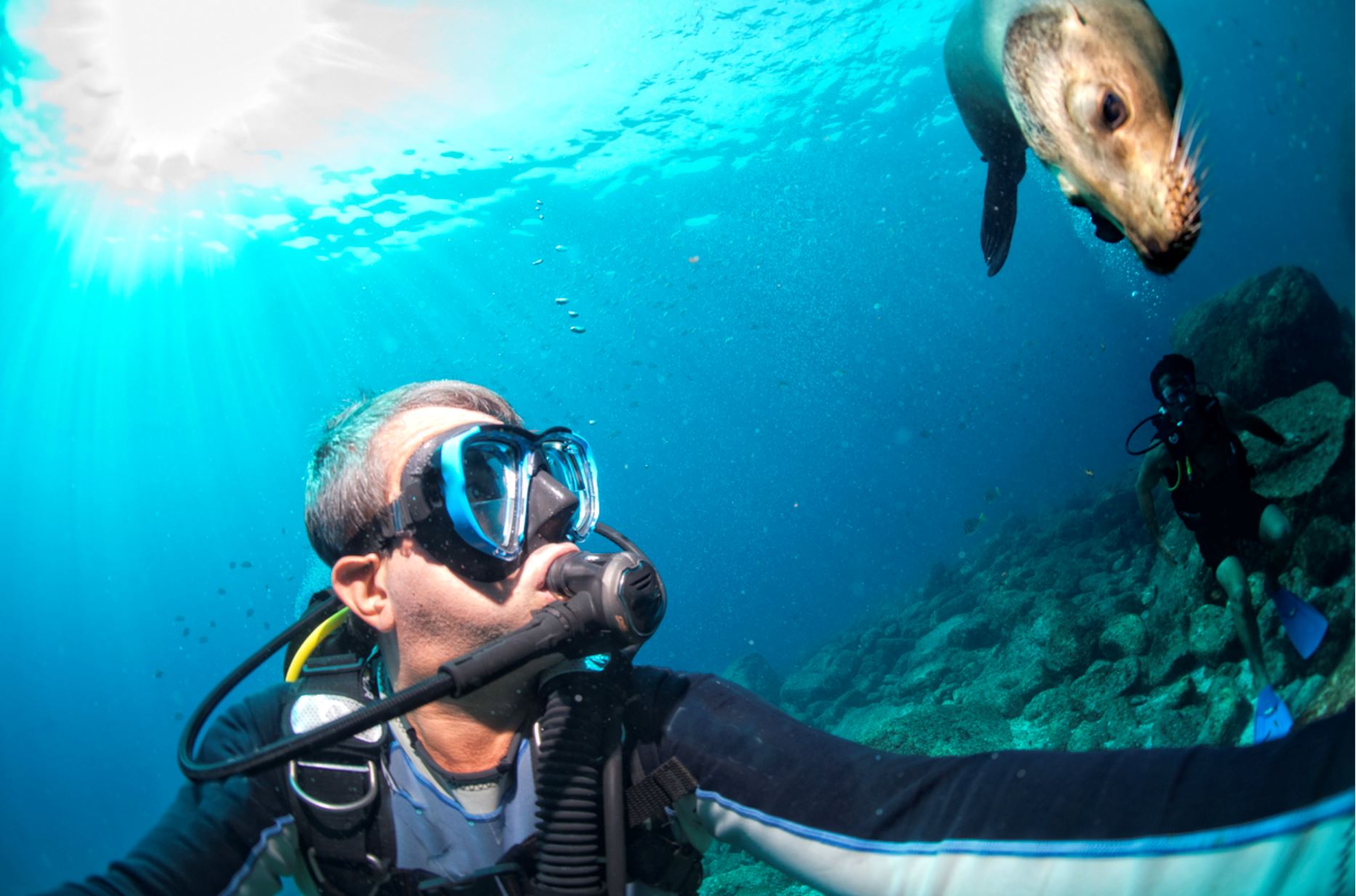
Snorkeling




Beaches




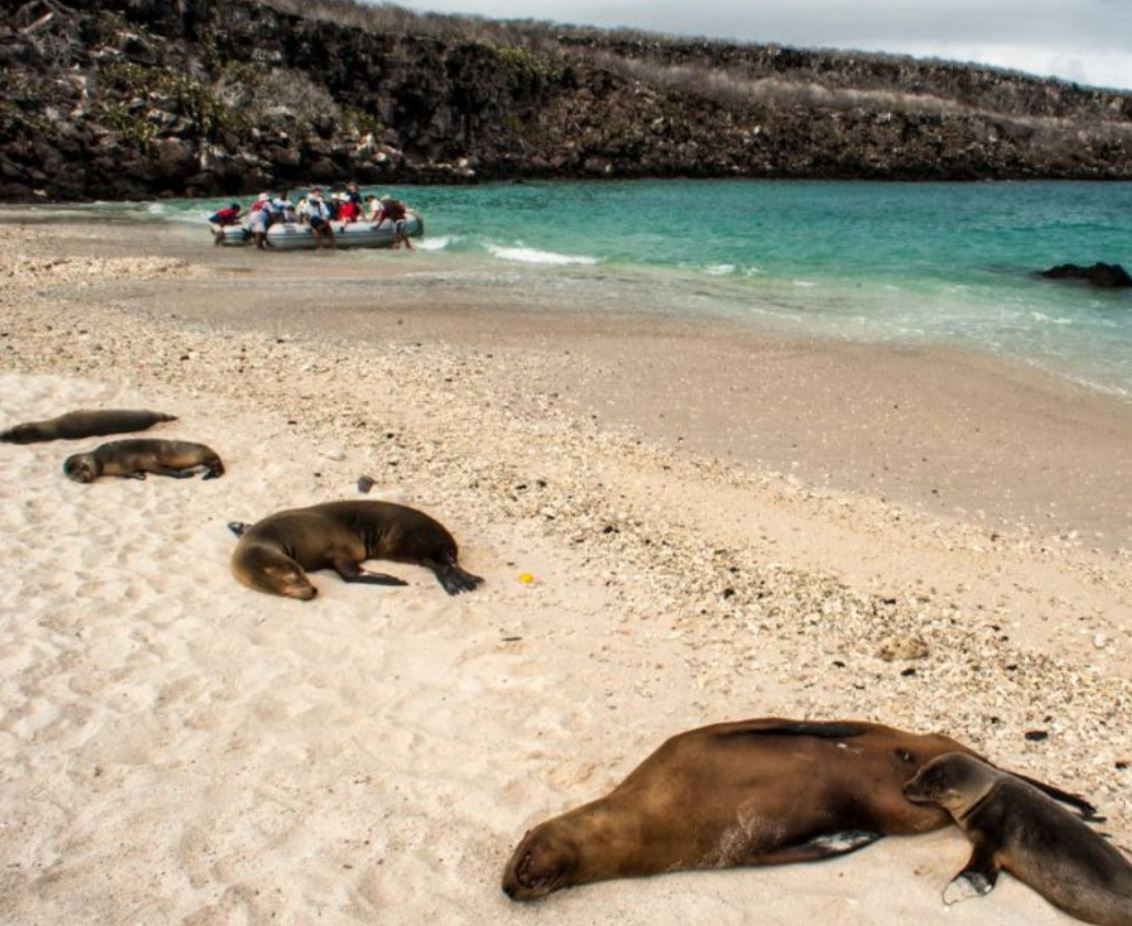
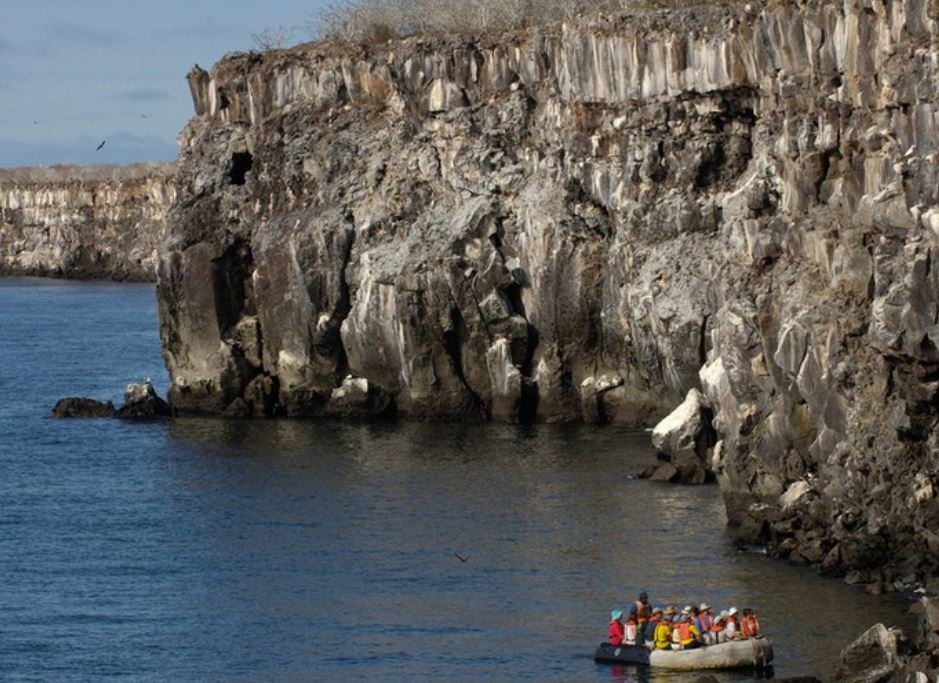
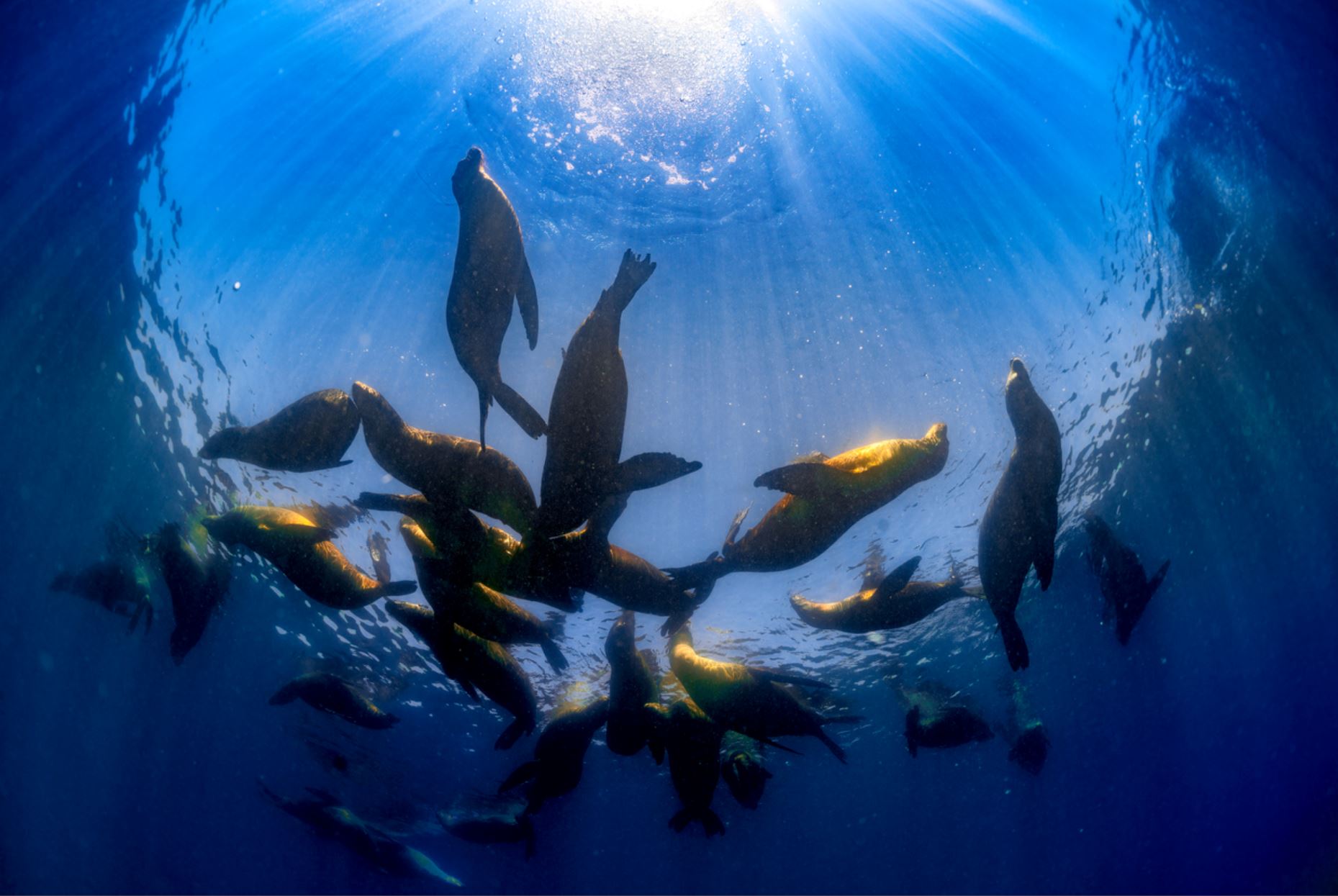
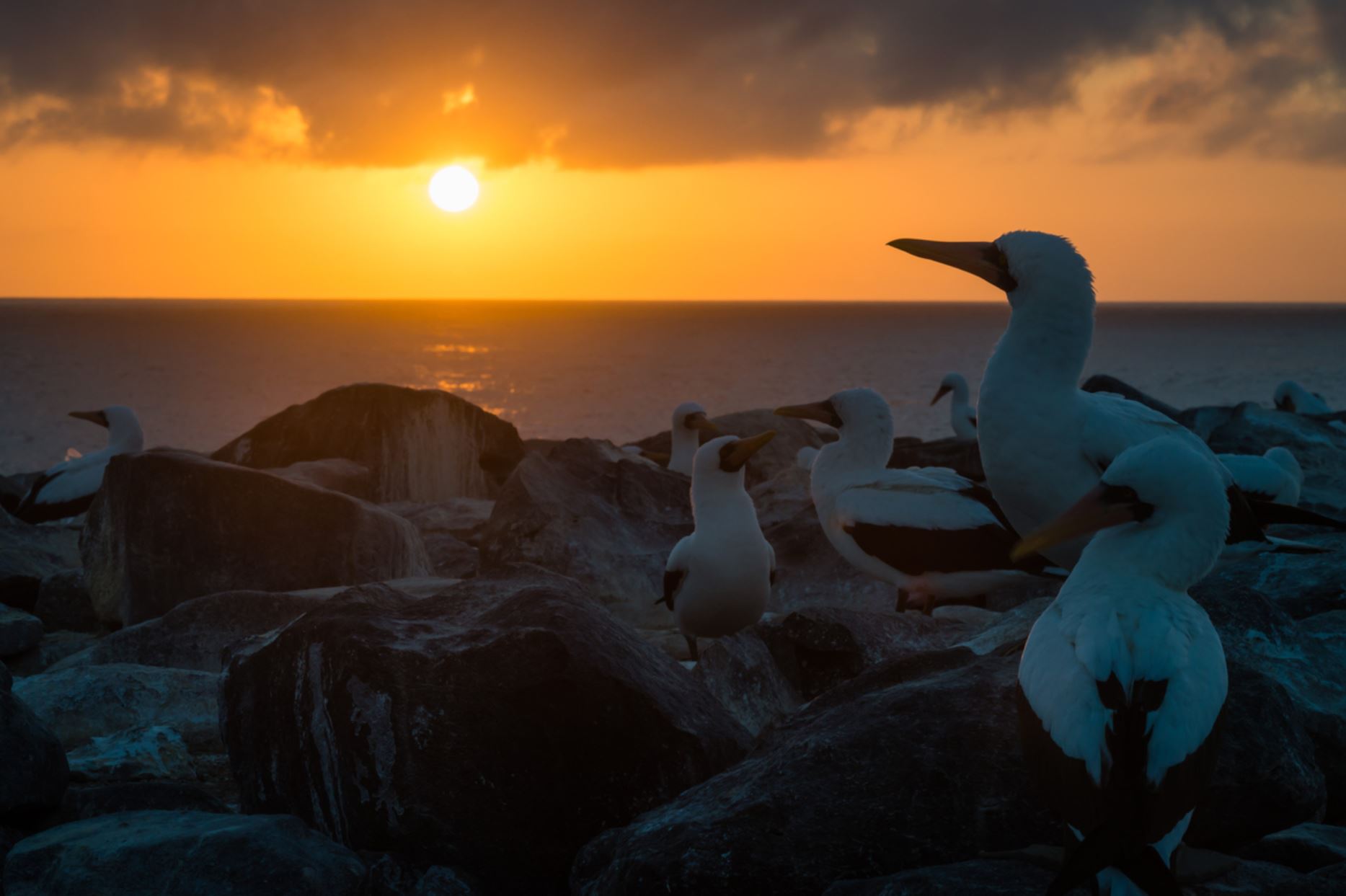
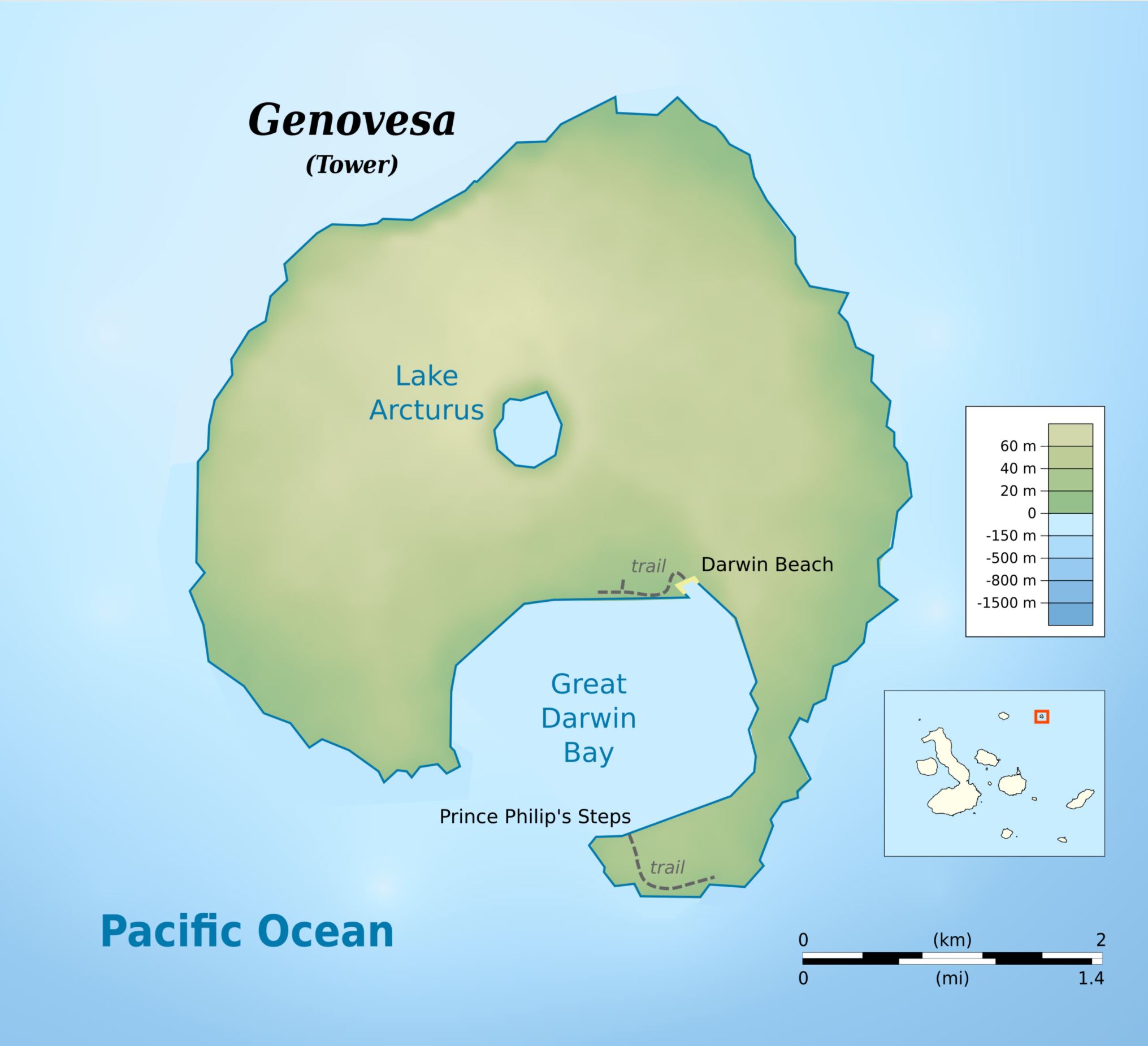
Genovesa Island (Spanish: Isla Genovesa), named after the Italian city of Genoa, in honor of Christopher Columbus, (referred to in English as Tower Island) is a shield volcano in the Galapagos Islands in the eastern Pacific Ocean. The island occupies about 14 square kilometres (5 sq mi), and its maximum elevation is 64 m (210 ft). The horse-shoe shaped island has a volcanic caldera whose wall has collapsed, forming the Great Darwin Bay, surrounded by cliffs. Lake Arcturus, filled with salt water, lies in the centre, and sediment within this crater lake is less than 6,000 years old. Although no historical eruptions are known from Genovesa, there are very young lava flows on the flanks of the volcano. Genovesa is one of the most precious islands to visit in a Galapagos cruise! Genovesa is also known as the “Bird Island“, and it most certainly lives up to certain standard in a spectacular way. Passenger will have the opportunity to enjoy the most representative birds of Galapagos as: Puffball–chicks, white both yellow–crowned and lava herons, Red footed boobies contrasting with the Nazca booby and also the Sawllow–tailed gulls, the only nocturnal gulls in the world that will be nesting at the cliff’s edge.
Visitors sites: Darwin Bay, Prince Philp´s Steps
Pictures
Highlights / Places to Visit
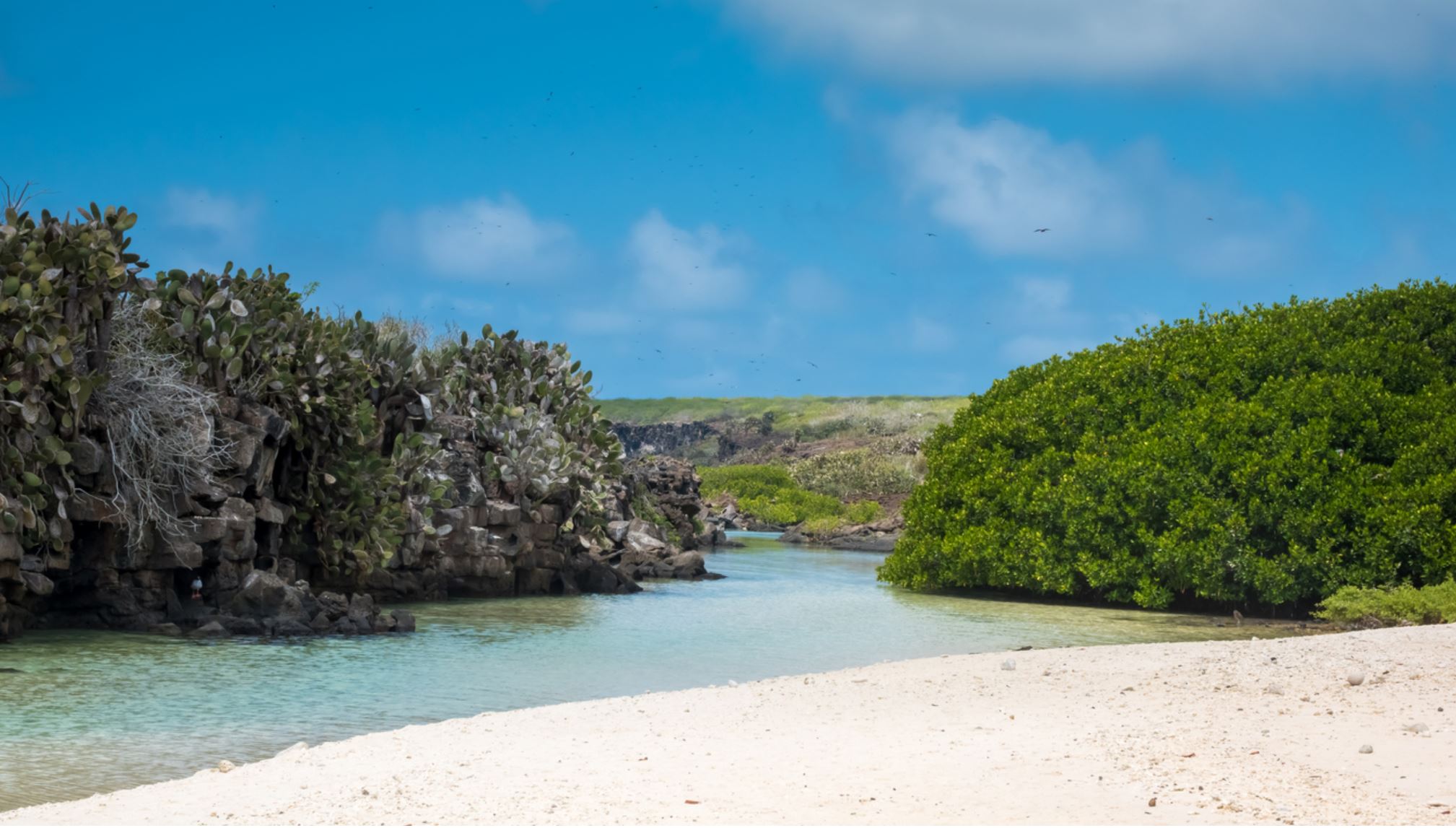
Darwin Bay
Sandy coral beach with a great viewpoint of the bay. From within the flooded caldera of Tower Island, we set foot onto a sandy beach to be greeted by swallow-tailed gulls often said to be the most beautiful gull in the world. Our short, flat, trail leads us past stands of mangroves and saltbush on which we have our best possible look at nesting red-footed boobies and great frigatebirds. At the tidal lagoon, we may also see the rarest gulls in the world, our very own, endemic lava gulls.
- Activities: 45 min kayaking / 25 min glass-bottom boat / 1-hour deep or beach snorkeling / 1 hour 15 min hike
- Highlights: Swallow-tailed and lava gulls, frigatebirds (minor & magnificent), mockingbirds, yellow-crowned night herons, large beaked cactus finch, the smallest marine iguanas of the islands.
Prince Philip´s Steps
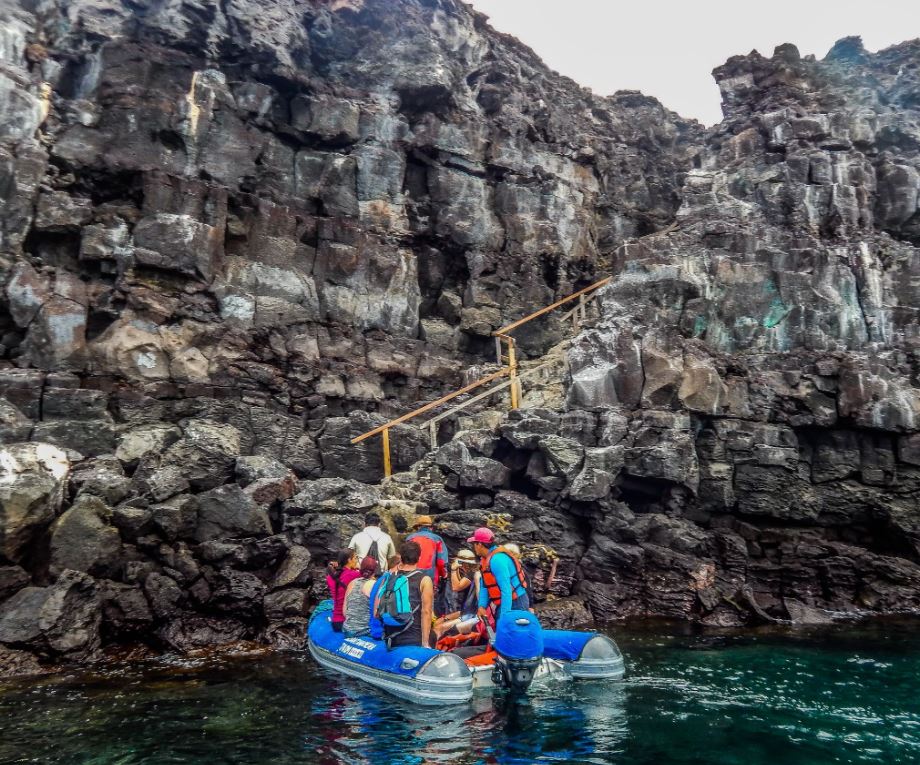
Prince Philip's Steps is an amazing steep path climbing up to 25m high cliffs. It was named after the husband of Queen Elizabeth II, Prince Philip, who visited the island twice. The path will lead you through a diversity of lively seabird colonies, including Nazca, blue-footed and red-footed boobies, Galapagos pigeons and owls. At the top, you're met by a striking panorama of lava plains. You can reach this spot by taking a dinghy ride and at the landing site you'll most likely be welcomed by a small colony of fur seals.
Difficulty: Moderate
Disembarkation: Dry Landing
Interactions: Hiking
Highlights at Prince Philip's Steps
- Panoramic View
- Birdwatching
Animals:
Blue-Footed Booby, Darwin’s Finches, Galapagos Dove, Galapagos Frigatebirds, Galapagos Fur Seal, Galapagos Hawk, Galapagos Land Iguana, Galapagos Lava Gull, Galapagos Marine Iguana, Galapagos Mockingbird, Galapagos Petrel, Galapagos Shearwater, Galapagos Short-eared Owl, Nazca Booby, Red-Billed Tropicbird, Red-Footed Booby, Swallow-Tailed Gull
Animals that can be seen on the island
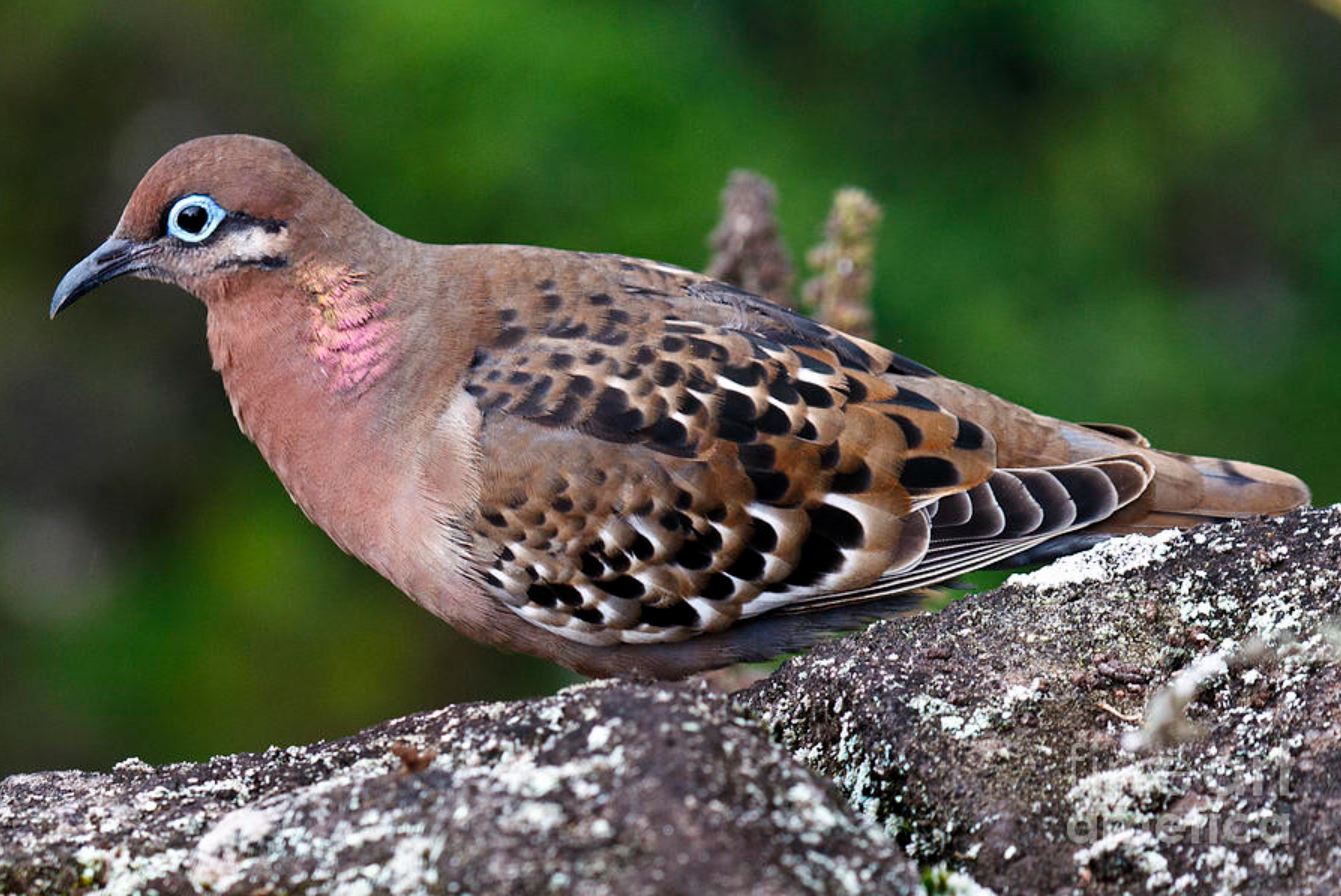
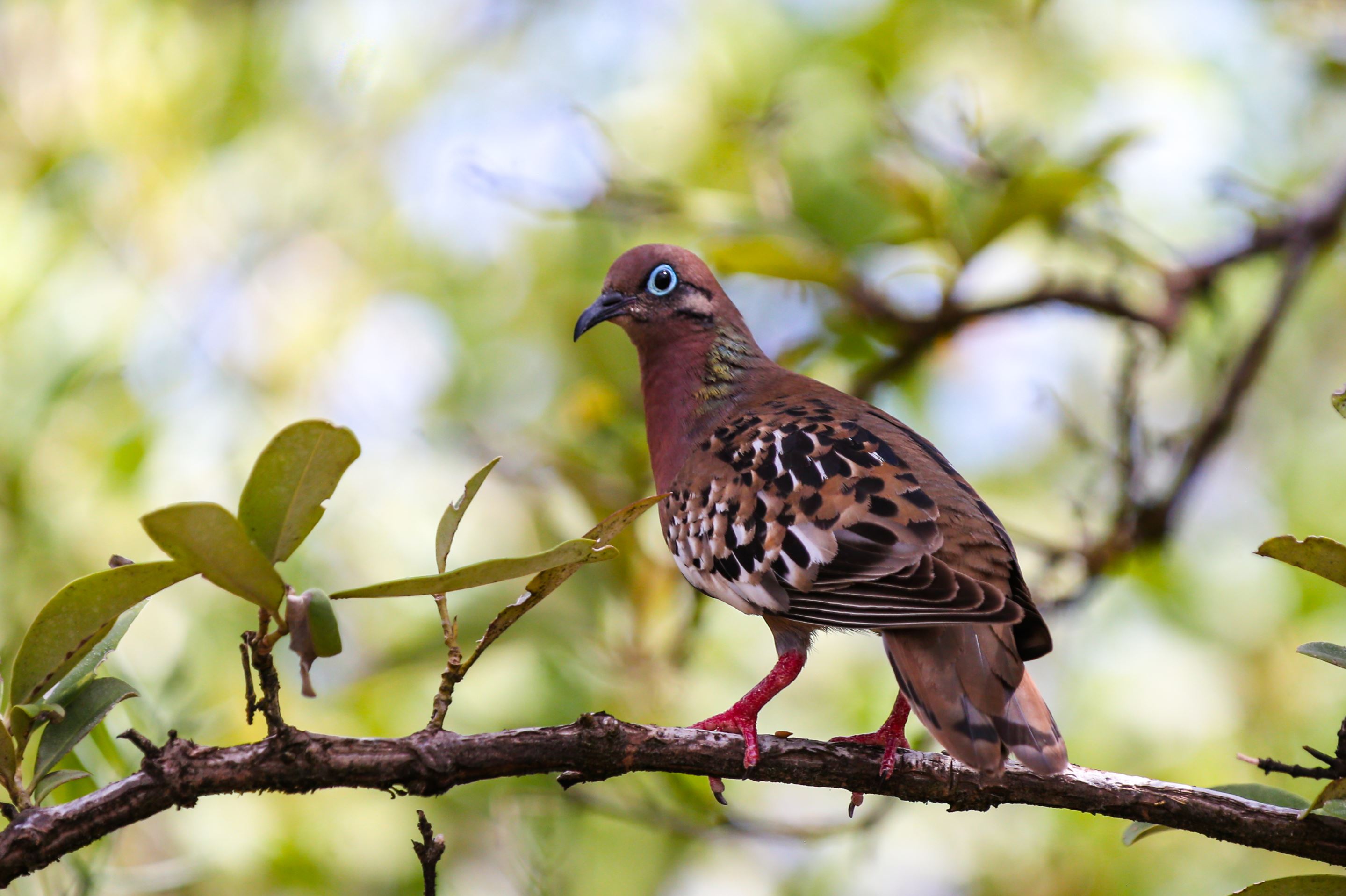
Galapagos Dove
One of the more attractive and pleasant birds to encounter on the islands is the Galapagos Dove. The Galapagos Dove is a tame and well-mannered creature. It is reddish brown with black and white markings, touches of incandescent green, red feet and a bright blue eye ring. The Galapagos Dove grows to measure between 18 and 23 centimetres long. Its beak is curved downward, larger and more curved than most other doves.
The Galapagos Doves curved beak helps it feed mainly on seeds picked from the ground mainly from the Opuntia cactus. Cactus pulp forms part of their diet and is probably their main source of water.
The Galapagos Dove is endemic to the islands and is found in the more arid parts of the main islands. A process of evolution on Genovesa Island has softened the spines of cactus plants and thereby allowed the Galapagos dove access to pollinate the flowers. This has occurred due to the lack of bees that would normally perform this function.
The Galapagos Dove is most commonly seen on the ground where it forages for seeds and fruits. Even if disturbed it is reluctant to take to the air and if it does, it only flies for a short time.
- Animal Group: Landbirds
- Scientific Name: Zenaida galapagoensis
- Animal Average Size: 18 – 23 cm
- Animal Average Weight: 180 - 350 gr
Places where you may see this animal:
Isabela
Santiago
Rábida
Genovesa
Santa Cruz
North Seymour
Floreana
Española
San Cristobal
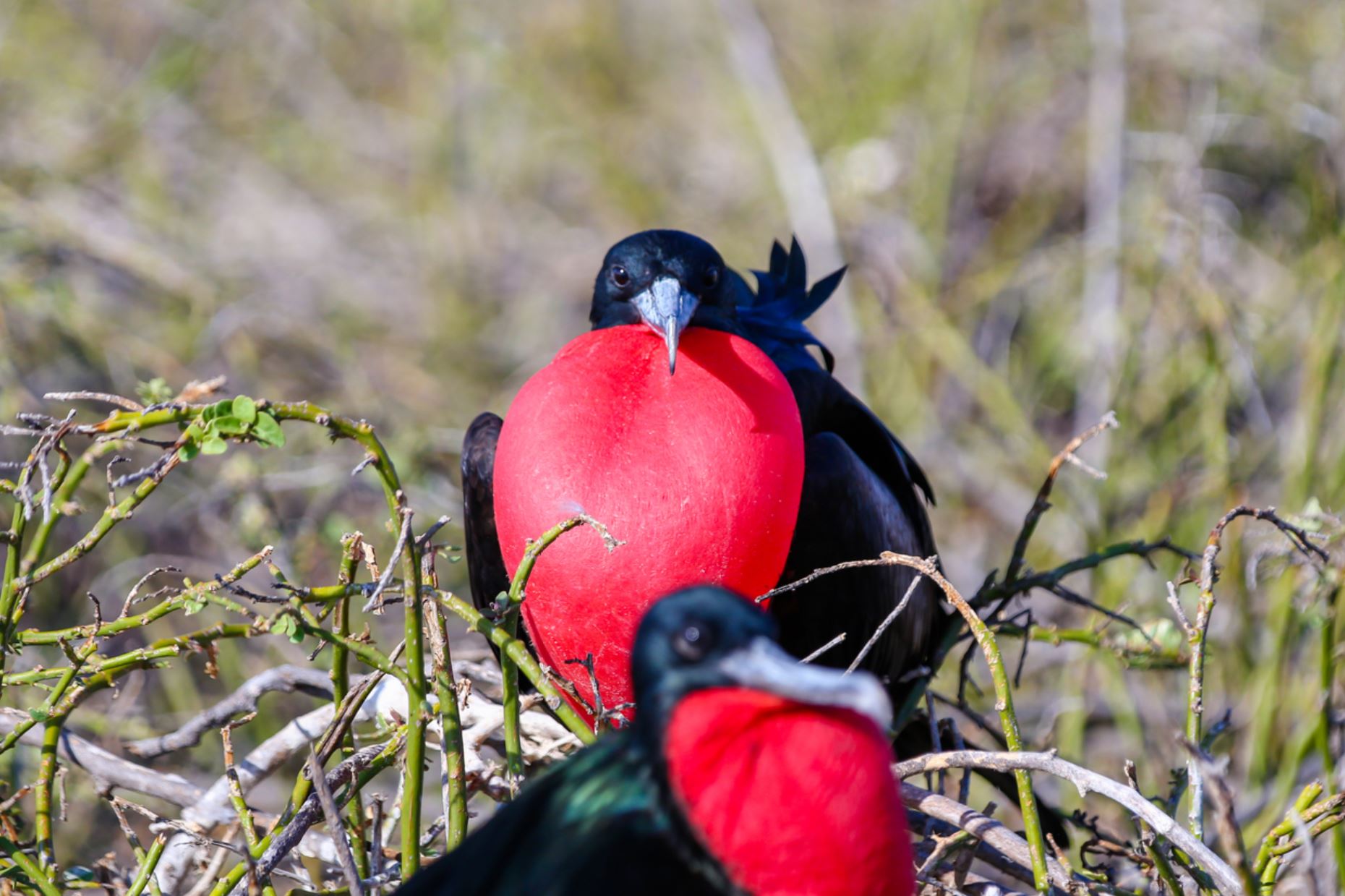
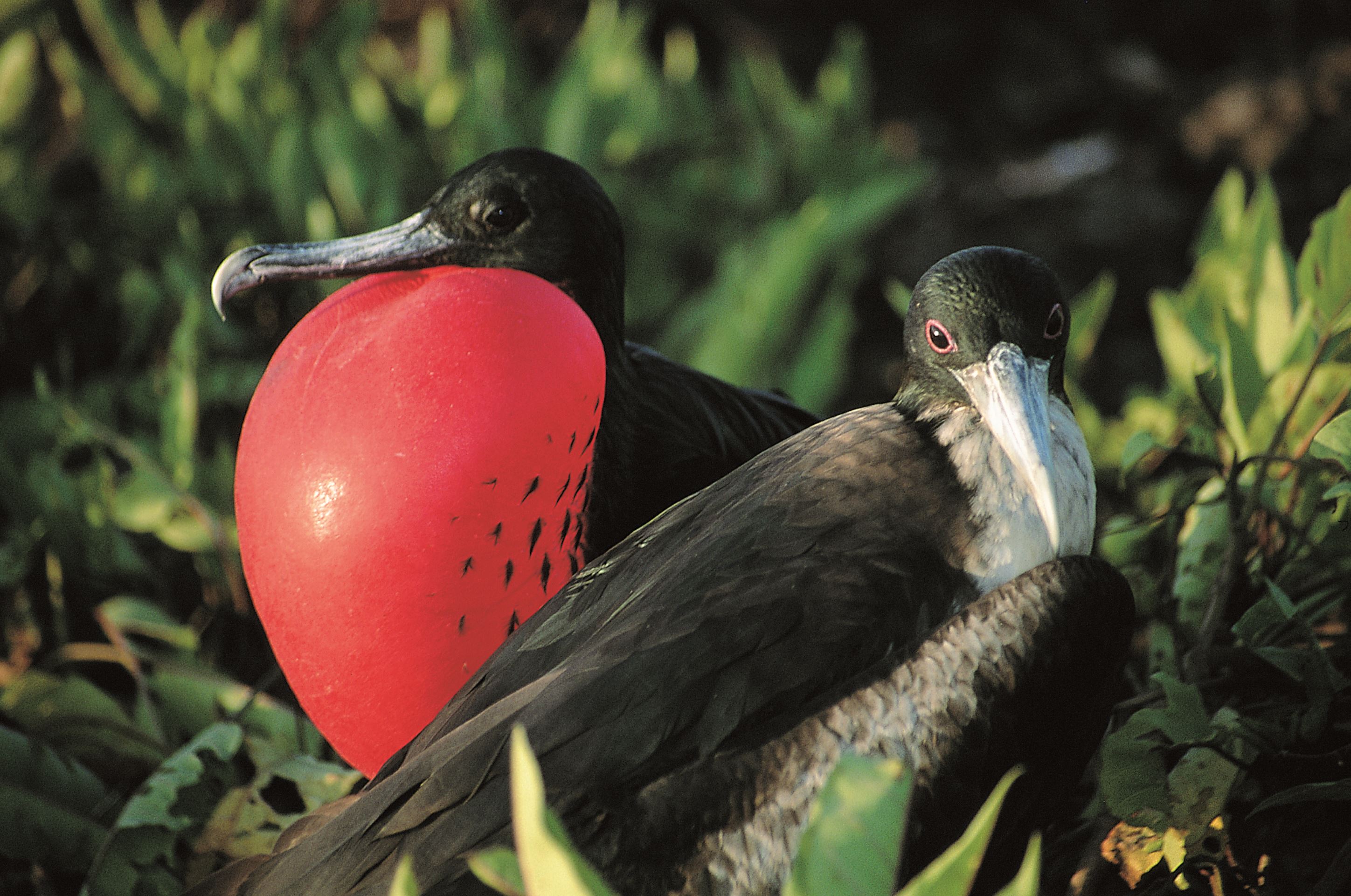
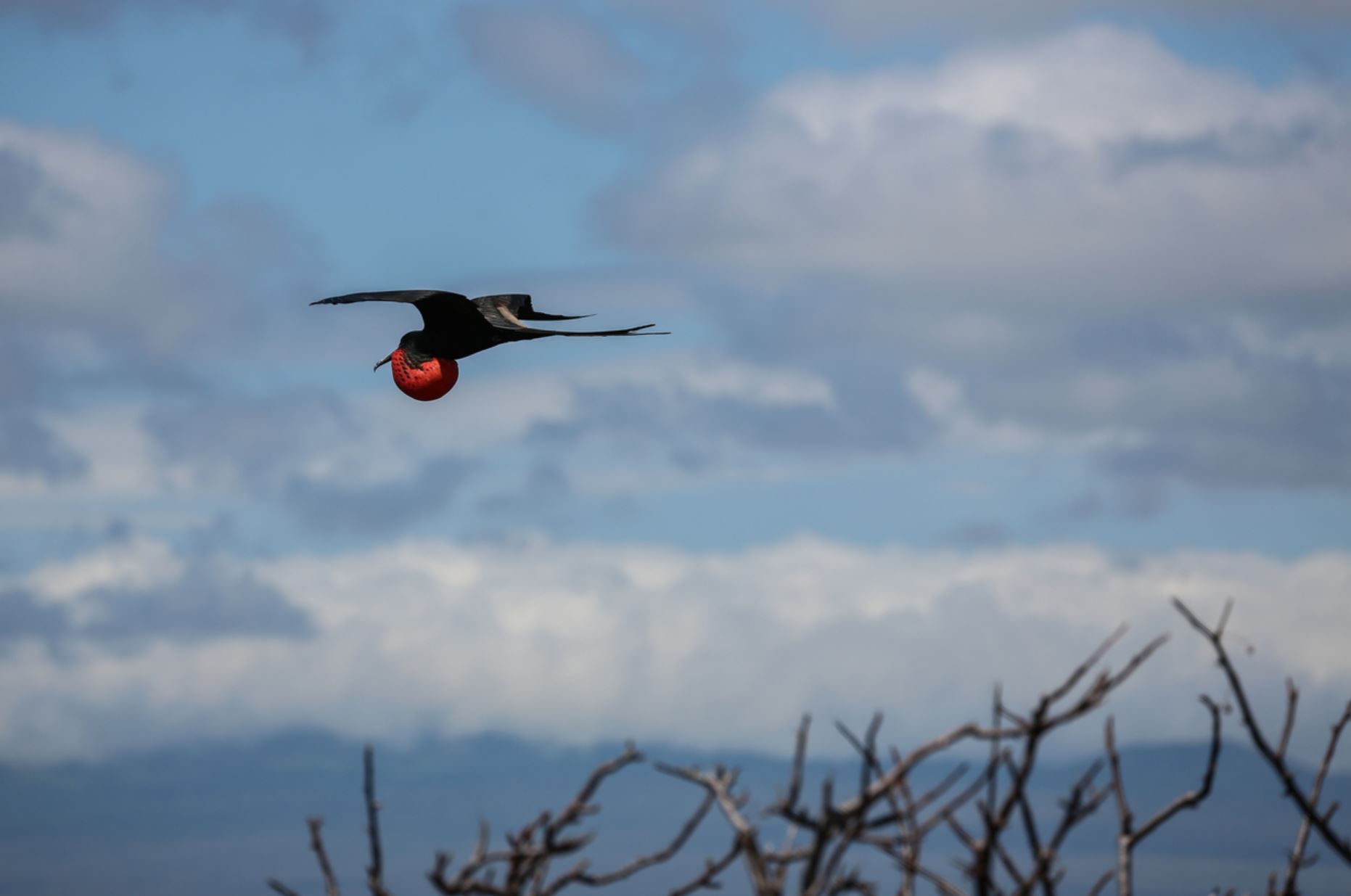
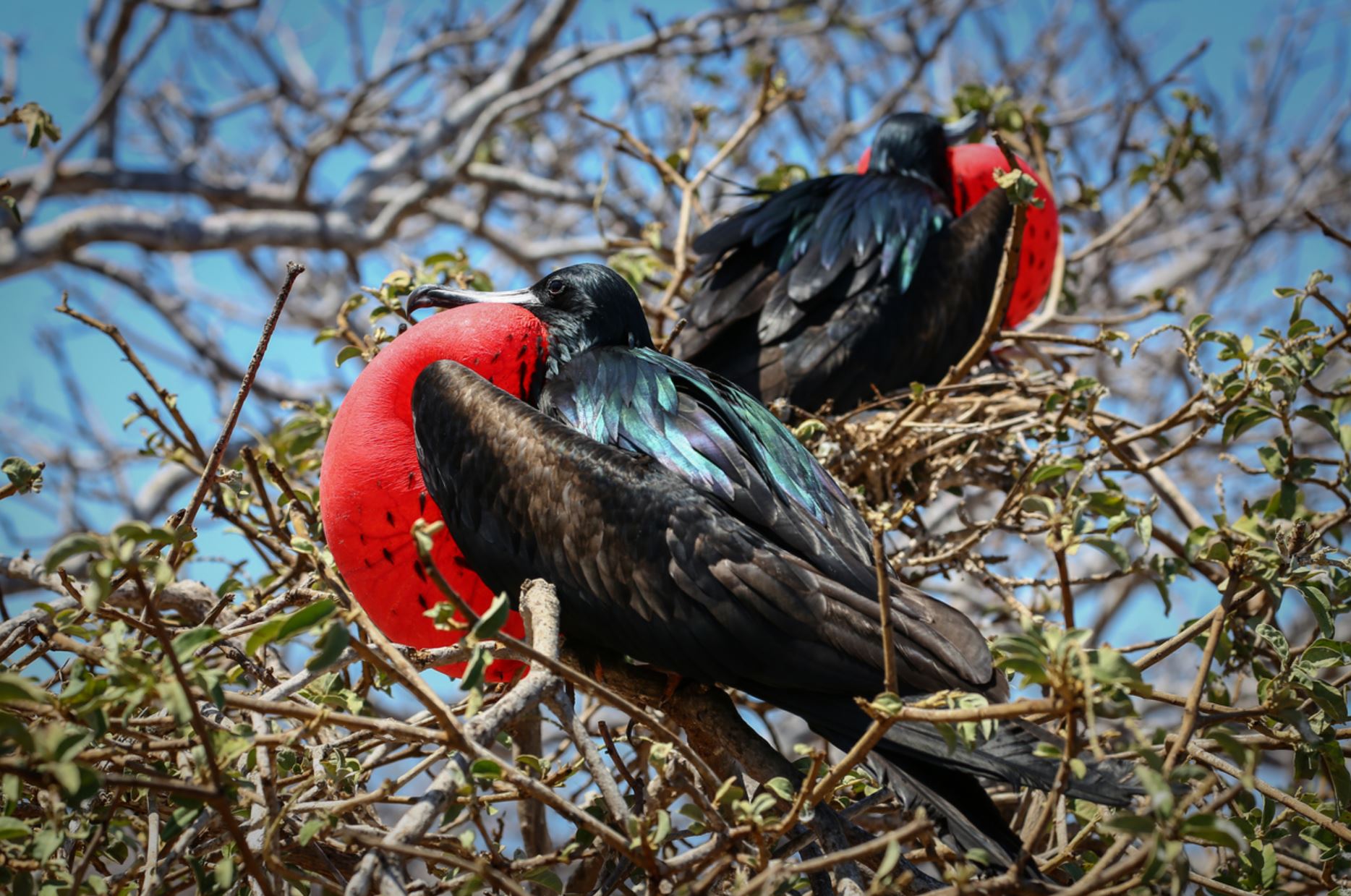
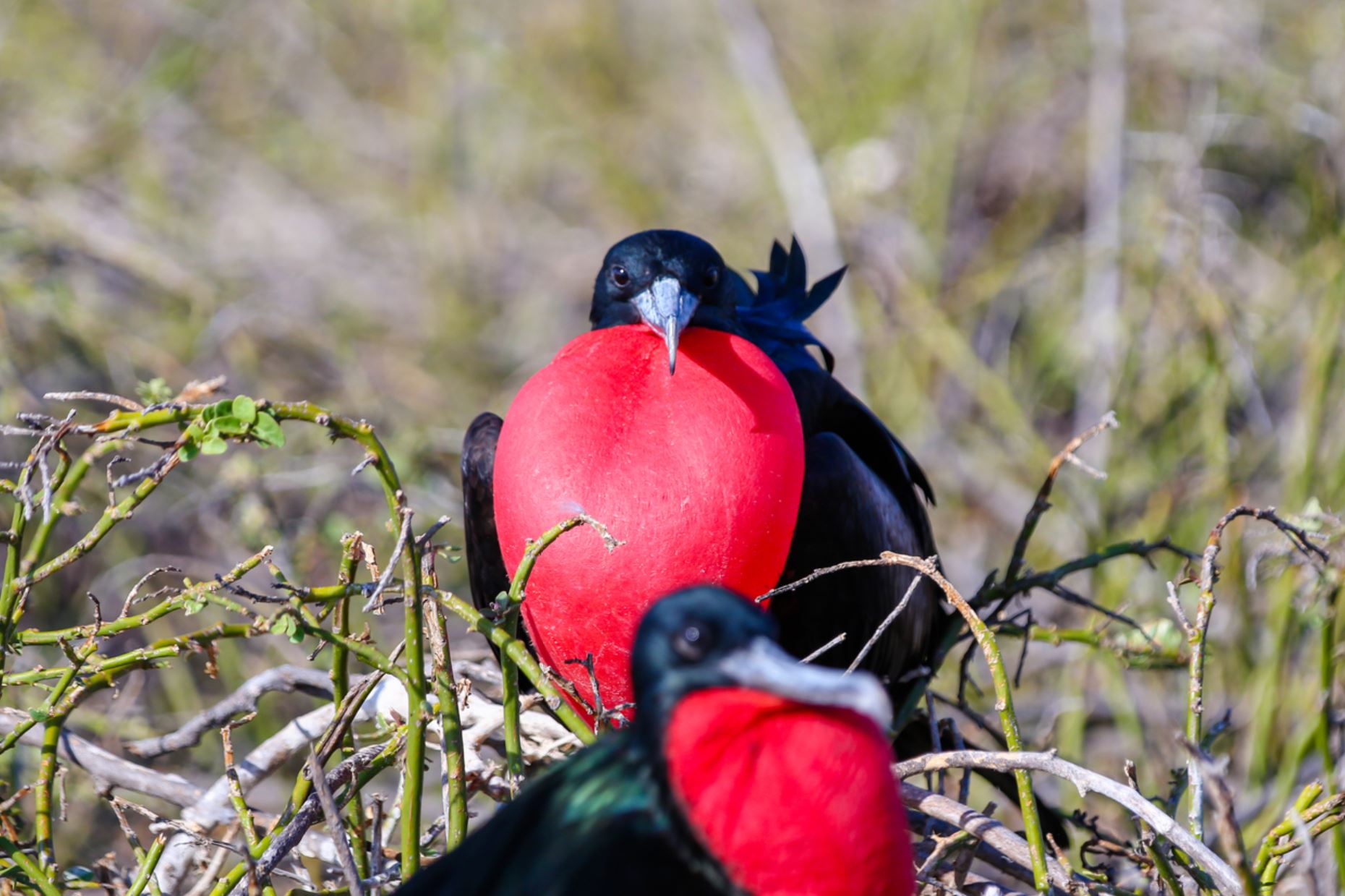
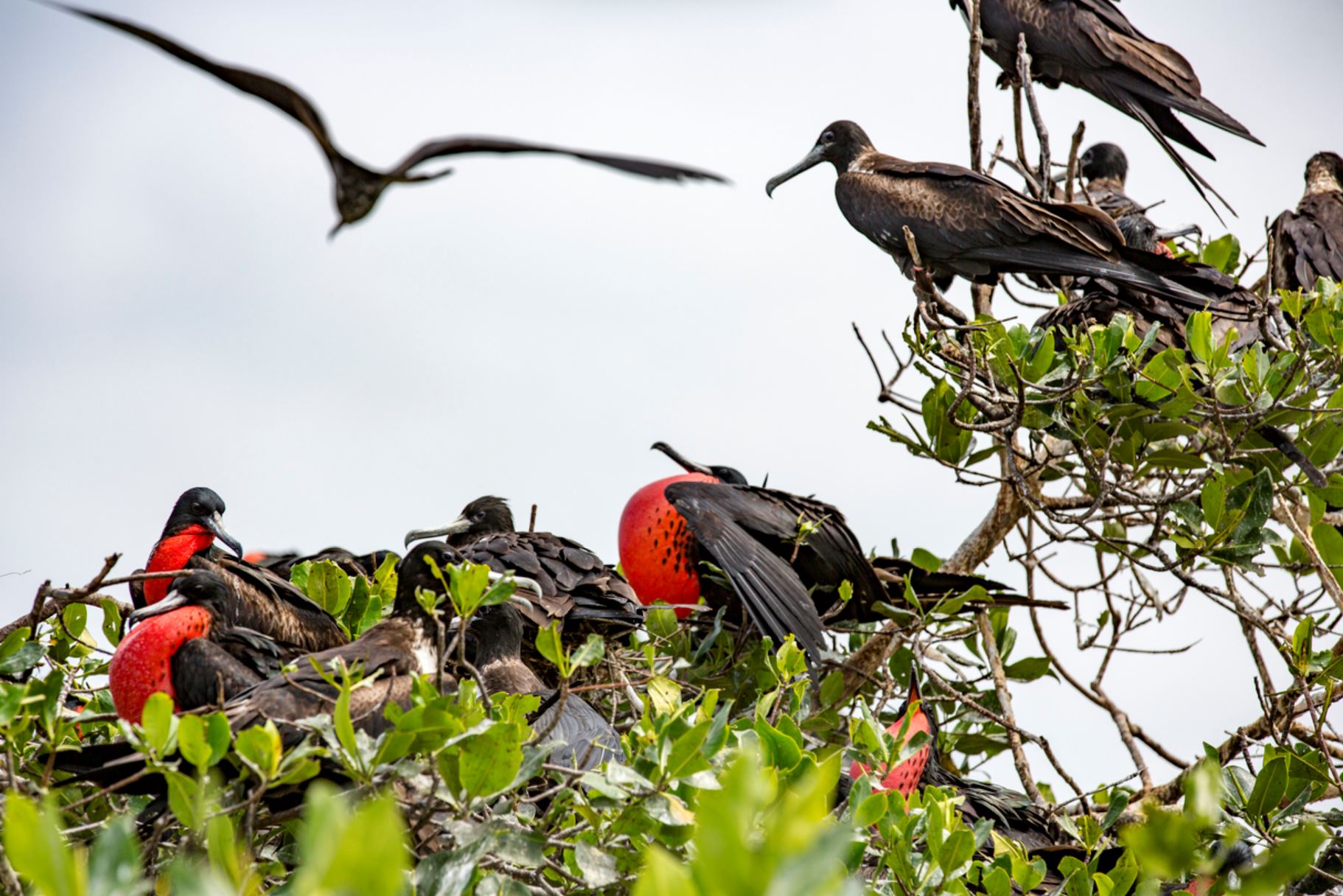
Galapagos Frigatebirds
The Great Frigate Bird resembles a huge blackbird that hovers lazily in the sky. Frigate birds belong to the family Fregatidae, which contains five species world-wide. In the Galapagos there are two species: the Great Frigate bird and the Magnificent Frigate bird. Of the two, the Great Frigate bird has the greater world-wide distribution, being found primarily throughout the tropical Pacific and Indian Oceans.
The Magnificent Frigate bird is found in the Caribbean and on the Pacific and Atlantic coasts of the Americas. The Galapagos population of Magnificent Frigate birds is considered to be an endemic subspecies.
In the Galapagos, the two species can be seen nesting side by side, but when Frigate birds are sighted in the air, they typically are Magnificent Frigate birds, as Great Frigate birds tend to forage much further out at sea. As with the three similar species of Booby birds, similar species of Frigate Birds avoid competition by feeding in different locations.
You can tell the two species of Frigate birds apart by their sounds – a Great Frigate bird makes a ‘gobbling’ noise like a turkey, while a Magnificent Frigate bird will make a rattling or drumming sound.
Great Frigate birds are large, with iridescent black feathers (the females have a white underbelly), with long wings (male wingspan can reach 2.3 metres) and deeply-forked tails. The males have inflatable red-coloured throat pouches, which they inflate to attract females during the mating season.
Both species of Frigate bird have extremely high wingspans to bodyweight ratios allowing them soar and to fly extremely well and with excellent control. Using this control, Frigate birds routinely steal food from other birds by grabbing them by their tail feathers and shaking them until they regurgitate their food.
However, Frigate birds are also capable of capturing their own prey. Since Frigate birds have only a small oil gland and very little waterproofing in their wings, Frigate birds cannot dive and must instead rely on their superb aerobatics to snatch flying fish out of the air.
- Animal Group: Seabirds
- Scientific Name: Fregata magnificens
- Animal Average Size: 215 cm
- Animal Average Weight: 1.1 kg
Places where you may see this animal:
Genovesa
North Seymour
San Cristobal
Floreana
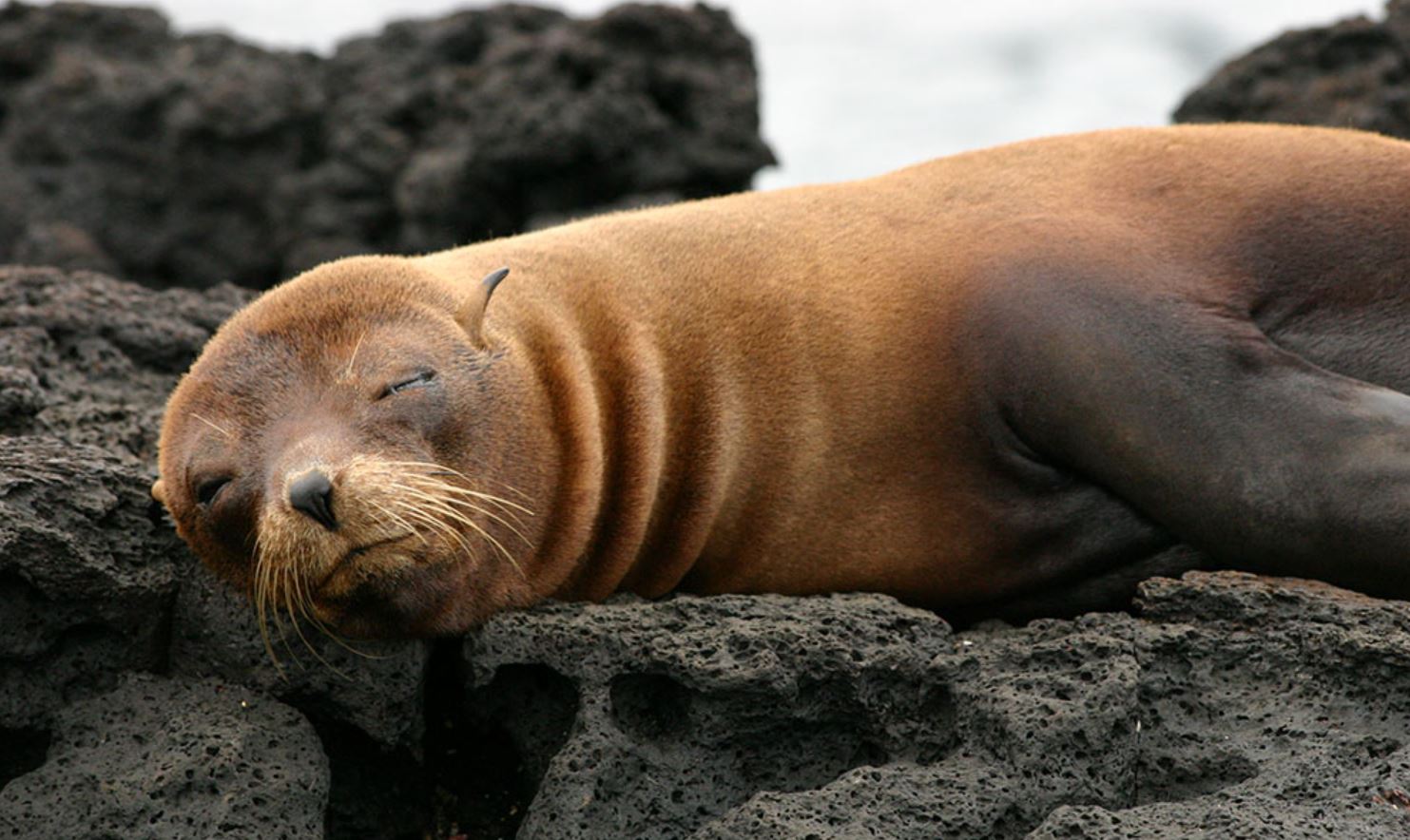
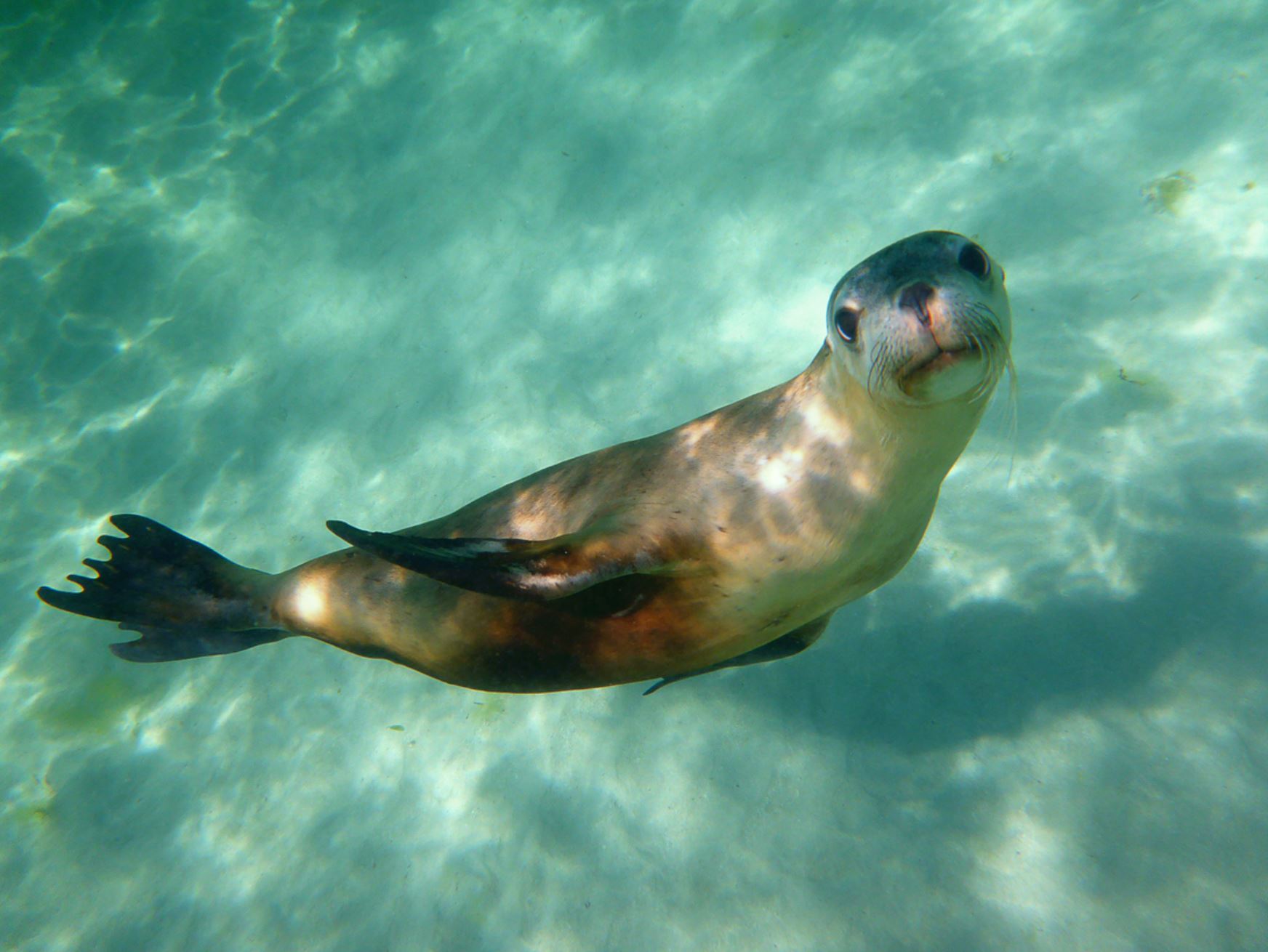
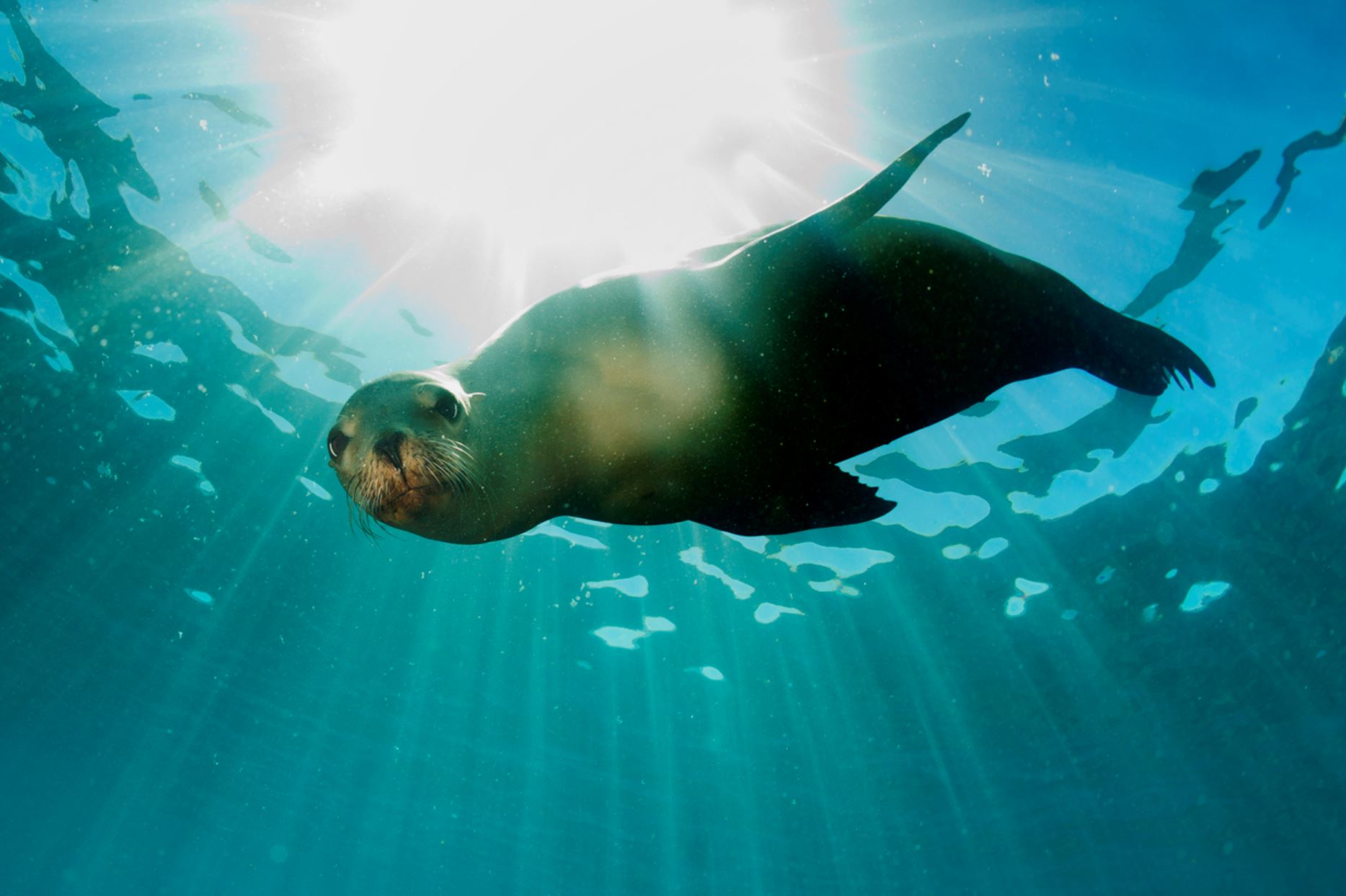
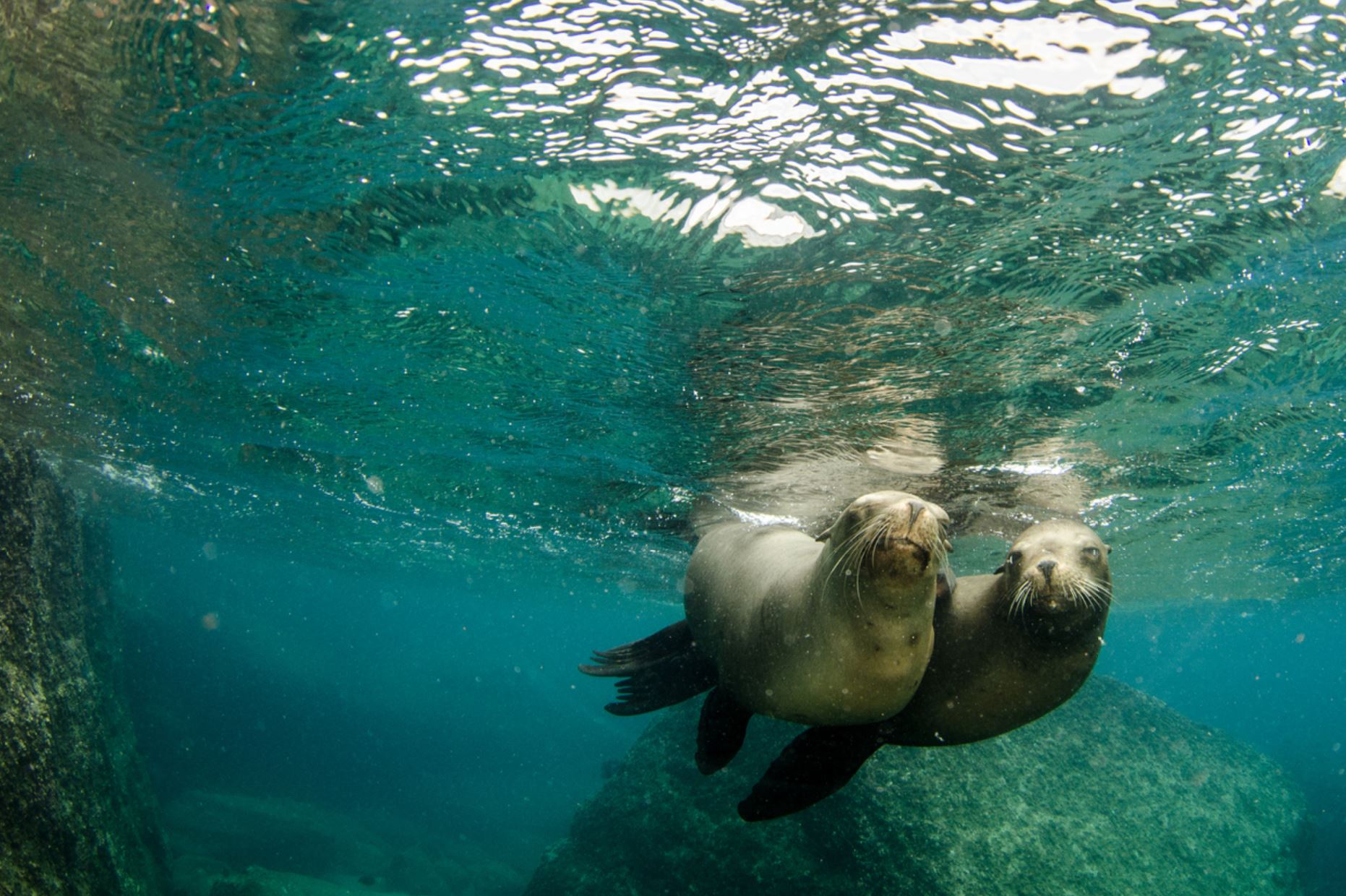
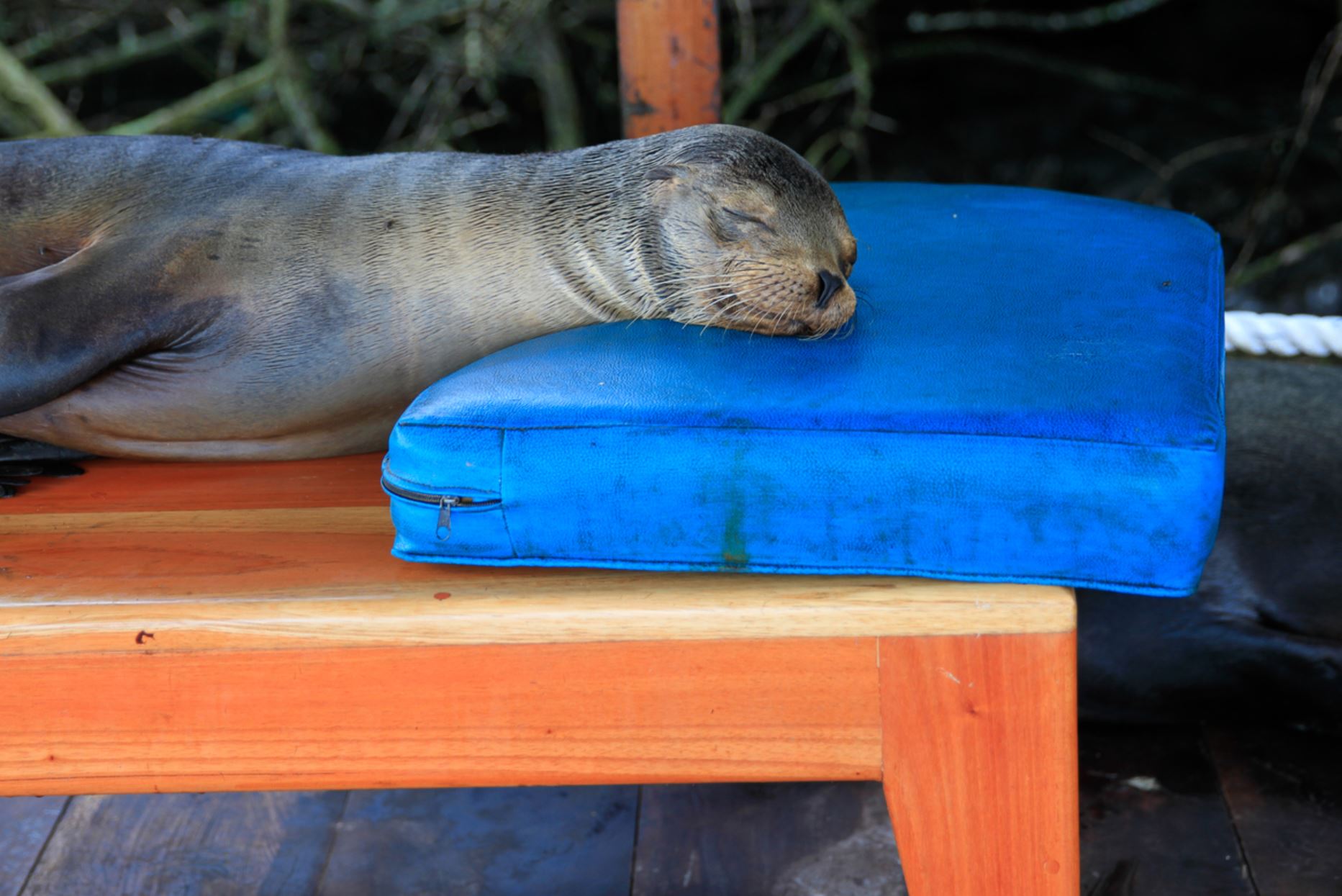
Galapagos Fur Seal
The Fur Seal is the second species of sea lion, that can be found in the archipelago. Such species is more nocturnal and less social when compared to the sea lion. However, their wildness, impressive vision and swimming skills make them very interesting to watch and no one can deny that they are very adorable and extremely cute to watch, also they are the fluffiest species.
The fur seal is smaller than the sea lion, about 1,5m (5 ft) and is very shy and rare to see. They prefer the rocks rather than the beaches and they have nocturnal habits.
Fur seals are less in numbers when compared to the sea lion, as they were heavily hunted back in the day by the first colonizers,.and sailors in the 19th century.
The fur seal spend more time in land than they do in water.
Fur seals are usually found in the west side of the archipelago, where the quantity of food is almost always higher. They feed mostly on cephalopods and small fish. As they hunt mainly at night, they have developed accurate techniques and tools such as their whiskers, which can be used to track the waves the fish make on the dark water.
The fur seal females are very territorial, claiming an area for breeding. This species unfortunately has a low rate of reproduction, they breed one pup a year. Females typically go hunting for about 1 day and return to feed the pup. The fur seal pup recognizes their mother by calls and noises, only known to them.
Fur seals can be found by the rocks, resting in small groups or by themselves around the islets. They mainly like places where they can sleep between rocks or dark hidden areas.
- Animal Group: Mammals
- Scientific Name: Arctophoca galapagoensis
- Animal Average Size: 120 - 150 cm
- Animal Average Weight: 22 - 34 kg
Places where you may see this animal:
Genovesa
Santiago
Rabida
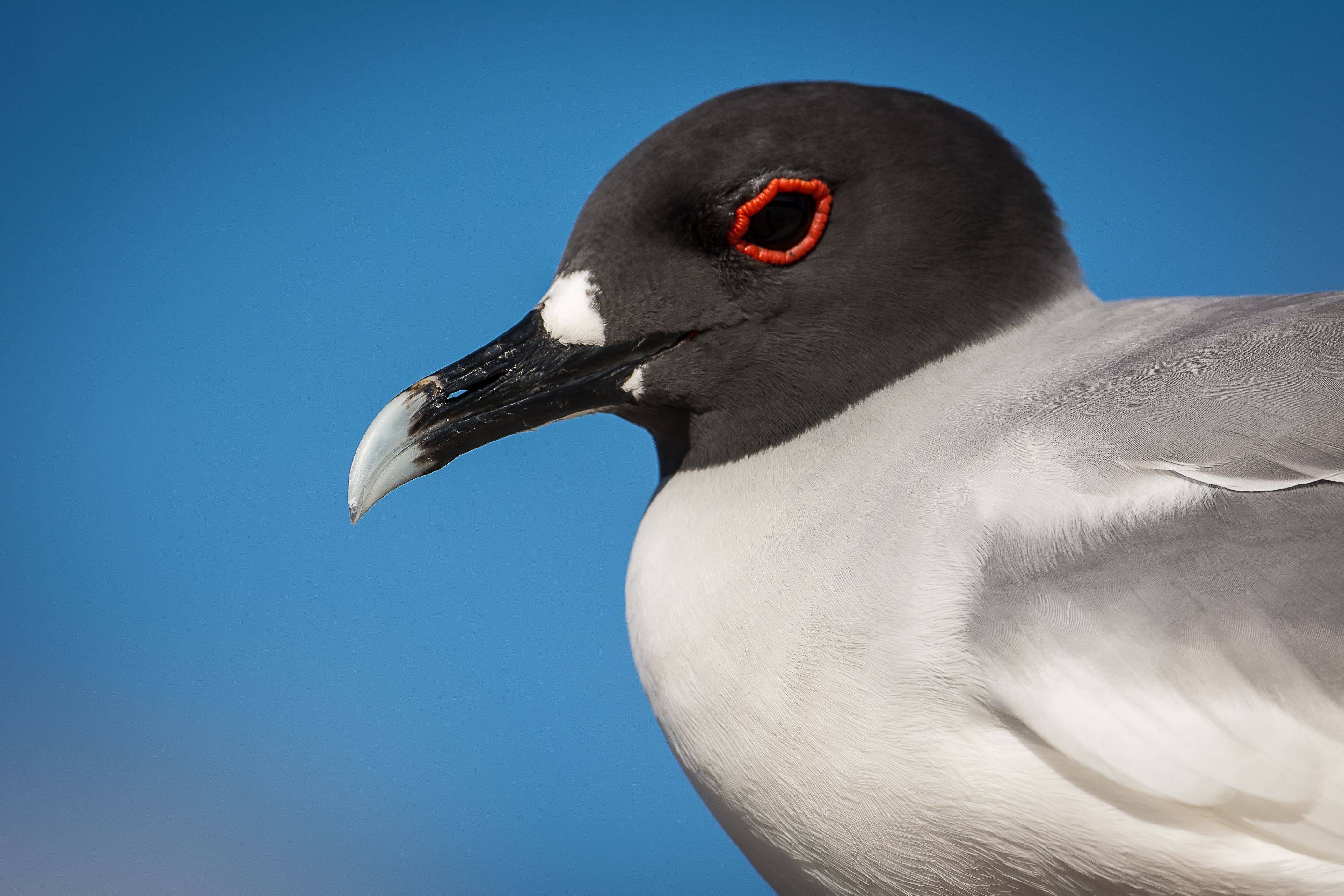
Galapagos Lava Gull
The Lava Gull (Larus fuliginosus) is a large gull, probably related to the Laughing Gull. One of the rarest gulls in the world, the entire population is endemic to the Galapagos Islands and is estimated at 400 pairs. Adult Lava Gull characteristics are a black head, black wings and with a dark grey body and a paler grey belly. Their bill and legs are black and the inside of the mouth is scarlet.
Lava Gulls are quite often seen as they frequently emit long raucous gull-like calls with their bills wide open. They have white upper and lower eyebrows, with red lids. Young gulls are generally dark brown in colour.
Lava Gulls are solitary nesters, laying two olive-coloured and well-camouflaged eggs that take 30 days to incubate. Young birds fledge at 60 days and are cared for by adults for a short period.
Lava Gulls are omnivores like most Larus gulls, generally scavenging or stealing from nests, but they will also catch fish, small crustaceans and newly-hatched lizards, iguanas and turtles. . Being scavengers, young Lava Gulls are more naturally self-sufficient than some species with more specialized feeding habits.
The Lava Gull is categorized as ‘vulnerable’ by the IUCN Red List because it exists in small numbers and though the population is stable, it faces numerous threats.
- Animal Group: hooded gull group
- Scientific Name: Larus fuliginosus
- Animal Average Size: 51 – 55 cm
Places where you may see this animal:
Santiago
Genovesa
Santa Cruz
Española
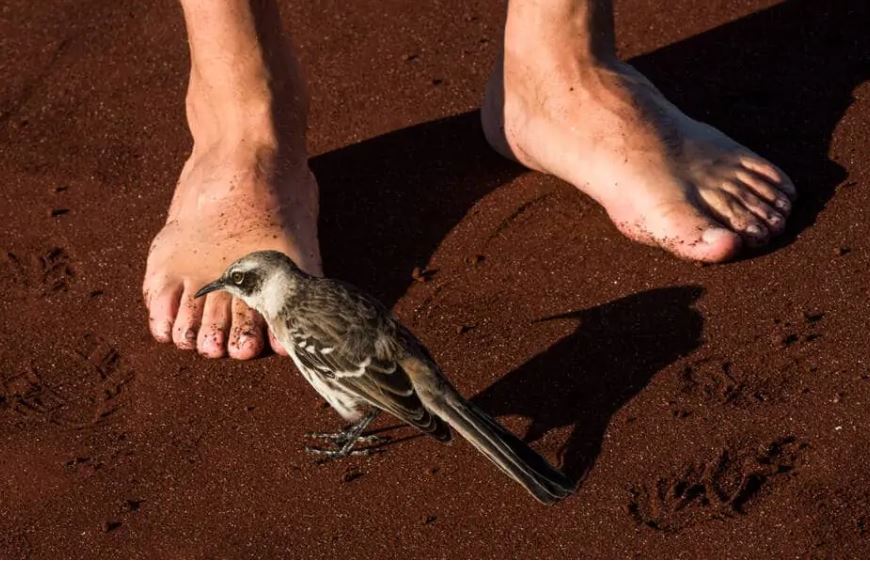
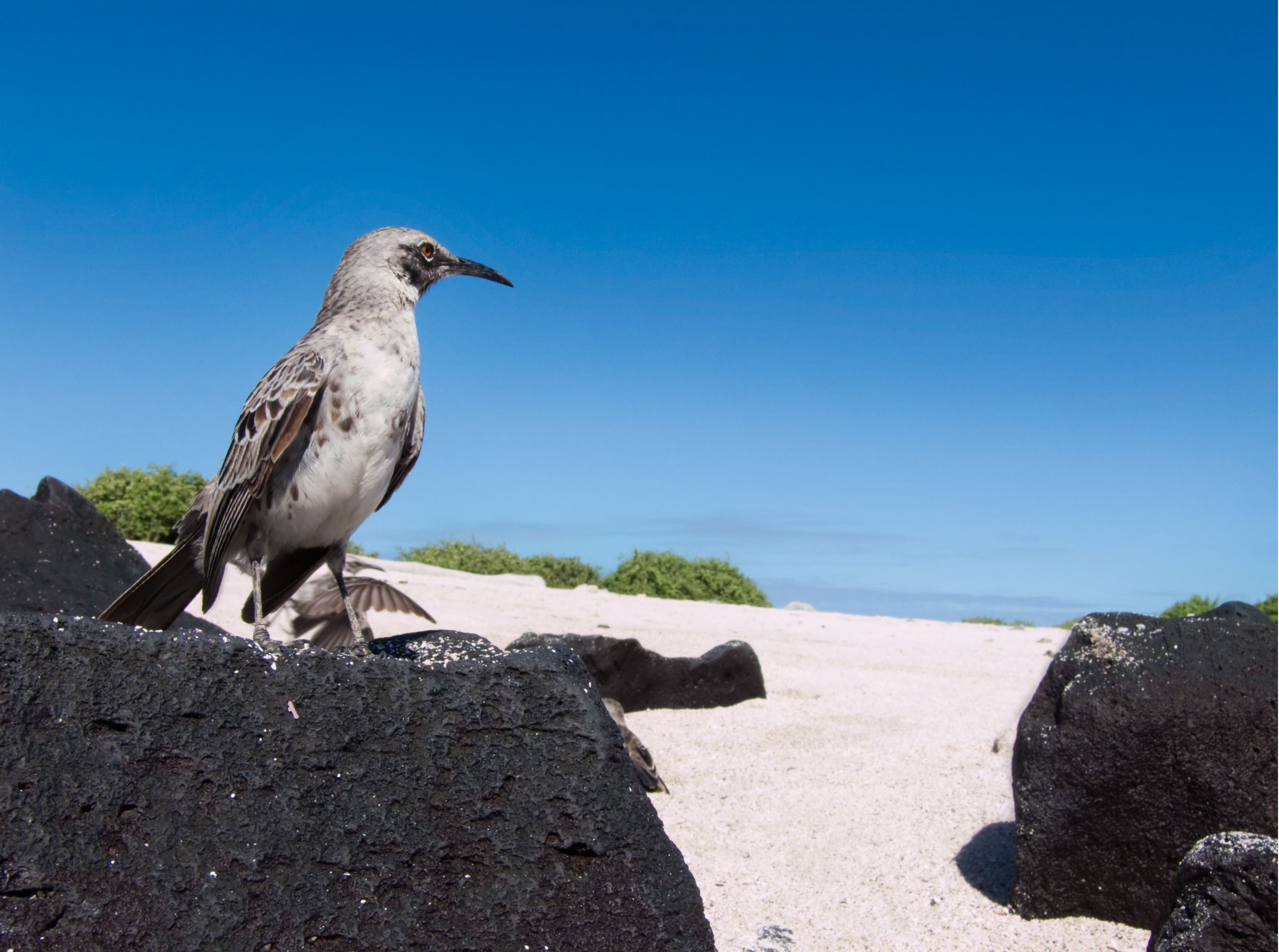
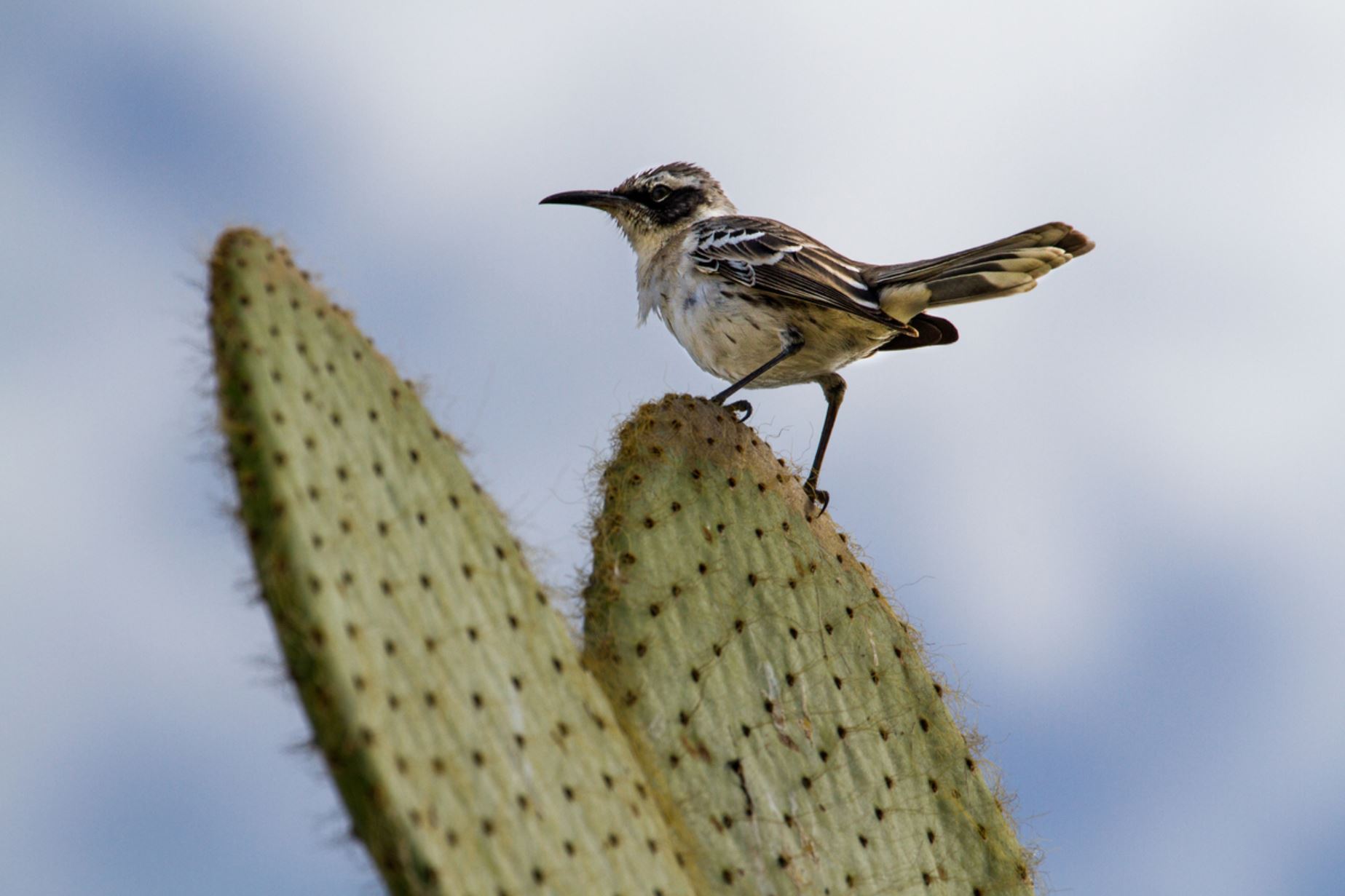
Galapagos Mockingbird
Mockingbirds in most regions of the world are known for having the ability to imitate the singing from other birds and several other kinds of noises. It is believed that this skill was developed in order to have a more successful feeding in other bird territories, and as a reproductive feature for males.
In the Galapagos there are four different subspecies. All of them are related to a single colonization event, but in four different islands. They are very similar to the other locations species physically. They protect the group and even feed newborns of other individuals of the group. They are omnivores and their curiosity has made them some of the most commonly seen bird of the islands.
- Animal Group: Landbirds
- Scientific Name: Mimus parvulus
- Animal Average Size: 25 - 26 cm
- Animal Average Weight: 51 -56 g
Fernandina, Isabela, Genovesa, Santiago, Santa Cruz, South Plaza, Santa Fé
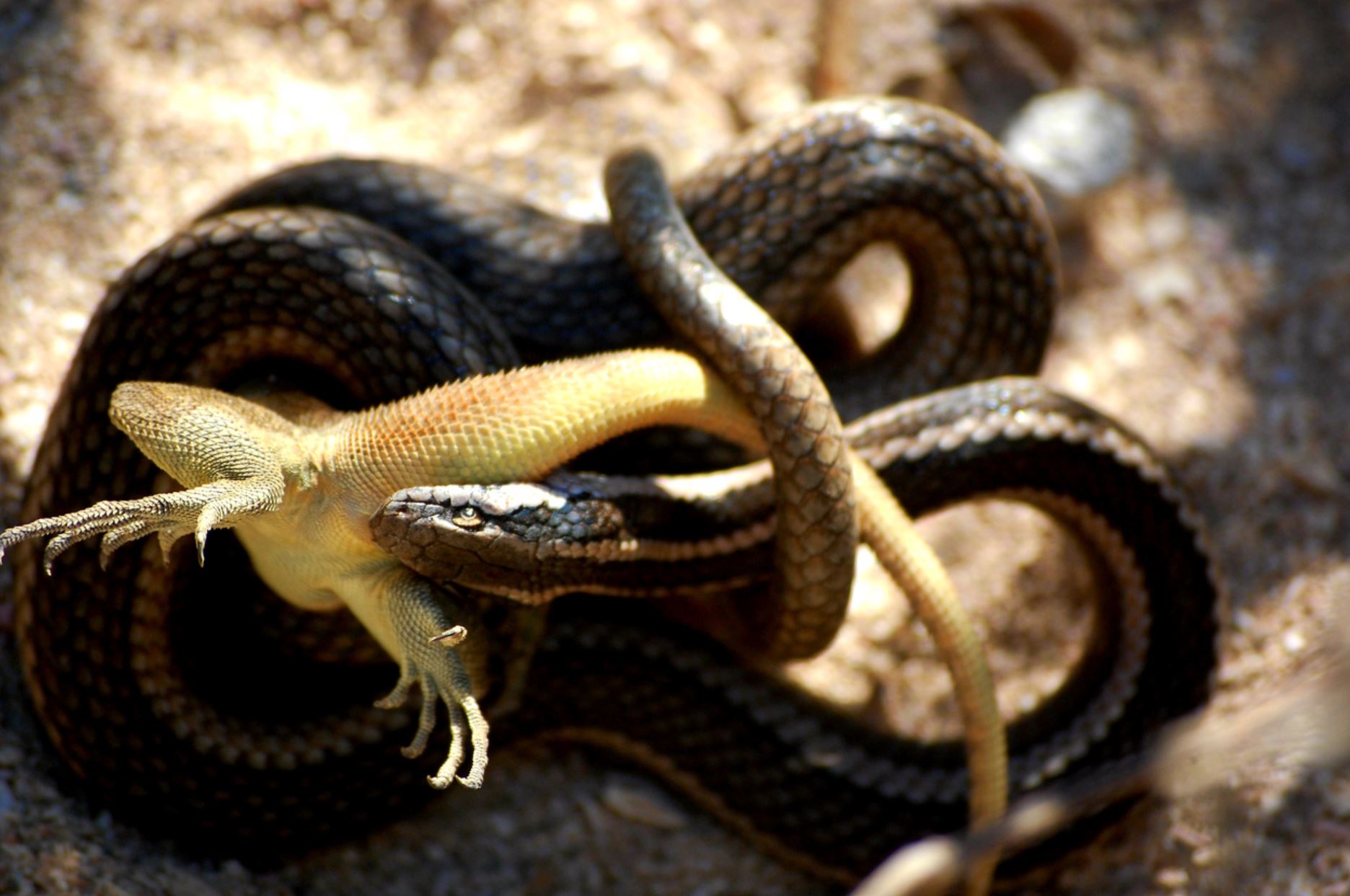
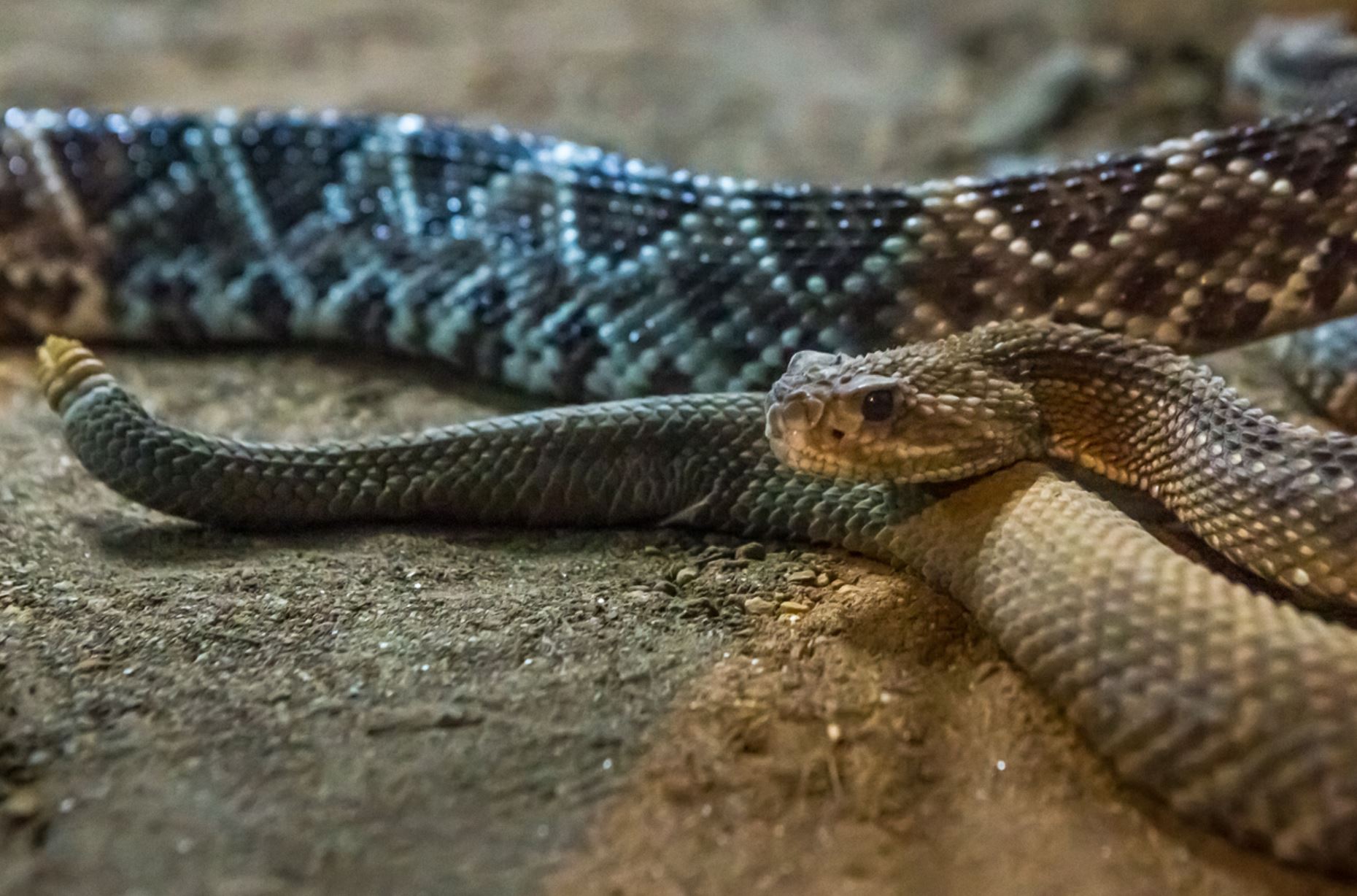
Galapagos Racer Snake
Racer snakes on Galapagos are constrictors and only mildly venomous. They are known to prey on lava lizards, geckos, insects, iguanas, mice, rats and hatchlings of several bird species. They are not at all aggressive towards humans and could not do much harm if they were to attack after being threatened. Racers tend to be dark brown with stripes or spots.
There is some confusion over the number of species of racer snake found in Galapagos due to poor research. The latest research suggests that there are: the Galapagos racer (Pseudalsophis biserialis) from San Cristobal and Floreana – though it is locally extinct on Floreana and now only found on nearby islets; the Espanola racer (Pseudalsophis hoodensis) from Espanola and adjacent islets; Santa Cruz racer (Pseudalsophis dorsalis) from Santa Cruz, Baltra, Santa Fe and adjacent islets; Fernandina racer (Pseudalsophis occidentalis) from Fernandina, Isabela, and Tortuga; banded racer (Pseudalsophis slevini) from Pinzon; and the striped racer (, ) from Baltra and Santa Cruz.
It is the Fernandina racer which has been observed hunting for marine fish from rock pools and the shallows around Fernandina. The British biologist Dr. Godfrey Merlen was the first scientist to ever see this behaviour happening as he noted up to 15 individual snakes slithering around the lava rock pools around Cape Douglas. This is a unique behaviour of terrestrial snake not observed anywhere else in the world. The racers on Fernandina were also the stars of BBC´s Planet Earth II where they were filmed hunting juvenile marine iguanas.
Racer snakes can be found in Galapagos on most of the major islands, though they are now locally extinct on Floreana. The snakes are found throughout the year, but unlike many other Galapagos animals they are shy of humans and will hide away making them reasonably tough to spot without looking for them specifically. They are diurnal, most active around dawn and dusk, and often rest around midday. The native snake population has been decimated by introduced species such as cats, pigs and feral goats which forage for their eggs.
- Animal Group: snakes
- Scientific Name (depending from the islands): Pseudalsophis biserialis, Pseudalsophis hoodensis, Pseudalsophis dorsalis, Pseudalsophis occidentalis, Pseudalsophis slevini, Pseudalsophis steindachneri
- Animal Average Size: 80 cm bis 1,20 m
- Animal Average Weight: 8 – 10 kg
Racer males can be found in Galapagos on most of the major islands!
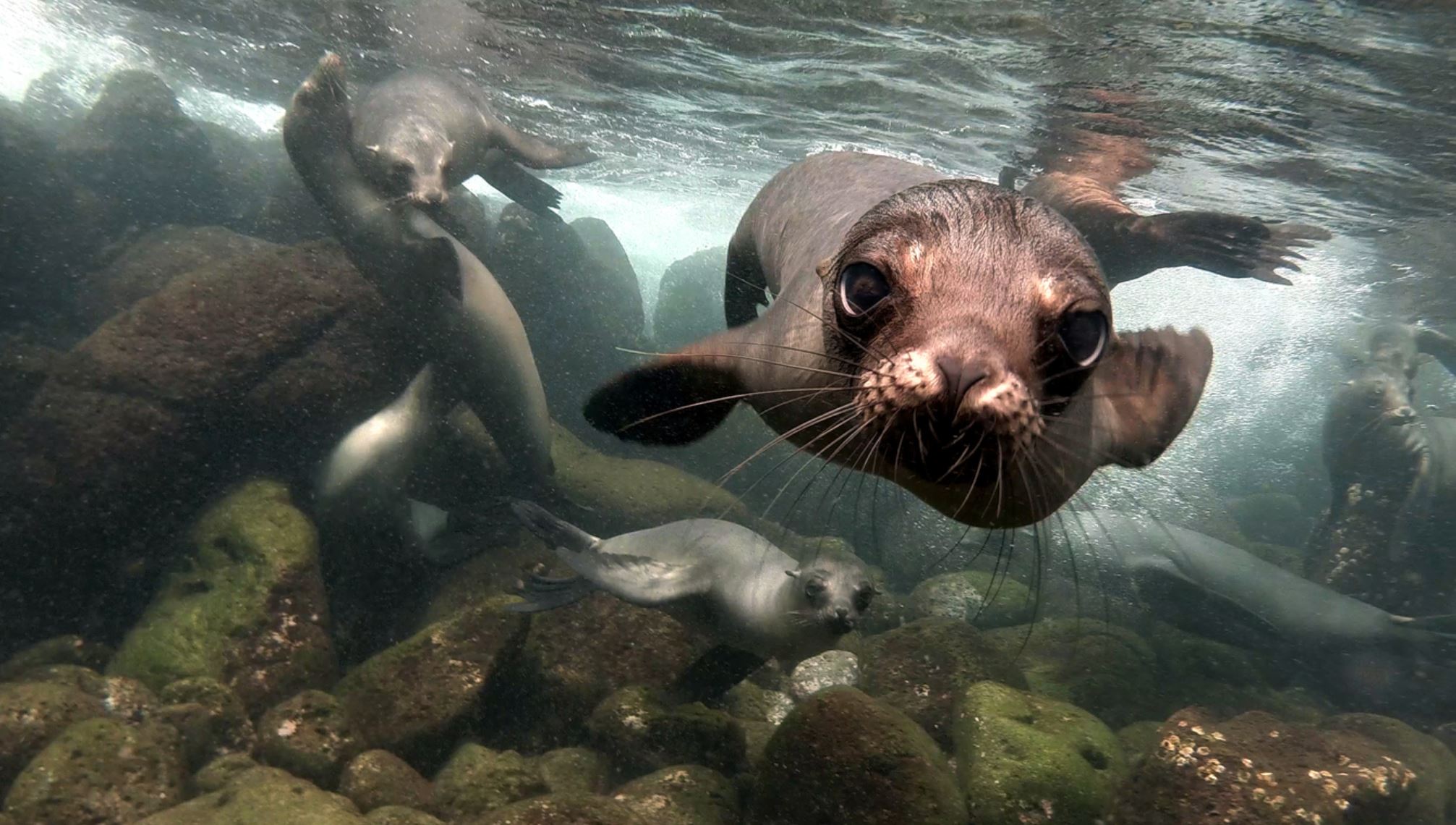
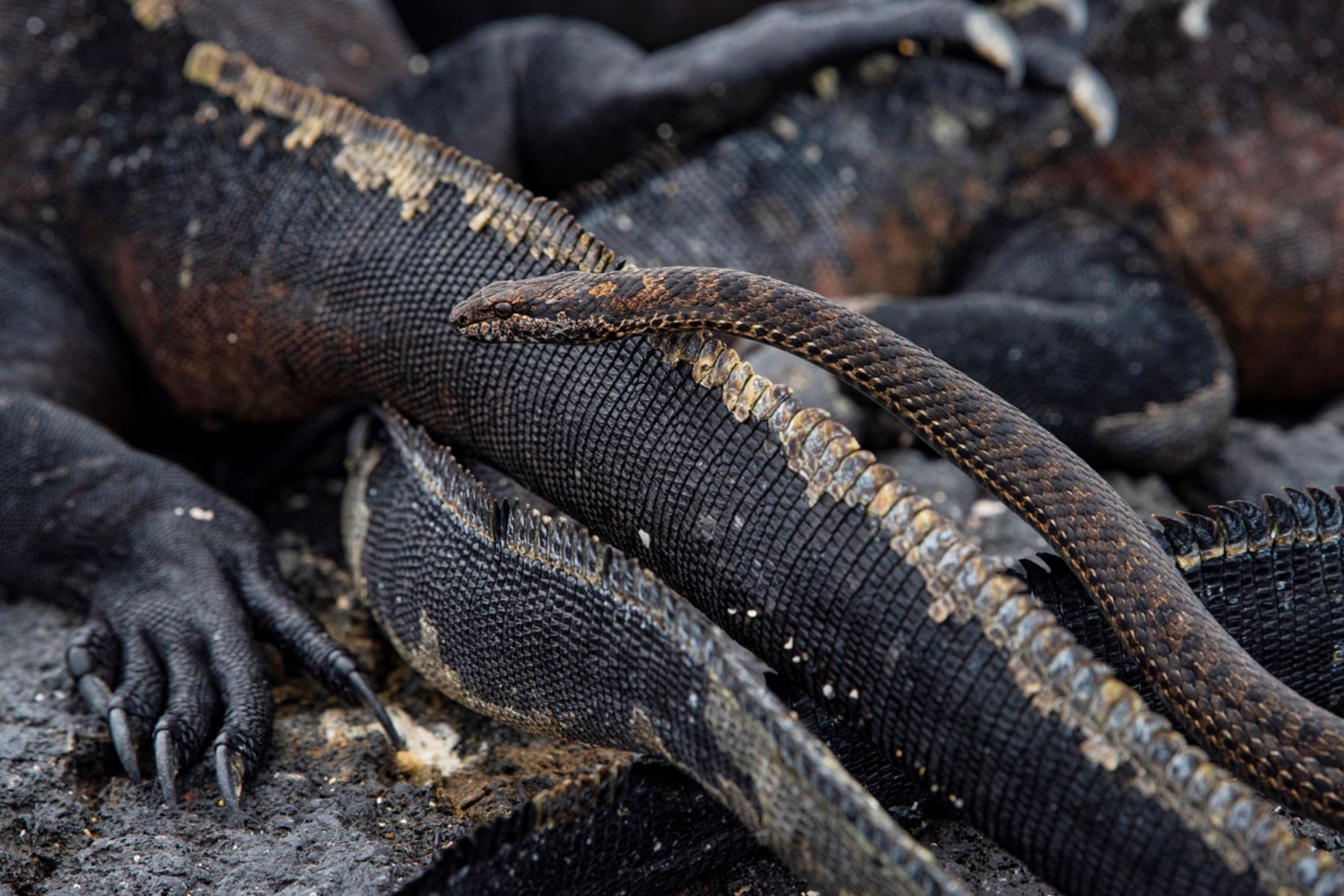
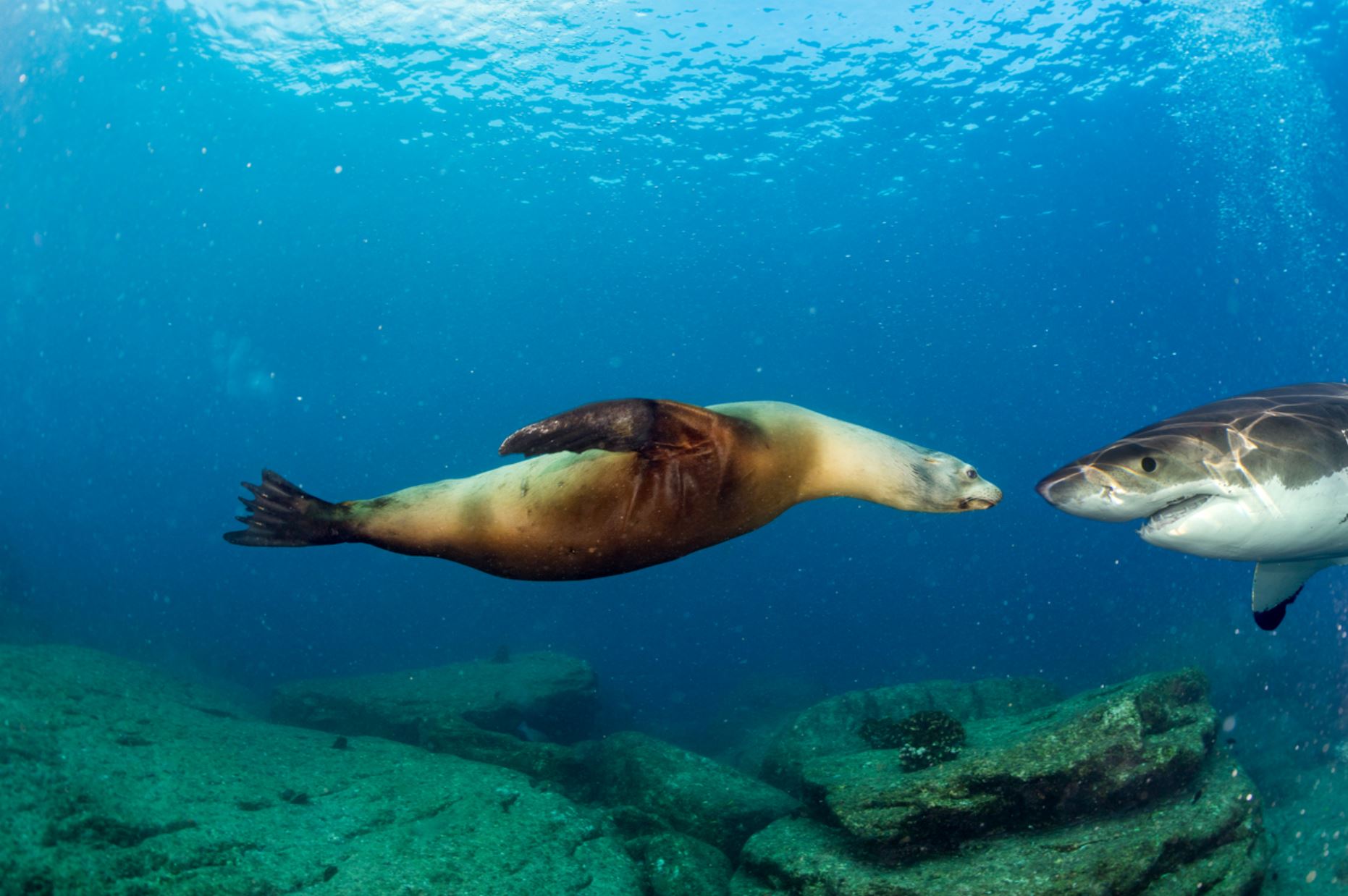
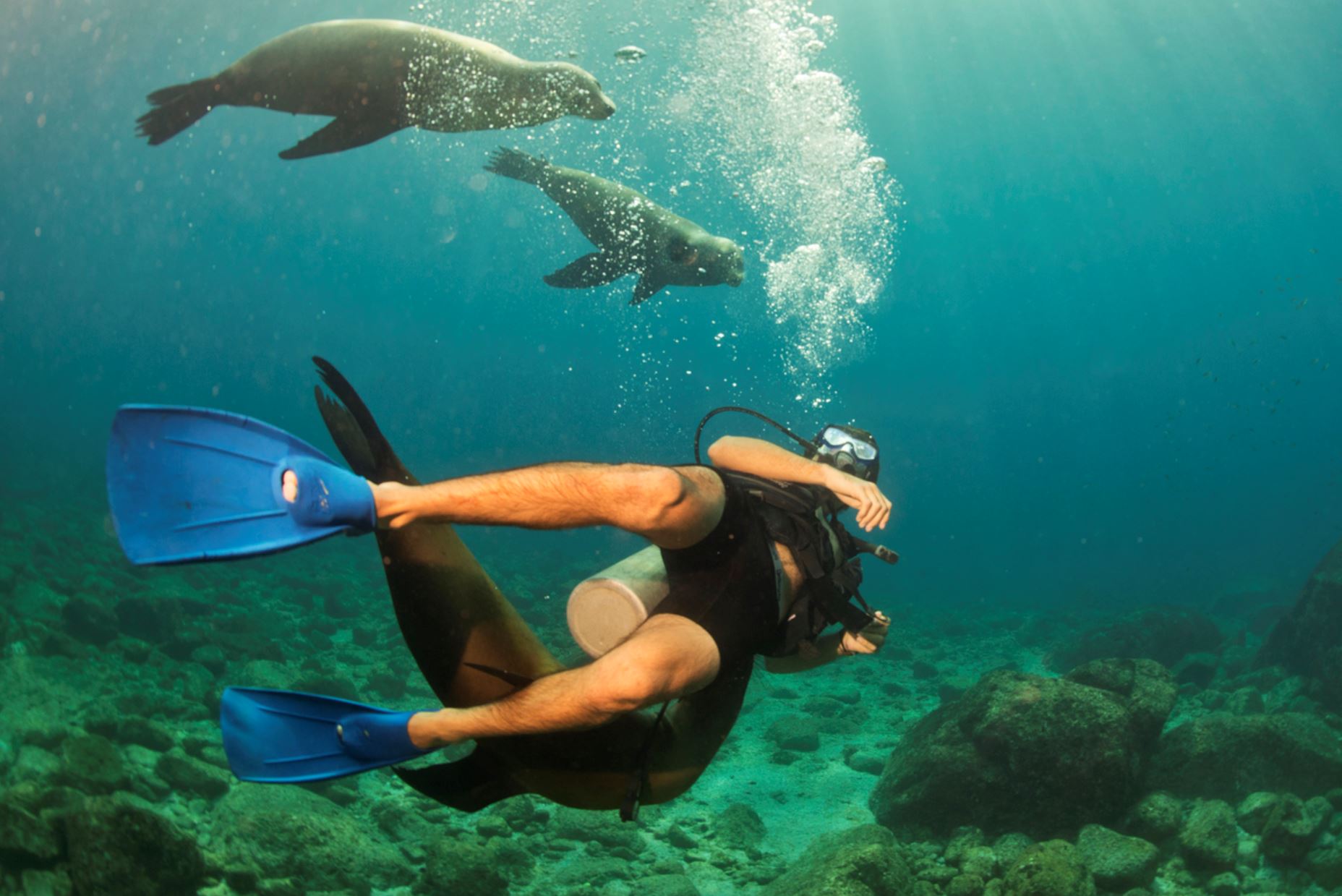
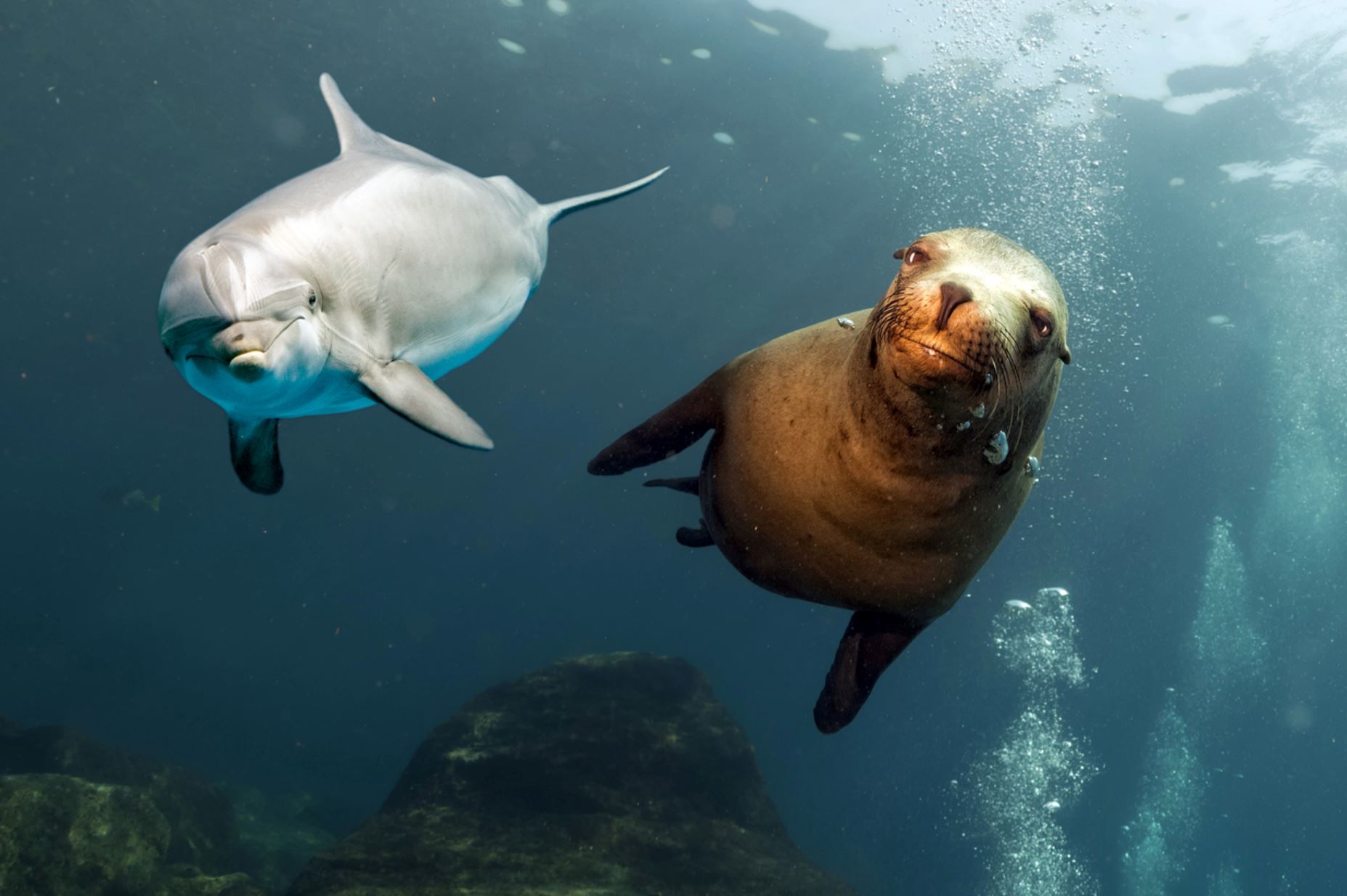
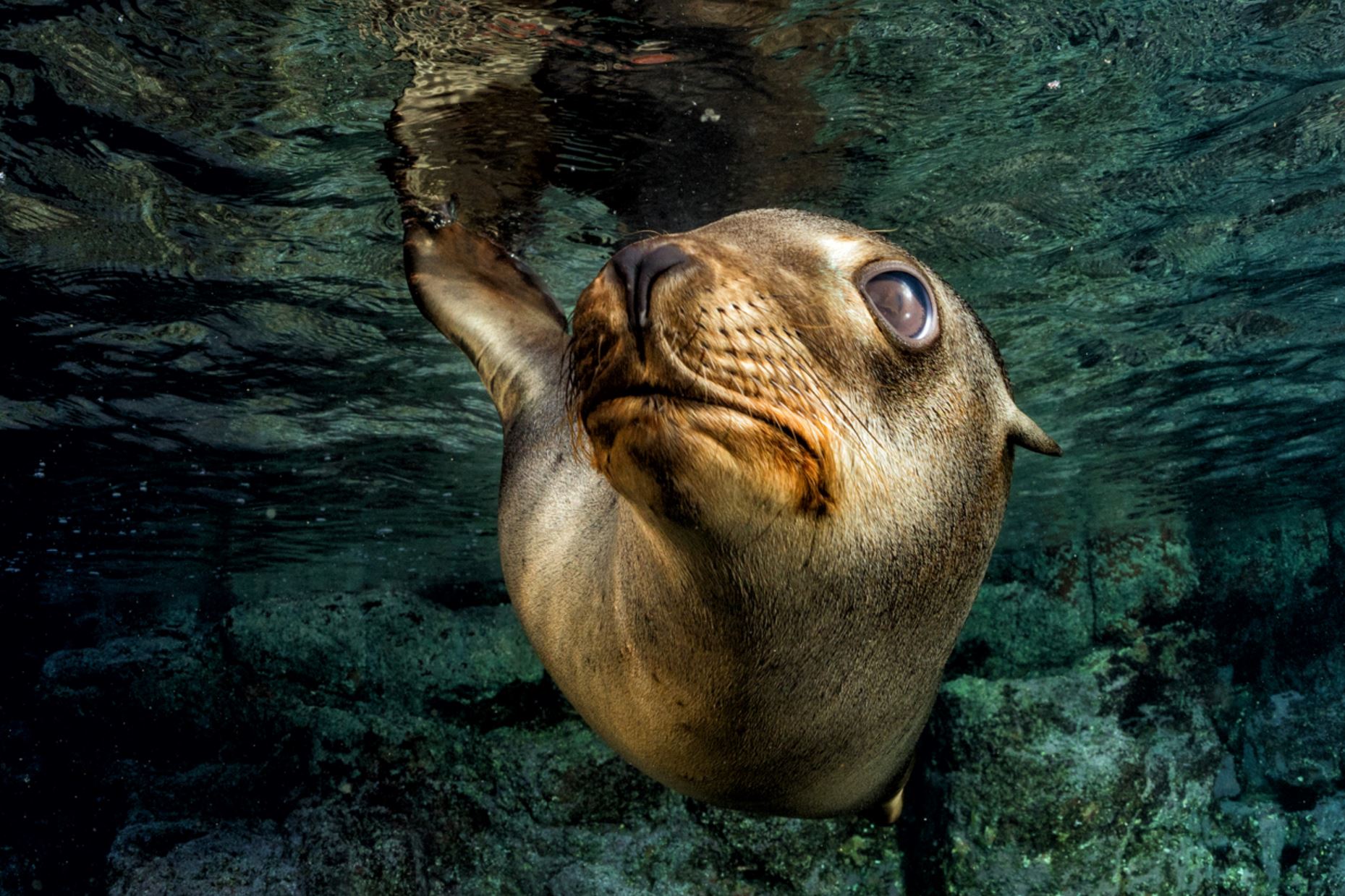
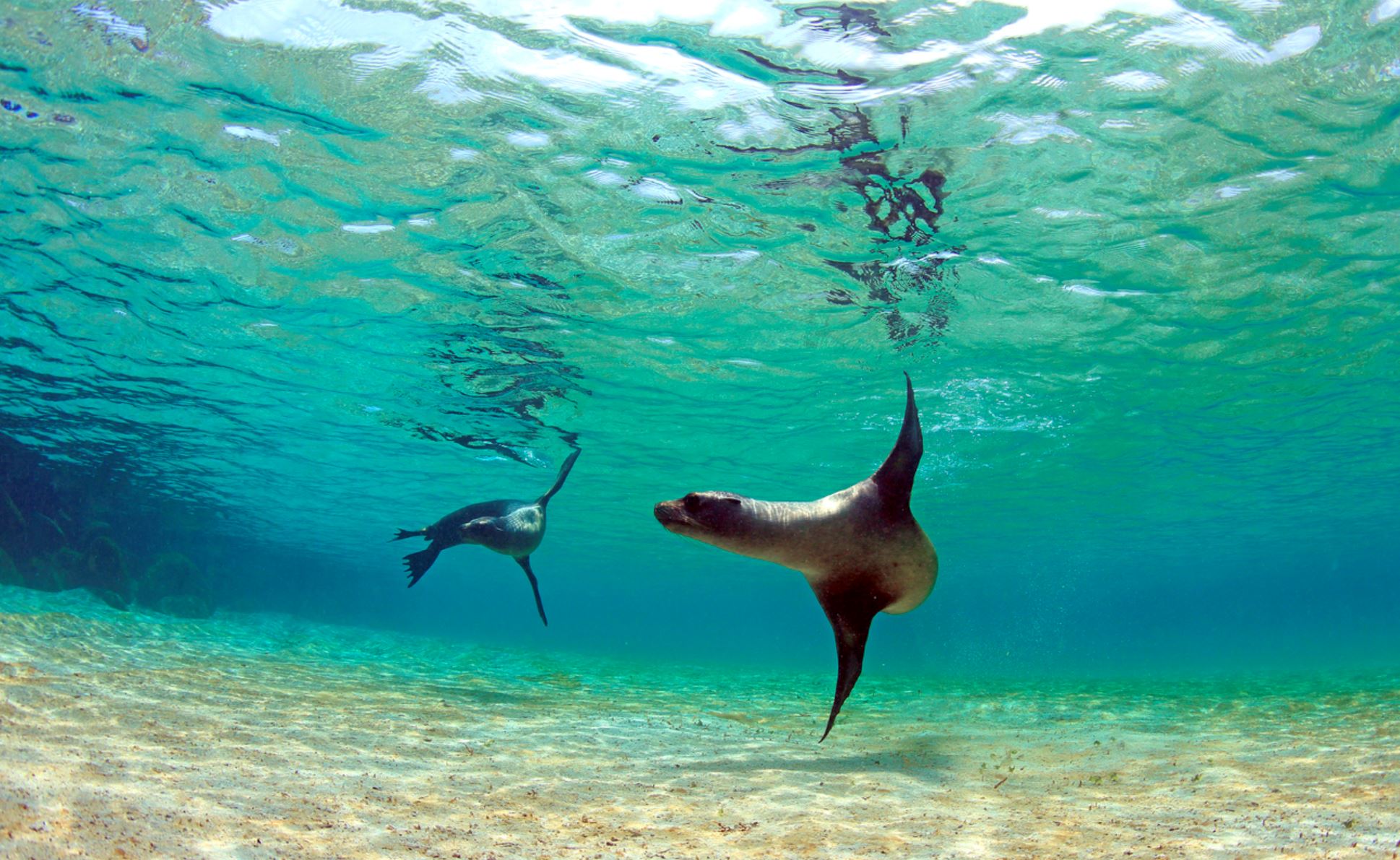
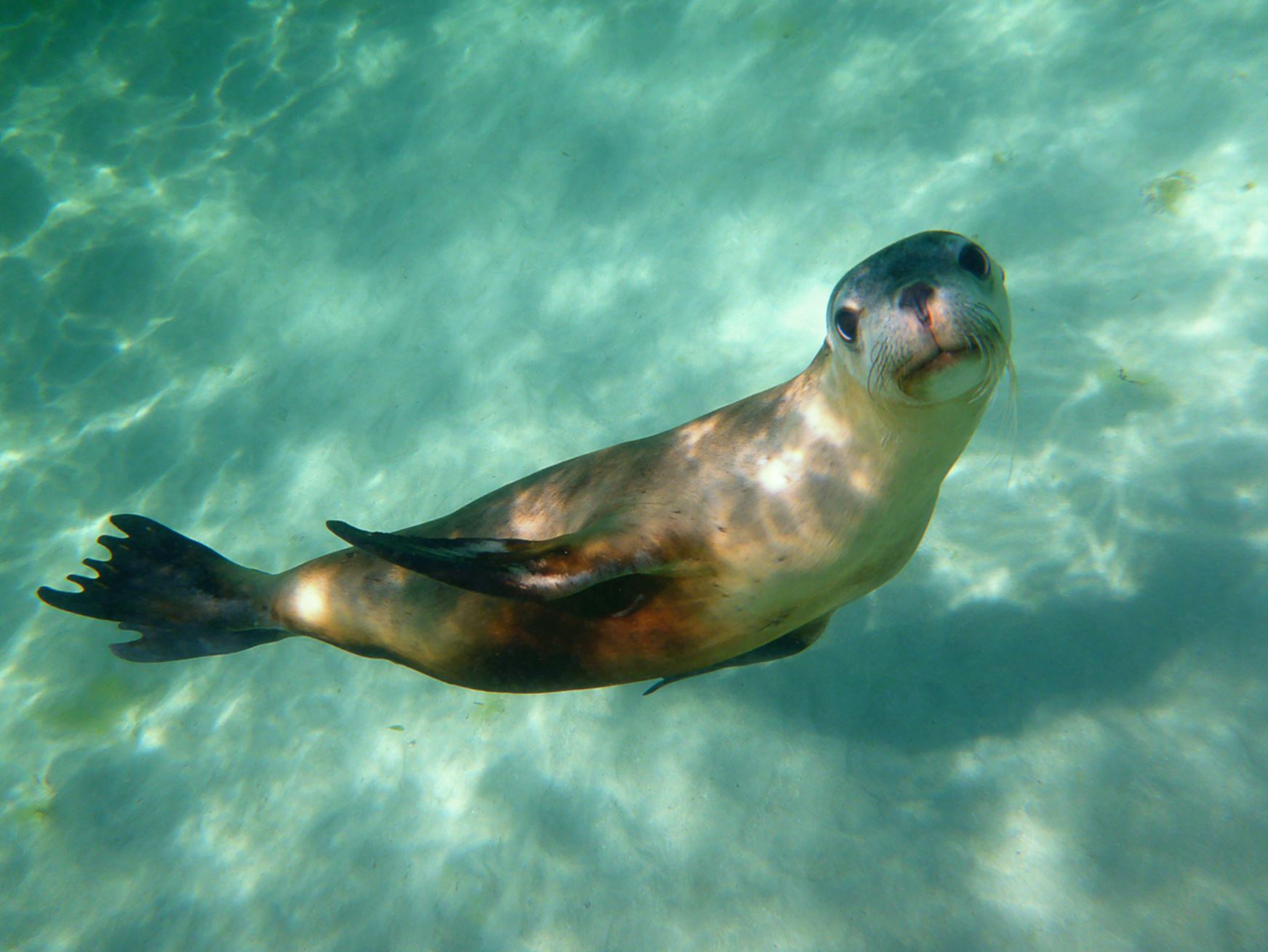
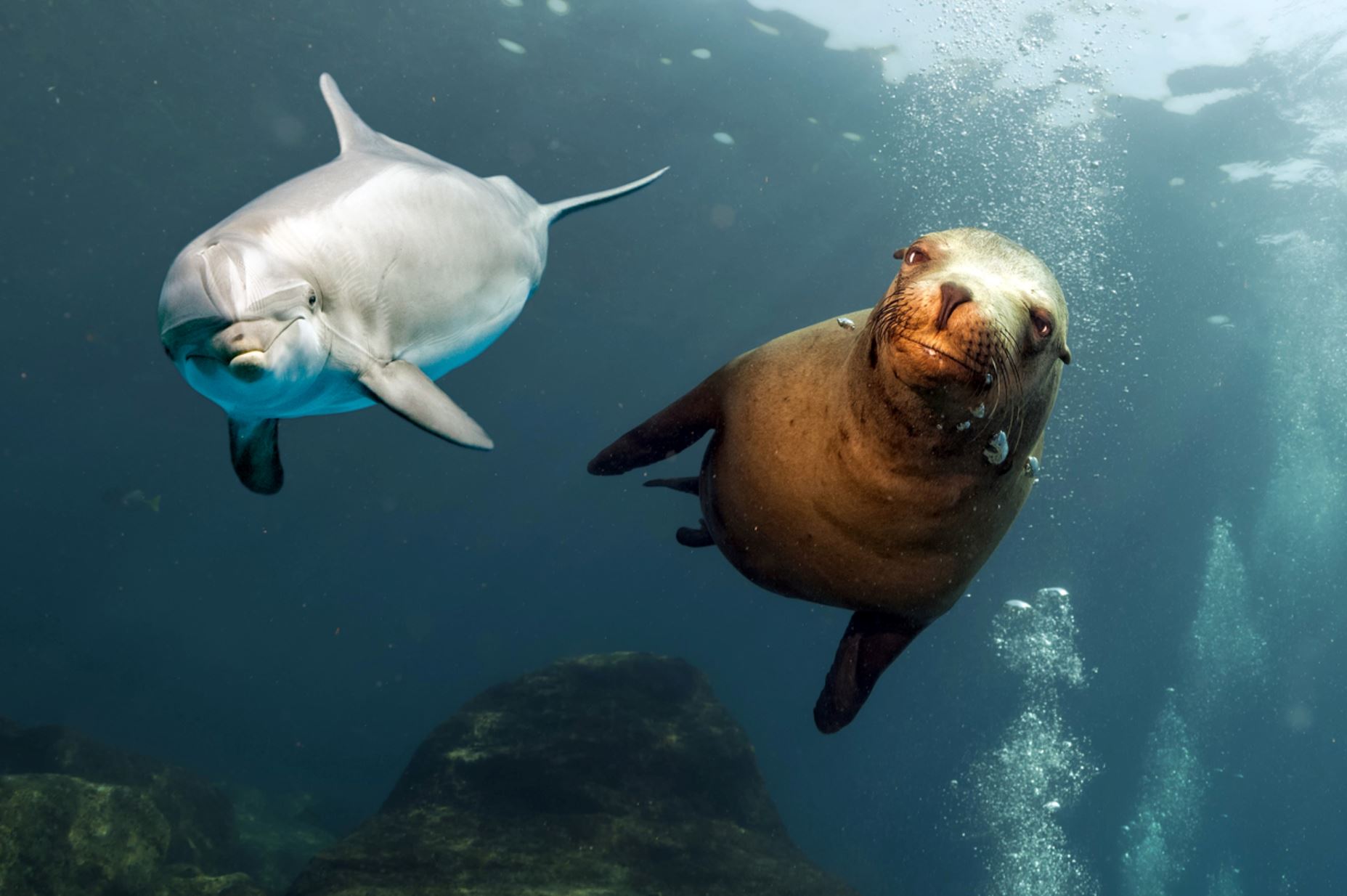
Galapagos Sea Lion
There are two species of sea lions in the Galapagos: the most common one is the Galapagos sea lion (Zalopus wollebacki) and the other one is the fur seal (Arctocephalus galapagoensis). Both are endemic to the Galapagos and are believed to have traveled south from North America and northern locations.
The Galapagos sea lion is one of the most emblematic animals of the Galapagos, with a hight of 1.50m to 2.50m (60 to 100 inches) and can weigh up to 250k (550lb). These sea lions are different from their relatives in California, being smaller and more sociable. They have external ears and the capacity of using their strong frontal fins to gallop inland and climb the rocky shores of the islands. The Galapagos sea lion, prefers the beach to the rocks and form colonies on them.
This species presents sexual dimorphism, which means they have physiological differences between the genders. Males are usually three to four times bigger than females and are usually darker in fur tones, additionally, the adult males present a bump in the head known as sagittal crest. Sea lions are fully developed at the age of ten years old but are sexually active at six years old. Females live up to 24 years and males usually about 18 due to the extra energy expense during all the reproductive life.
When forming a colony, only one Alfa male will reproduce and take care of the whole group, in some areas like San Cristobal you can observe colonies of more than 300 in a single beach. During mating season (July to December) the males fight for territory and for reproduction. This can be an extreme show of strength and speed.
Females have one pup a year that takes 11 months to be born. The pup lactates from the female every day, after she returns from fishing, for as long as two years, sometimes competing with the previous year new born. Sea lions, do not synchronize their breeding, this results in one of the reasons for the decreasing numbers.
Sea lions feed mainly on small fish, sardines, squid and other mollusks. Data has revealed that they can dive down to 200 meters and hold their breath for more than 20 minutes.
Their natural predators are sharks and orcas, whales very rarely fish sea lions in the Galapagos. The biggest colony of sea lions of the archipelago is in Puerto Baquerizo Moreno and San Cristobal. Here these animals cohabit with humans, preferring the populated beach, to the isolated ones of the island.
The fur seal is smaller than the sea lion, about 1.5m (5ft). This subspecies is very shy and rare to see. They prefer the rocks, to the beach and they have nocturnal habits. Fur seals are less in numbers when compared to the sea lion, as they were heavily hunted back in the day by the first colonizers.
- Animal Group: Mammals
- Scientific Name: Zalophus wollebaeki
- Animal Average Size: 150 - 170 cm
- Animal Average Weight: 60 - 100 kg
Fernandina, Isabela, Genovesa, Santiago, Rábida, Santa Fé, Daphne Major, North Seymour, Mosquera, Floreana, Española, San Cristobal.
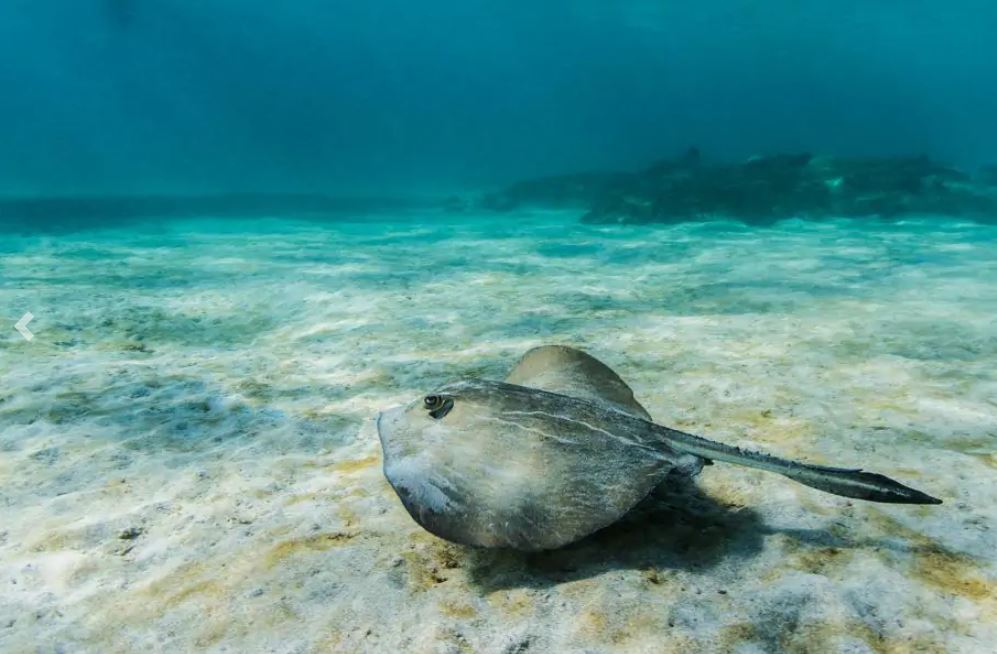
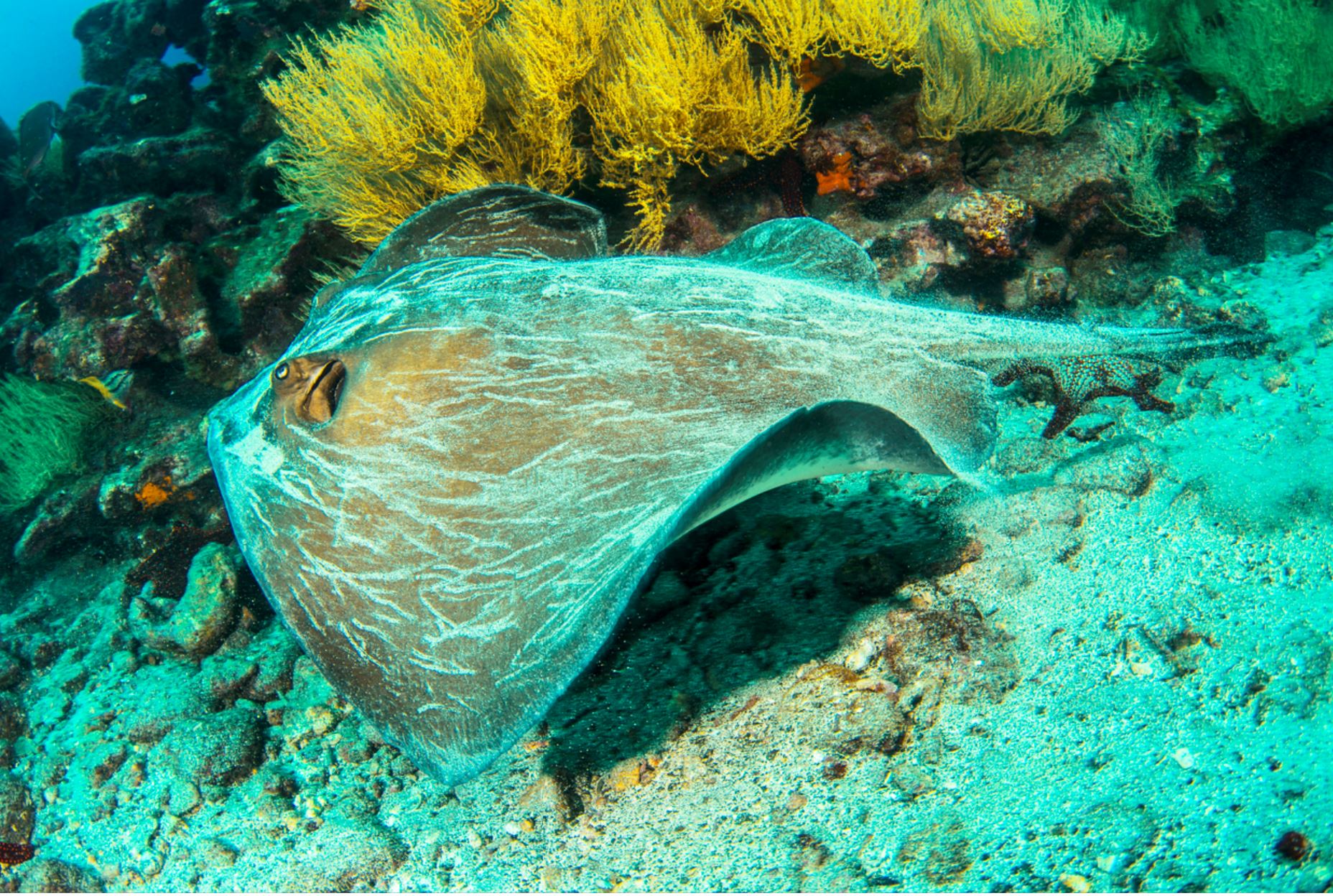
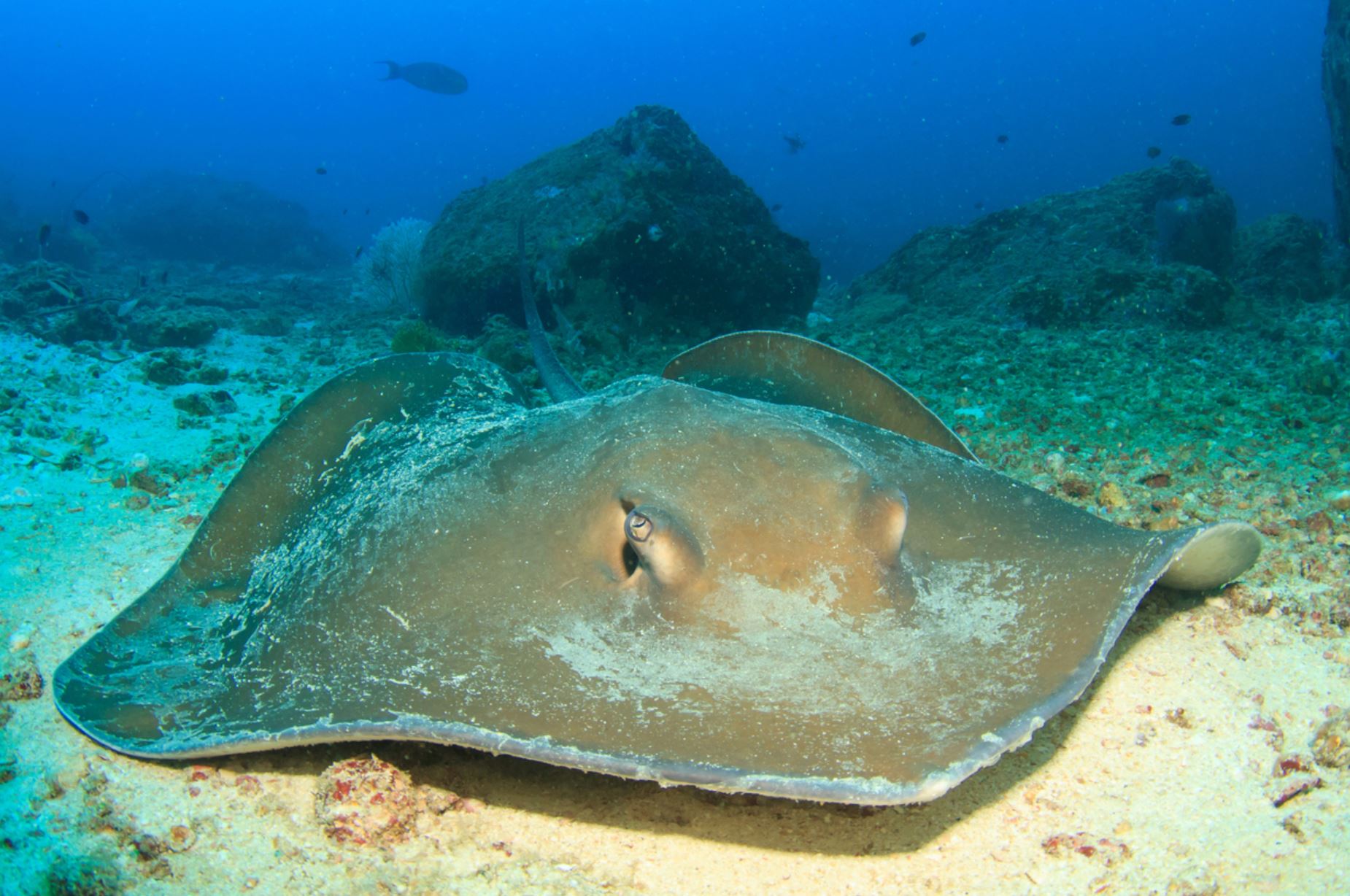
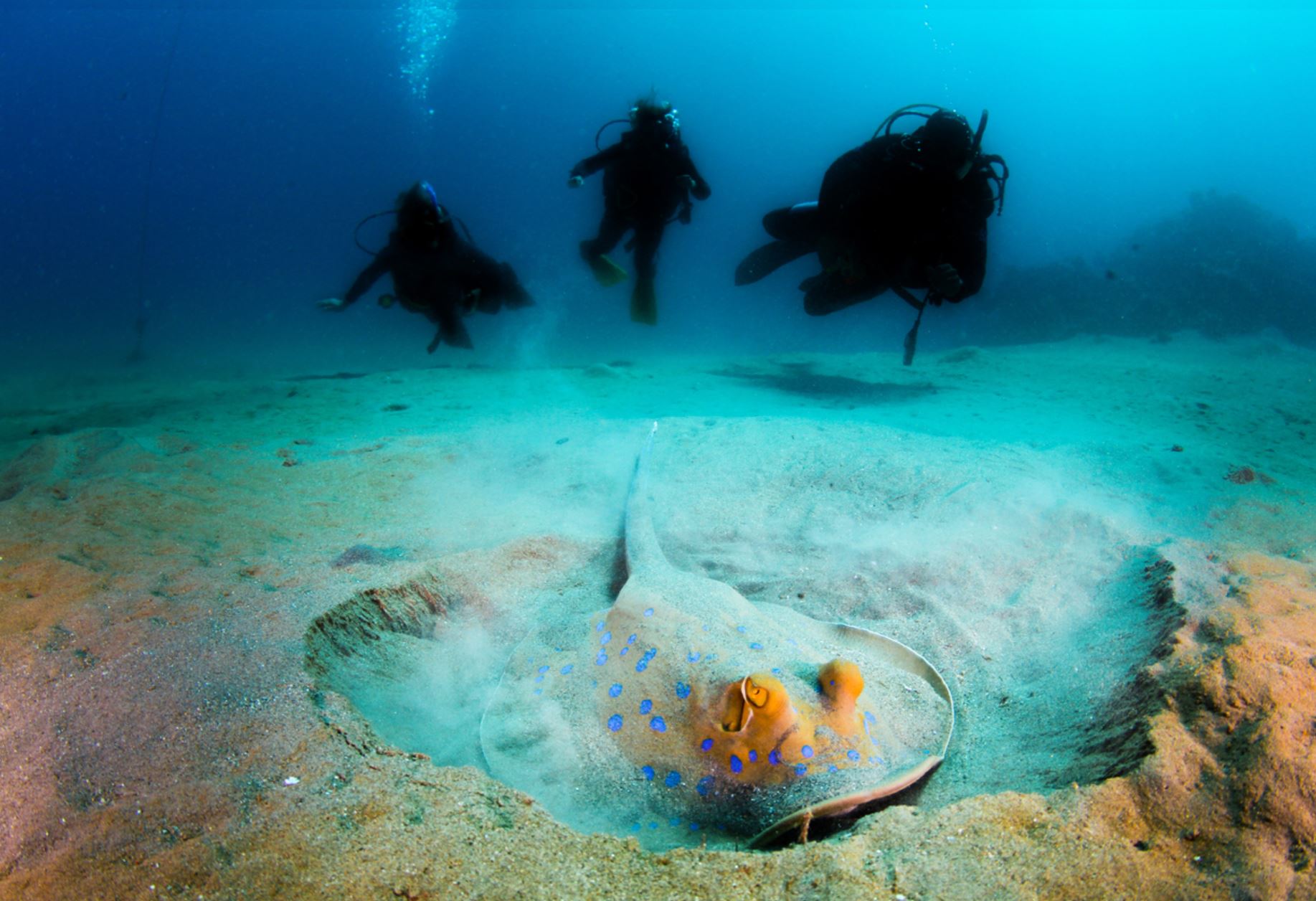
Galapagos Stingrays
Seen from the side, this animal is perfectly flat, with pectoral fins that extend to the head. The eyes are located at the sides of its head and with breathing cavities near. The diameter on average is from about 30 cm to less than 1 m. Stingrays are close relatives to sharks, with the common factor that both are cartilaginous fish that swim in warm waters of tropical oceans.
They will have one baby per year, and when the baby is born it will have to fend for itself. The females keep the egg and the juvenile in their uterus (ovoviviparous) from 2 to 4 months until the youngster is big enough to be born. No parental care is given to the newborn, it must be ready to feed and protect itself. Cartilaginous fish tend to mature at a slow rate, some studies say that they enter maturity when they are 20 to 30 years old.
Stingrays can spend most of their time buried on the seafloor and they have electrical receptors in their skin to help them read electrical charges in the ocean when looking for food and for orientation. Their favorite food is worms, fish, mollusks, crabs, and shrimp that they get by scooping through the ocean sand.
There are also other species in the ray family that can be spotted in the Galapagos: manta rays (the biggest of all, measuring about 4 m across its fins), golden rays, and spotted eagle rays.
- Animal Group: Marin Life
- Scientific Name: Dasyatidae
- Animal Average Size: 30 cm - 2 m
- Animal Average Weight: 7,6 kg
Places where you may see this animal in Galapagos:
Wolf, Darwin, Fernandina, Isabela, Genovesa, Santiago, Bartolomé, Rábida, Chinese Hat, Santa Fé, Santa Cruz, North Seymour Plaza Sur, Floreana, Española, San Cristobal
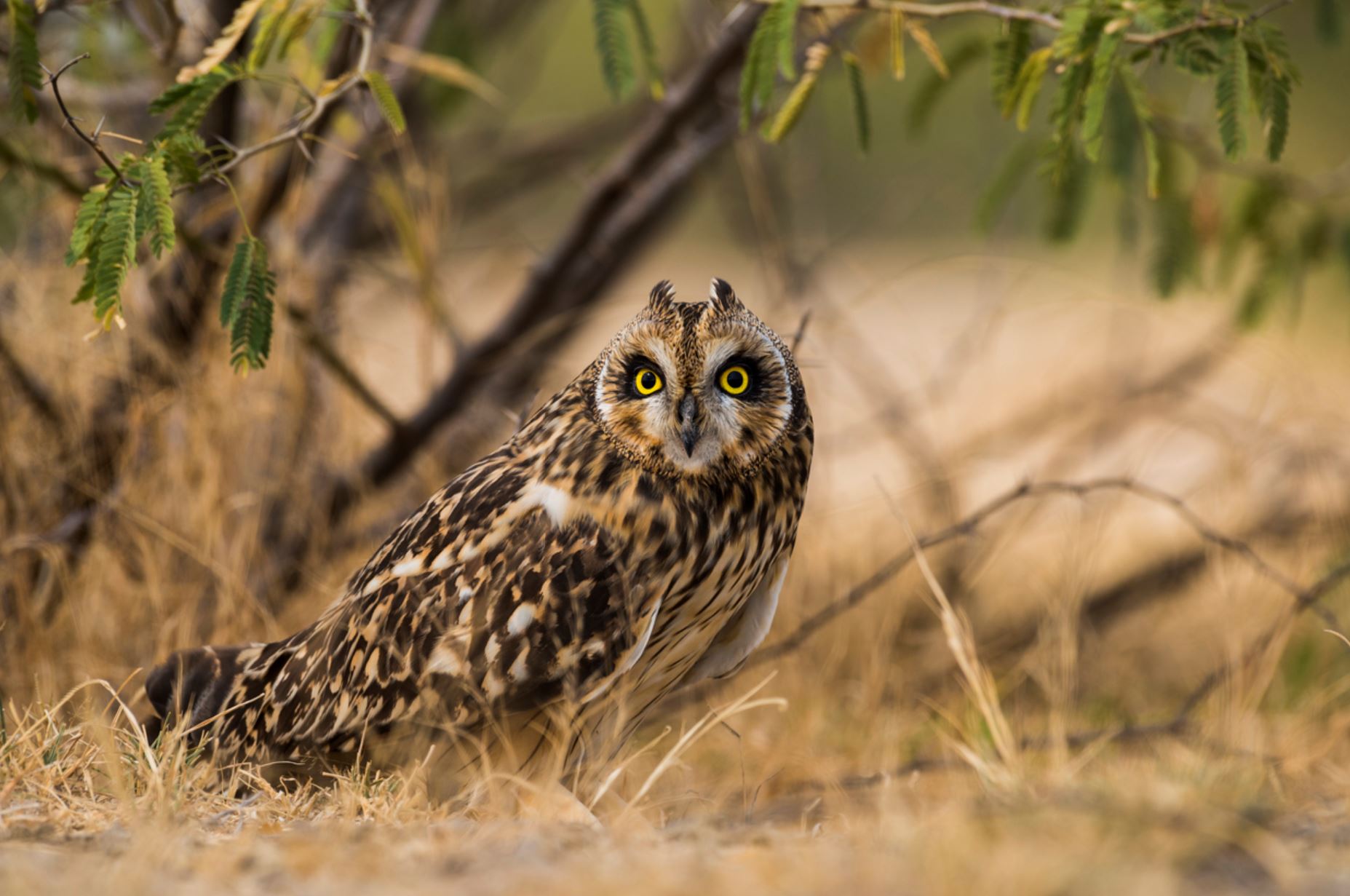
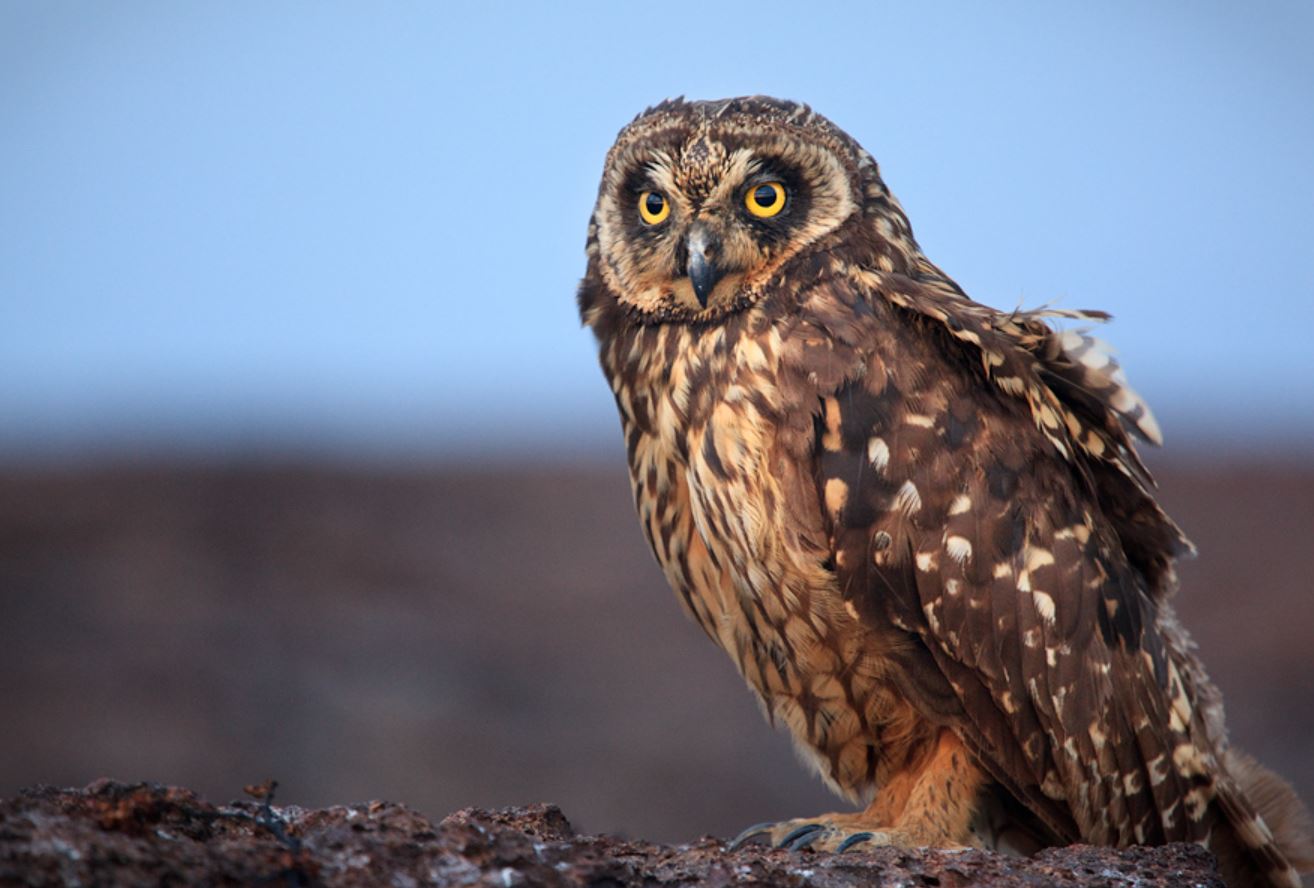
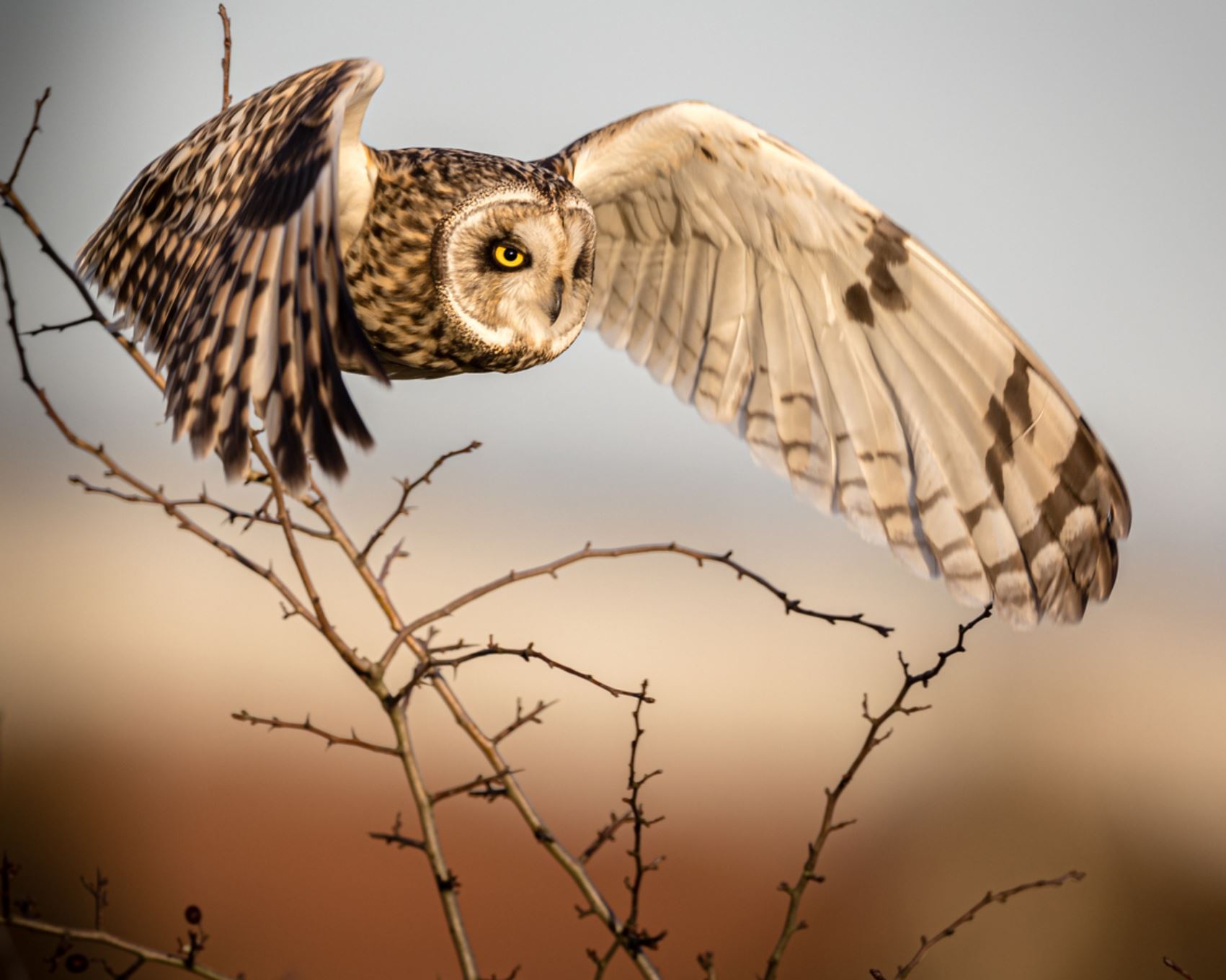
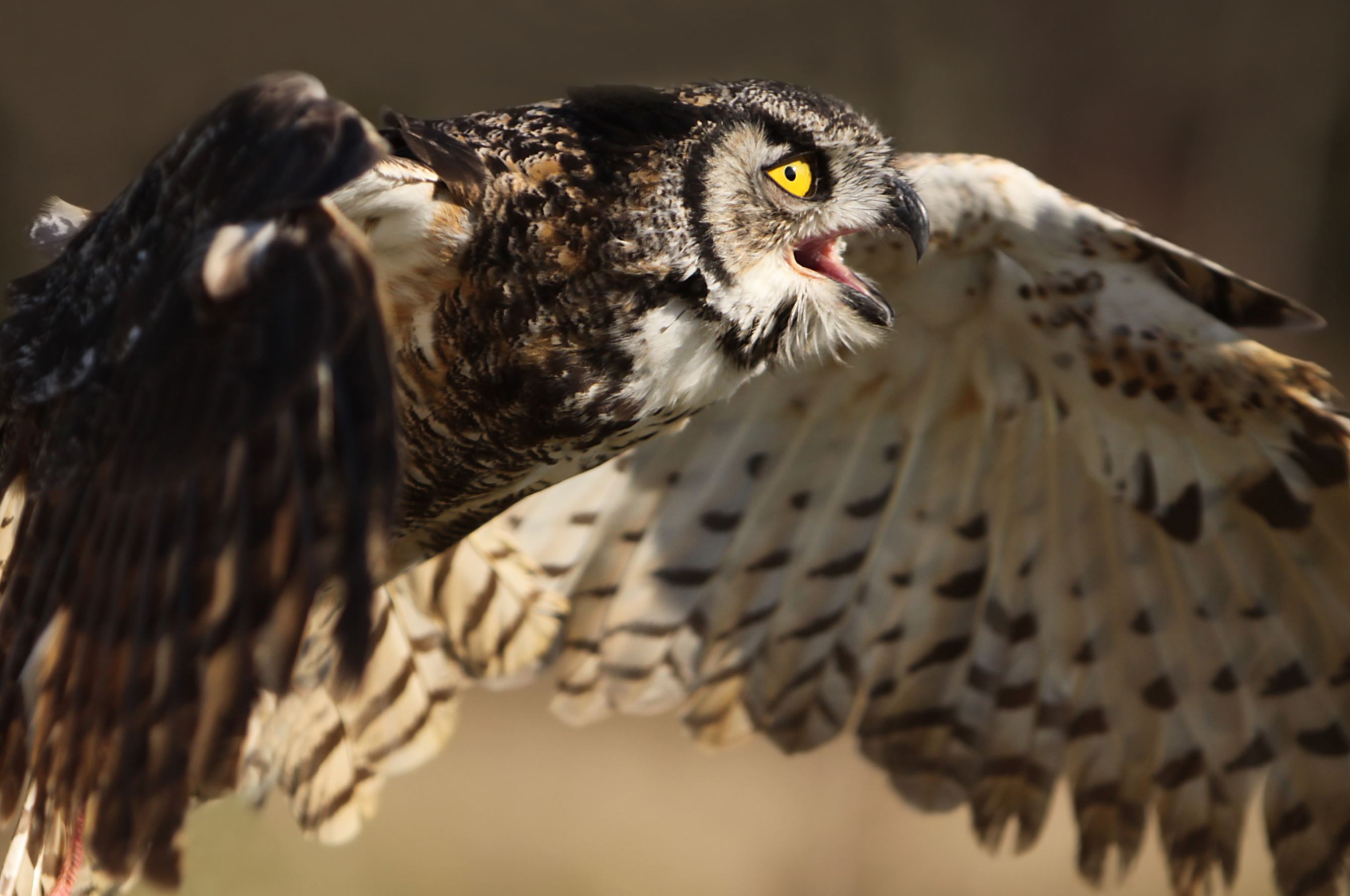
Galapagos Short-eared Owl
The Galapagos short-eared owl is a sub-species of the short-eared owl, a bird which found on all continents except Antarctica. Galapagos short-eared owls are endemic to the Galapagos Islands and, as is frequently the case with Galapagos endemics, their coloration is darker and they are smaller than their mainland counterparts.
Their name arises from their small ear tufts. They have a wingspan of 85-100cm and are silent fliers. The sexes are alike, though the females are generally larger than the males. Immature plumage resembles that of the adults.They are found in open areas of grassland or lava rock, and hunt by flying low over these areas, feeding on rats, lava lizards, and birds. Most owls hunt at night, however the Galapagos short-eared owl has adapted to hunt in the daytime as well, to avoid competition with the Galapagos hawk.
Animal Group: Owl
- Scientific Name: Asio flammeus
- Animal Average Size: 42 cm/16 inches
- Animal Average Weight: 300 - 500 g
Isabela, Santa Cruz, Genovesa, Floreana
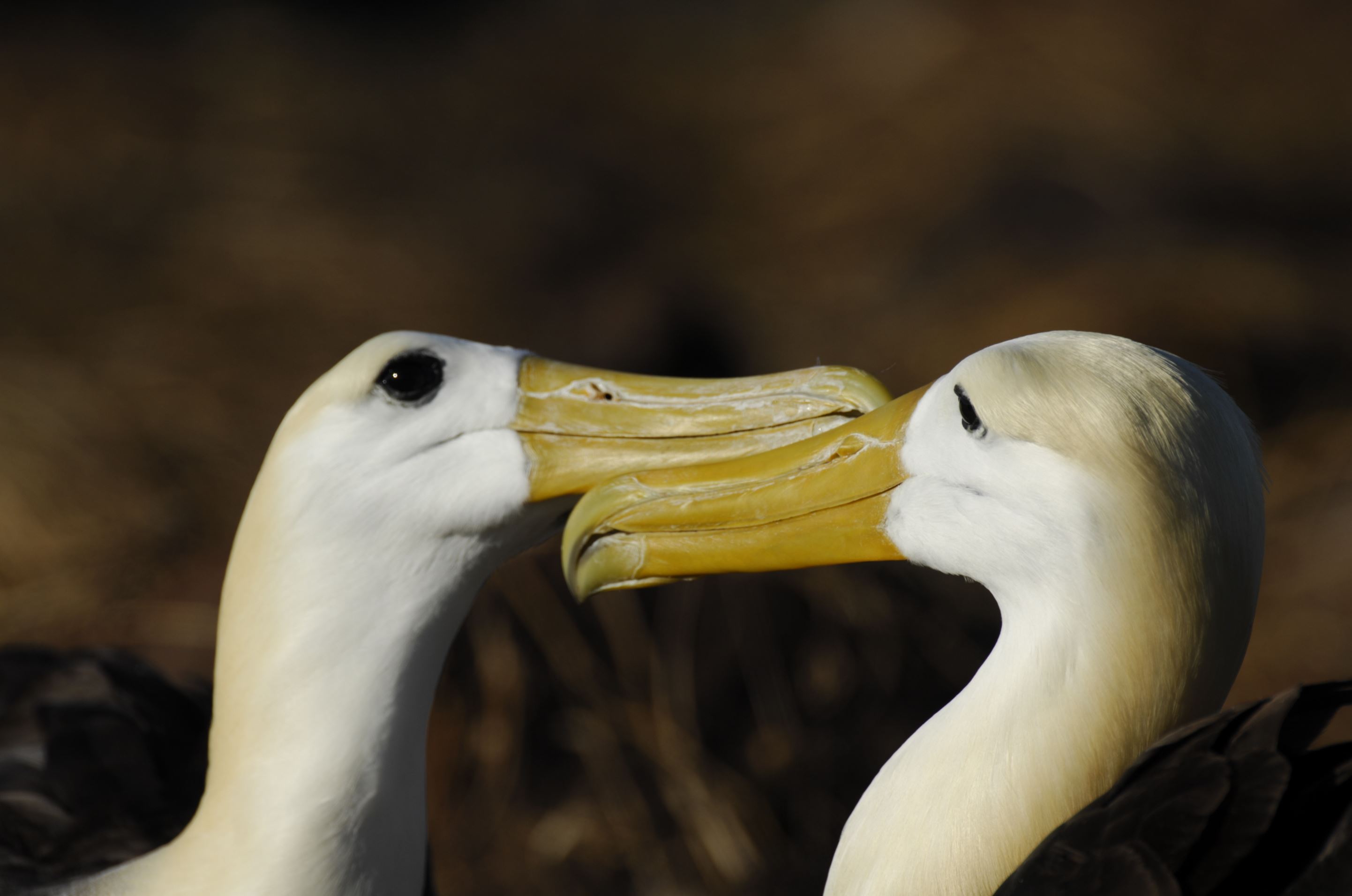
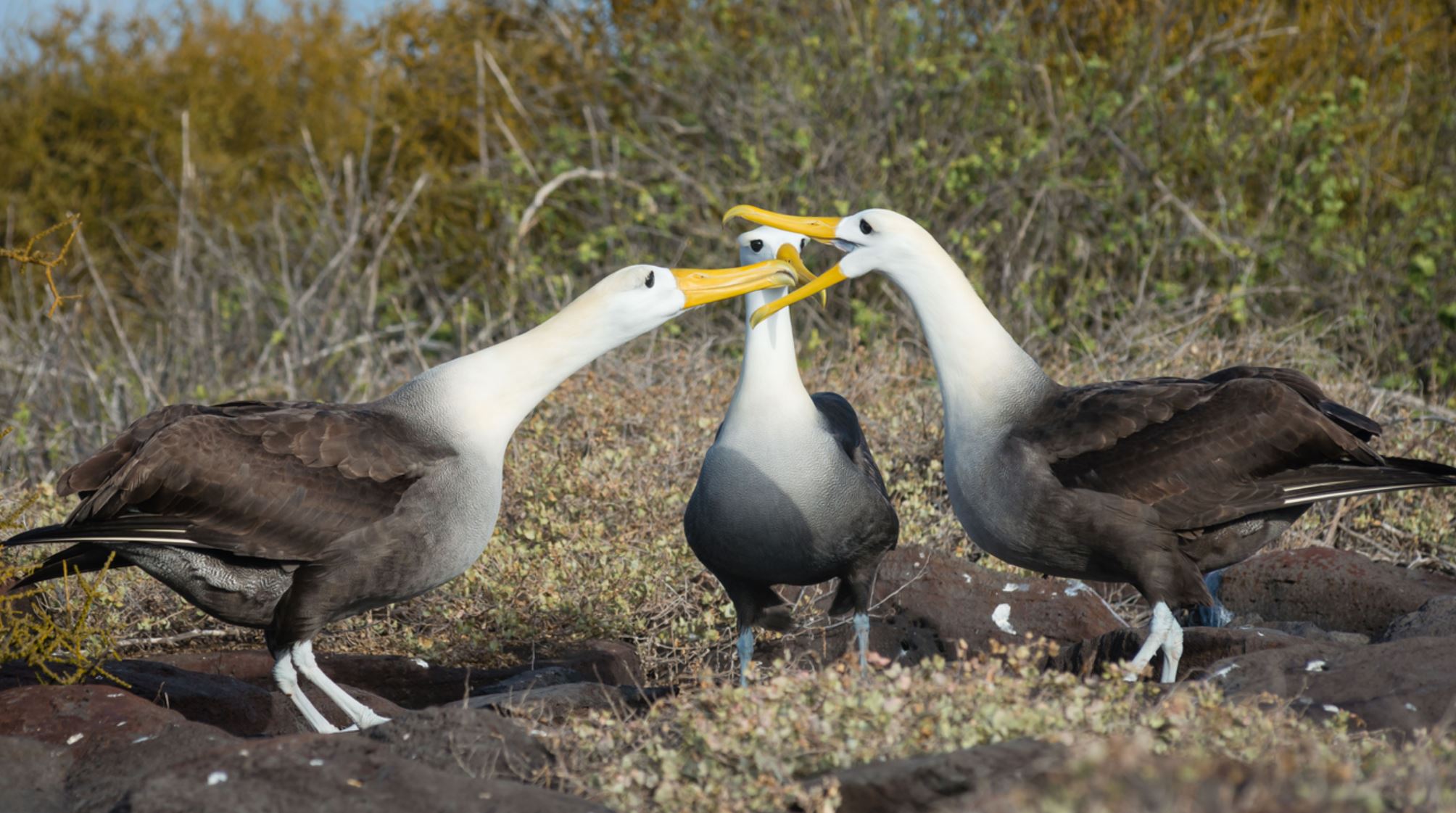
Galapagos Wawed Albatros
This bird is endemic to the Galapagos Islands and is also known as the Galapagos Albatross, found in the largest colony in the world located on Española Island.
The preference for Española Island for a couple has its reasons. The eroded field of the islands has helped to create flat areas where the Galapagos albatross can easy takeoff with its large wingspan and weight near cliffs. They are known for their perfect flying abilities when using the wind speed to travel far distances. The flat fields are also the perfect location for nesting sites and the nearby cold water currents bring plenty of food.
The colonies are deserted from January to March. Males arrive first and wait for the females to meet them. Their courtship ritual consists of spectacular mating dance, based on bill circling and bowing, uprising the beak and clacking beaks together. As a monogamous animal, the dance in the next breeding season will be less elaborated. Females lay one big egg between April and June which is incubated for two months and is also moved to improve the hatching success. When an egg is abandoned, it can be adopted by another couple of albatross and rarely by another bird species.
When parents go fishing, the chicks congregate together probably to reduce the chance of being preyed upon. Once the parents are back, they recognize unique tones from each other. Chicks are feed about 2kg of an oily nutritious substance made out of digested fish and squid that is rich in nutritional value, thus the youngsters can be ready to leave the nest in about 6 months’ time.
They are considered critically endangered due to their delicate and fragile sole nesting area. There are 35 thousand pairs on the islands that can live up to 50 years.
Animal Group: Seabirds
Scientific Name: Phoebastria irrorata
Animal Average Size: 89 cm
Animal Average Weight: 2 kg
Places where you may see this animal in Galapagos: Genovesa, Santa Cruz, San Cristobal, Española
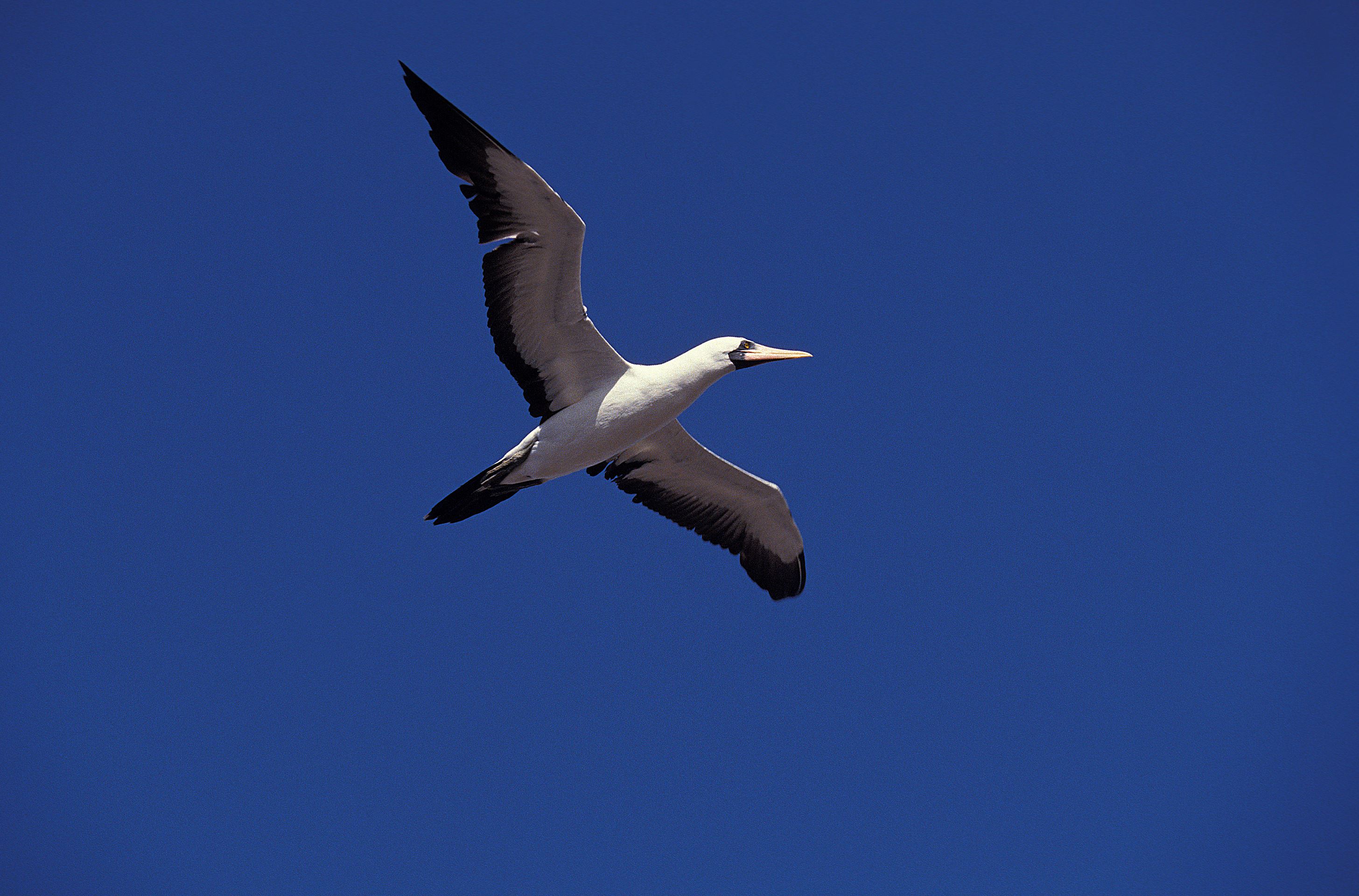
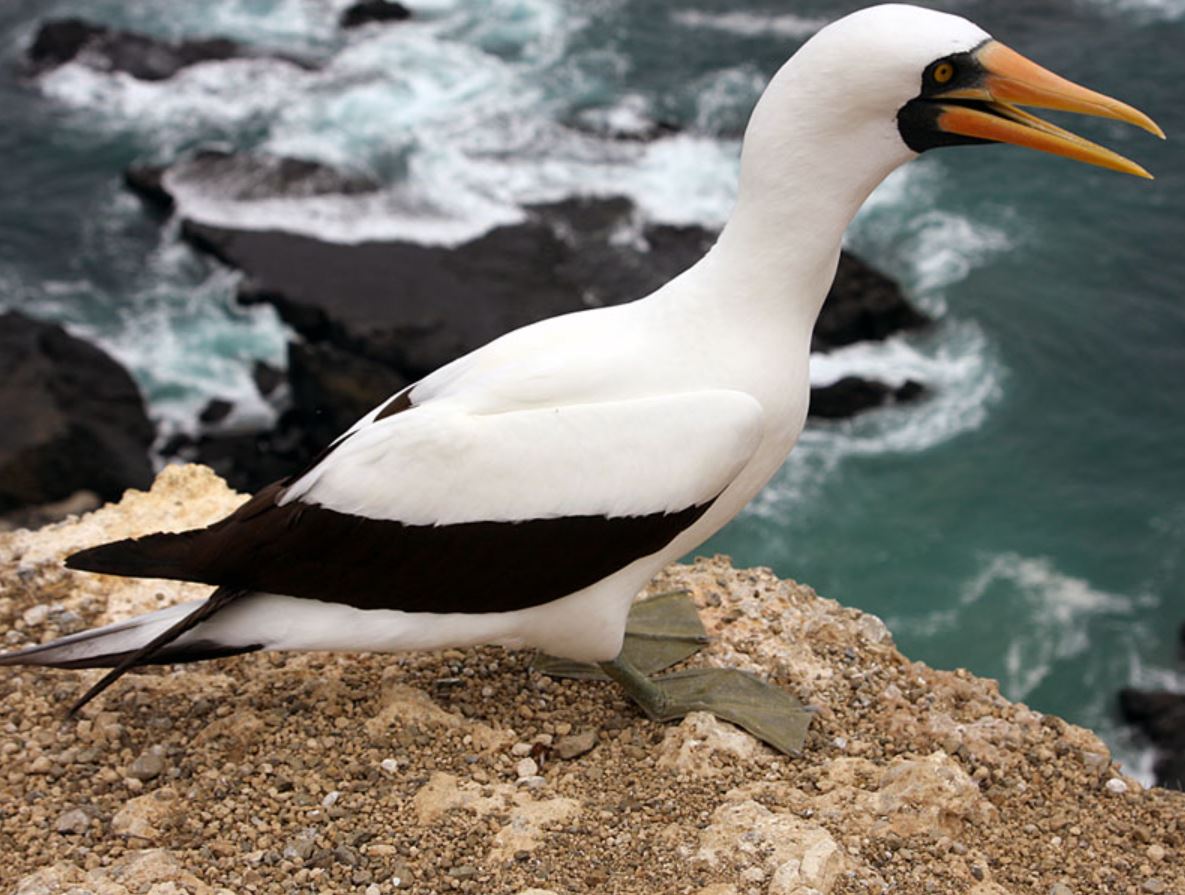
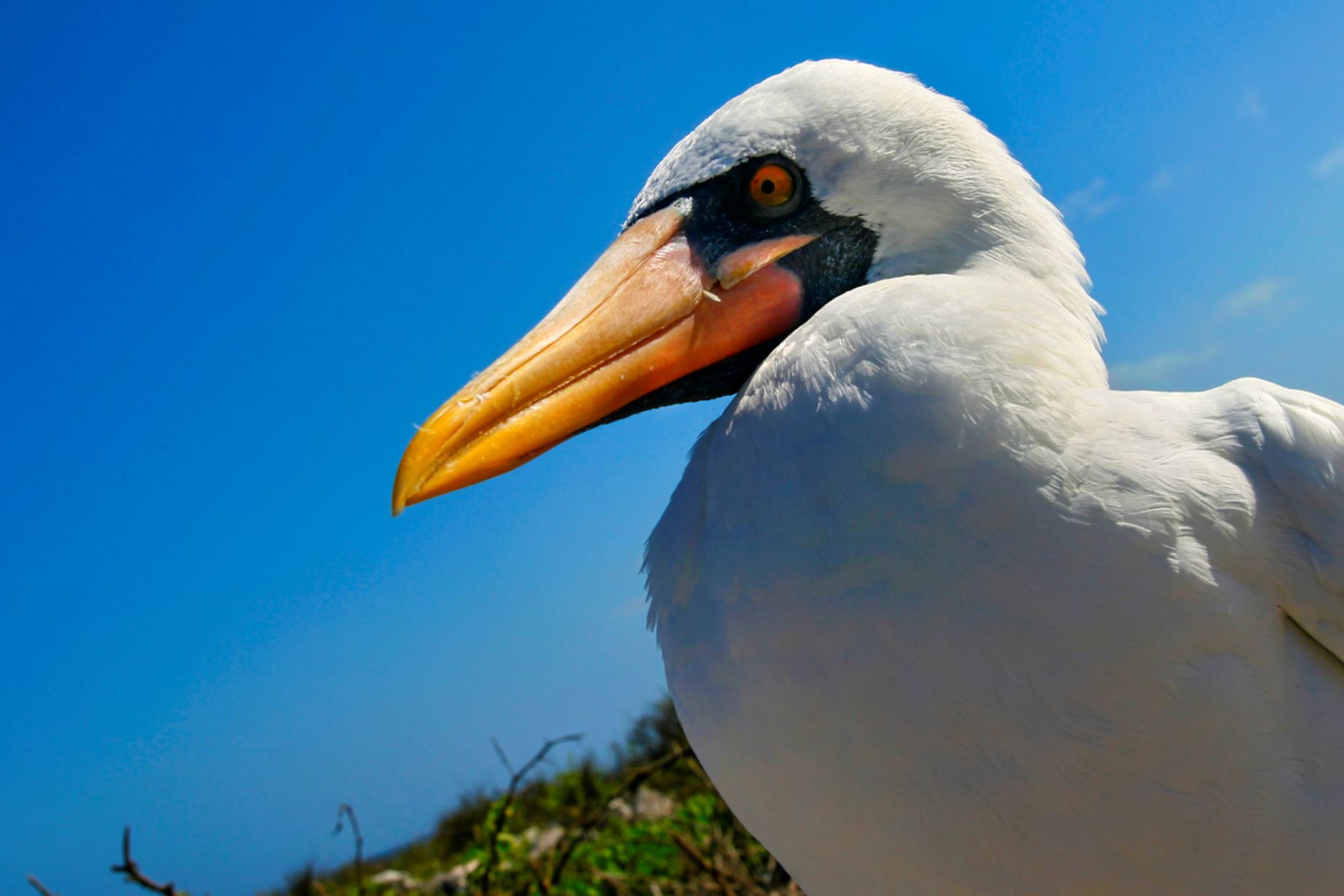
Naszca Booby
The Nazca booby bird is found in the Eastern Pacific region of the Galapagos. Named Nazca booby because of its inhabiting area, it is considered a subspecies of the masked booby. They feed by plunge-diving usually on flying fish, anchovies and sardines. Usually, they feed away from land and it is rare to see them fishing. They can live from 20 to 25 years.
Their courtship ritual involves the sky pointing position and shaking the head up and down and to the sides. After the male’s display, the female would join the male in the sky pointing position, knocking their beaks together.
Females lay 2 eggs that hatch, but only one would survive due to food availability and parental care. The fittest chick would push away the other from the nest or even kill it. Studies have shown that this behavior increases the surviving success of one chick, compared to the pairs that only lay an egg.
Their breeding season lasts 9 months, the months vary depending on the island. This species nests on the ground and the chicks grow as big as their parents, before developing feathers and need parental care until they strengthen their flying muscles. They have trouble taking off due to their weight and size, so they prefer nesting in cliffs and islets from where it is easier to fly off.
They can be seen on almost every island and in the walls of most cliffs, with about 20 thousand pairs living in the archipelago.
- Animal Group: Seabirds
- Scientific Name: Sula granti
- Animal Average Size: 81 – 92 cm
- Animal Average Weight: 1.8 kg
Places where you may see Nazca Boobies in Galapagos: Santiago, Genovesa, Santa Cruz, San Cristobal, Española
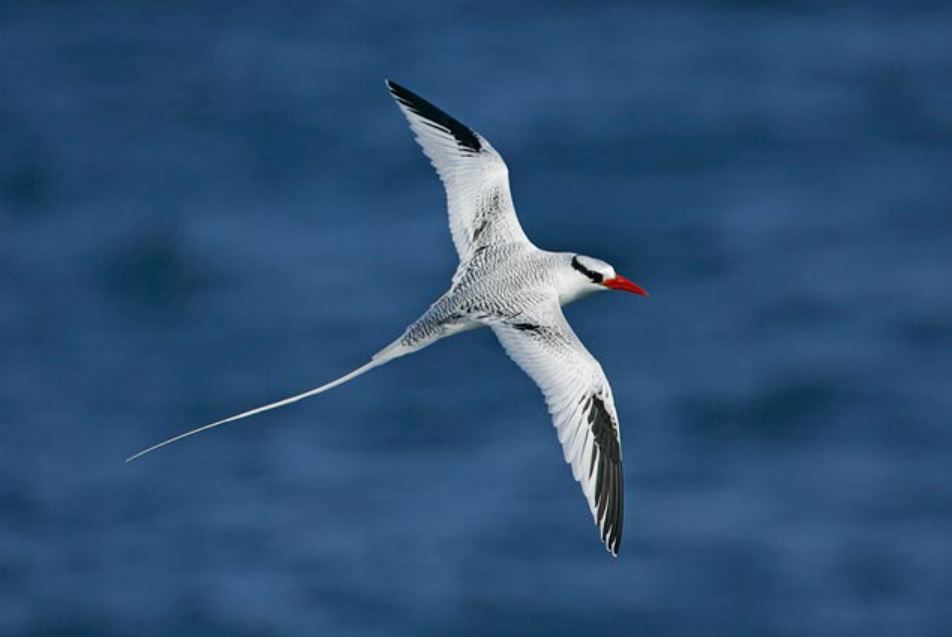
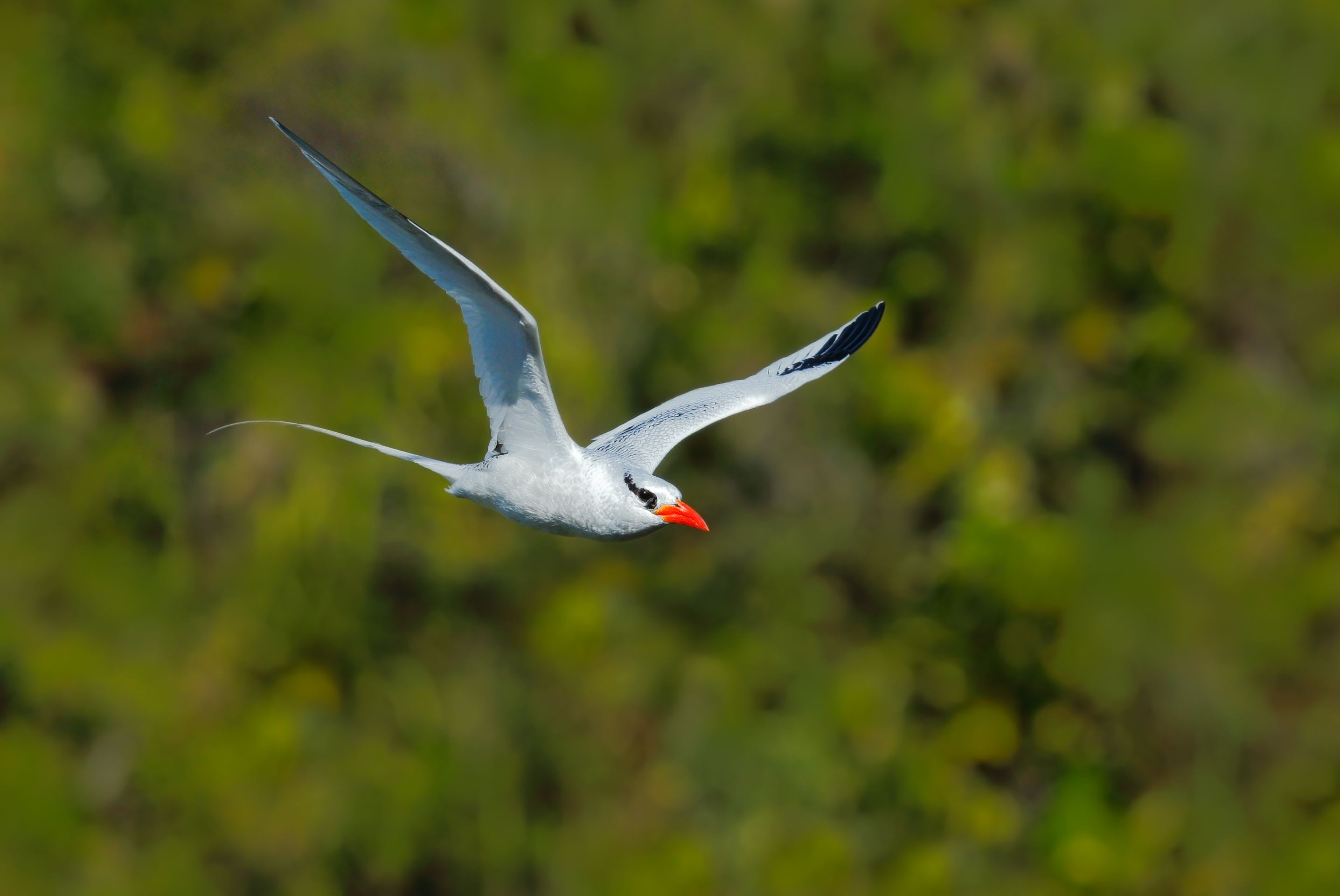
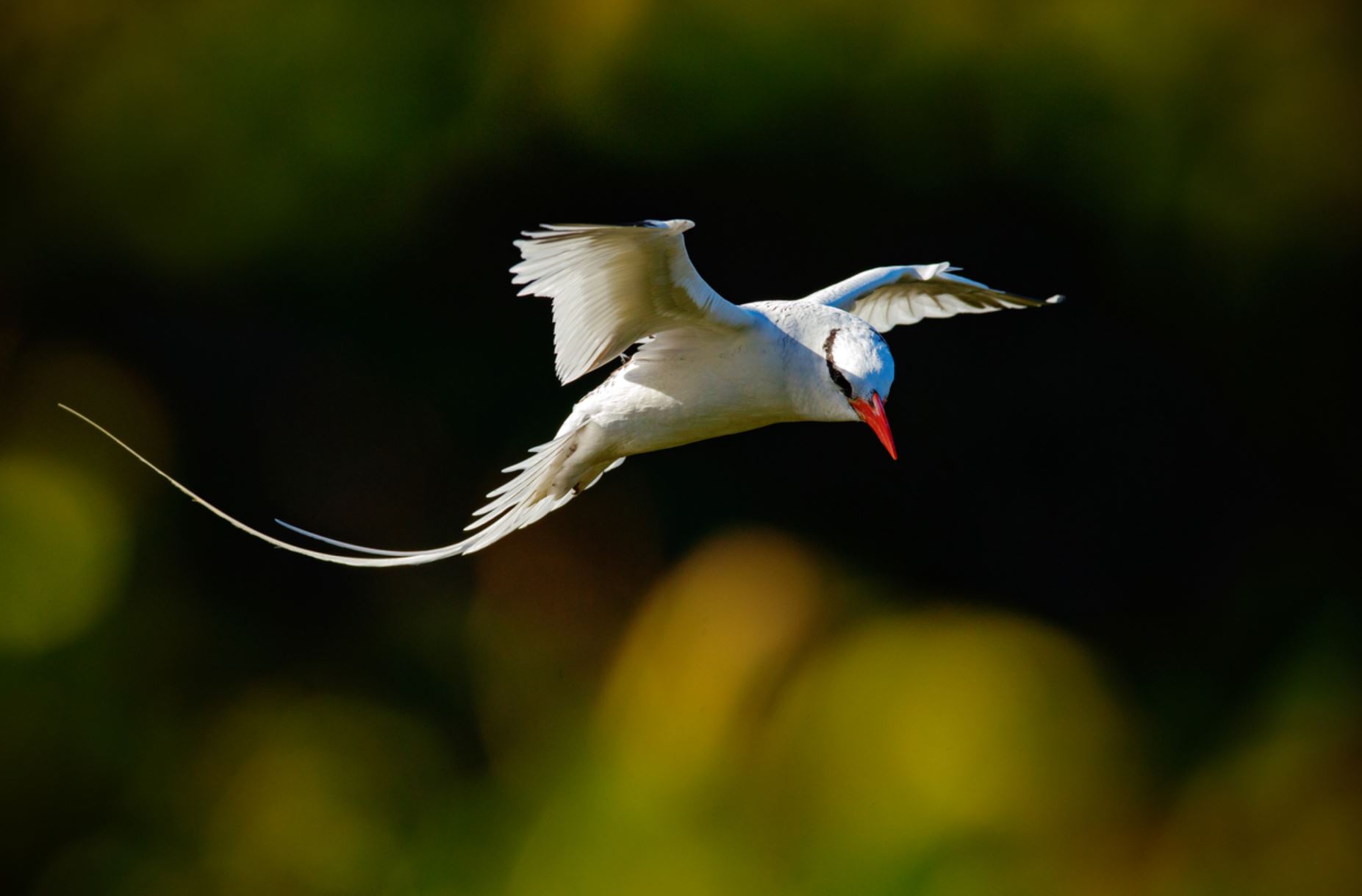
Red-Billed Tropicbird
The red-billed tropicbird is widely spread around the eastern pacific and the Caribbean and Indian oceans. In the Galapagos, they are found all around as they choose cliffs and rocky walls to nest.
They feed by plunge-diving mainly on squid and small fish, but they are poor swimmers. When sitting in the water after a catch, the tail feathers are locked in an upright position and this is usual to see.
Their courtship ritual is performed in the air by aerial acrobatics. Female and males are alike, but the male has a longer tail. Breeding happens all along the year and they lay one single egg.
Animal Group: Seabirds
Scientific Name: Phaethon aethereus
Animal Average Size: 90 - 105 cm
Animal Average Weight: 42 g
Places where you may see Red-Billed Tropicbirds in Galapagos: Santa Cruz, Genovesa, South Plaza, Española
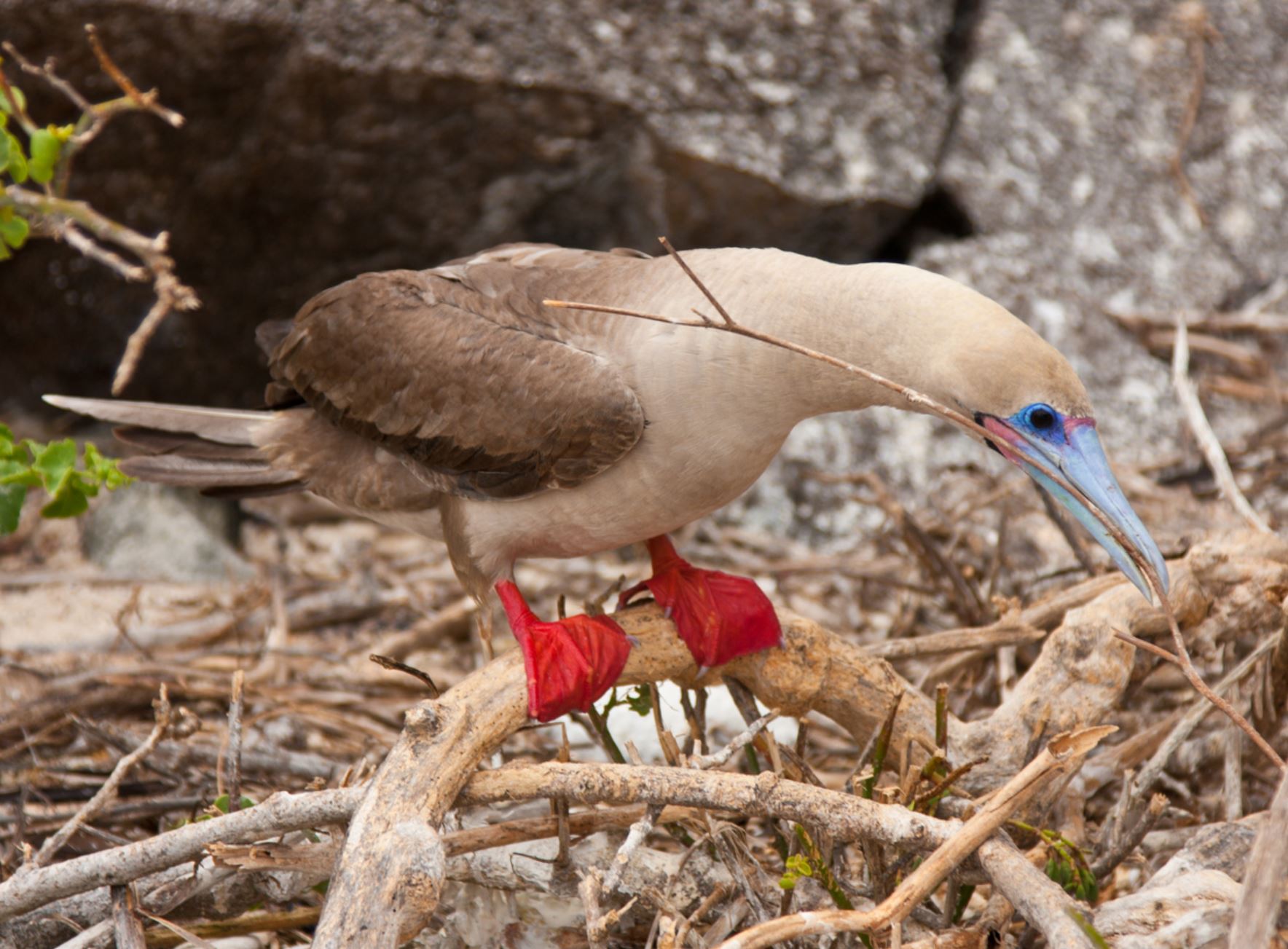
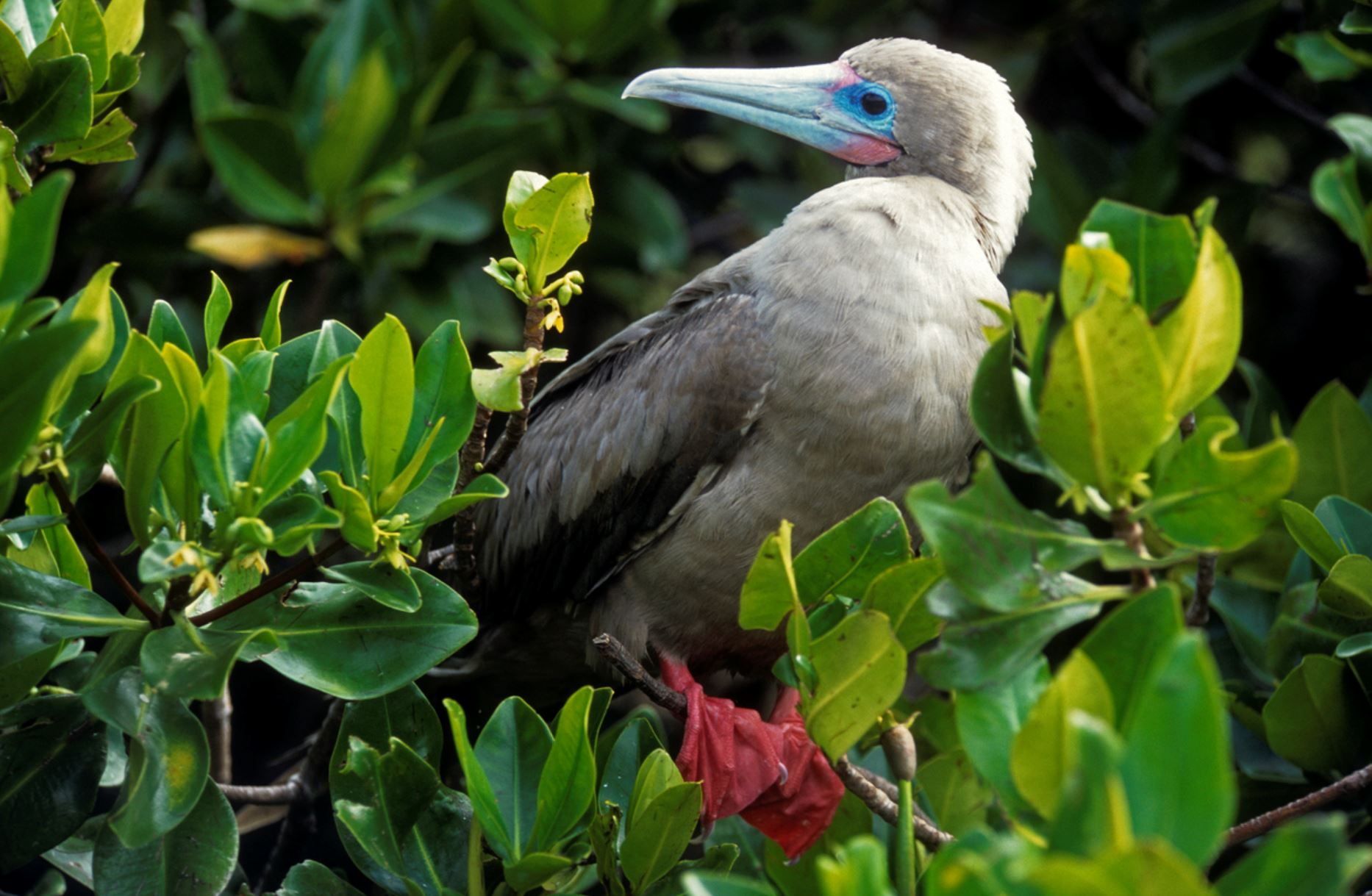
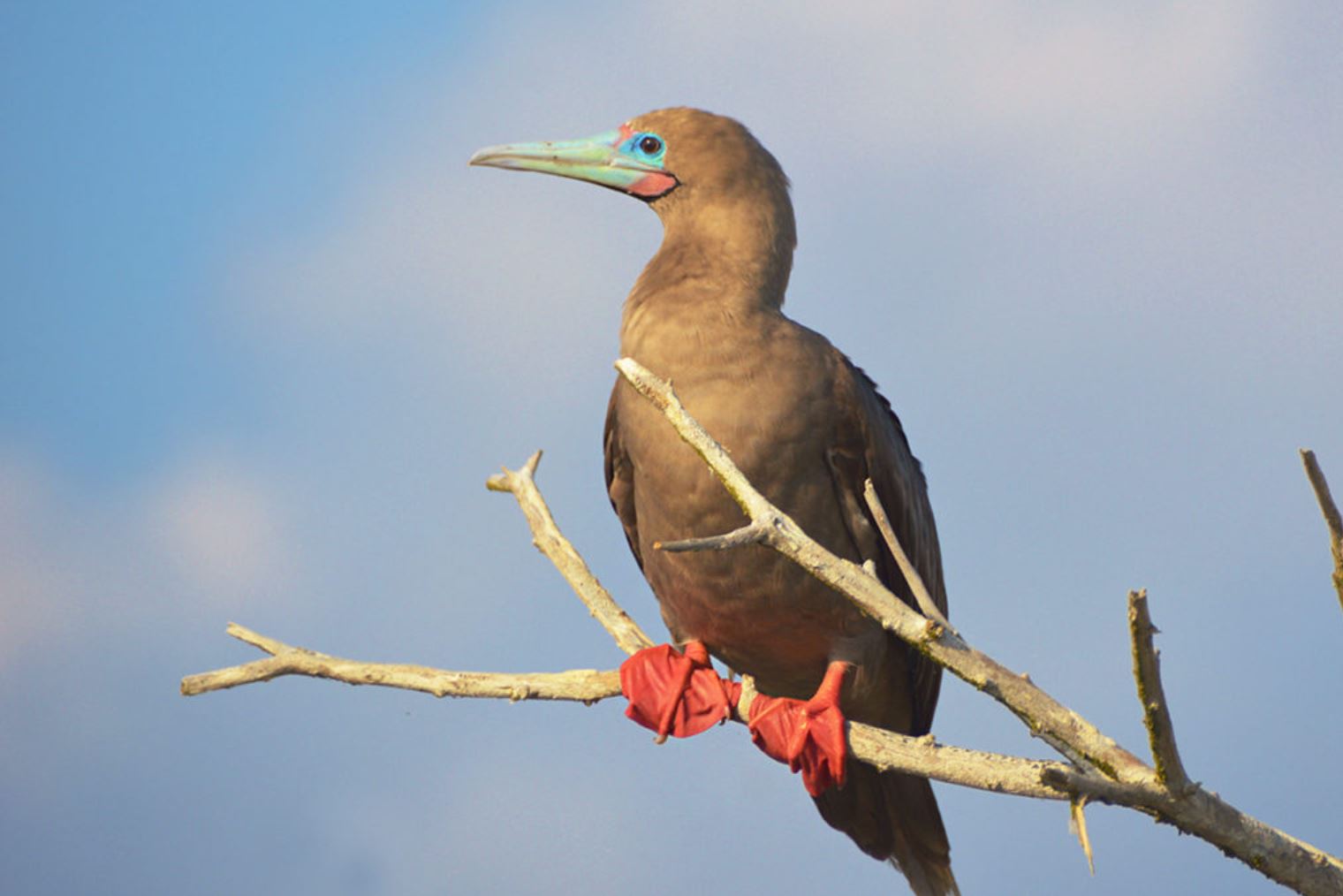
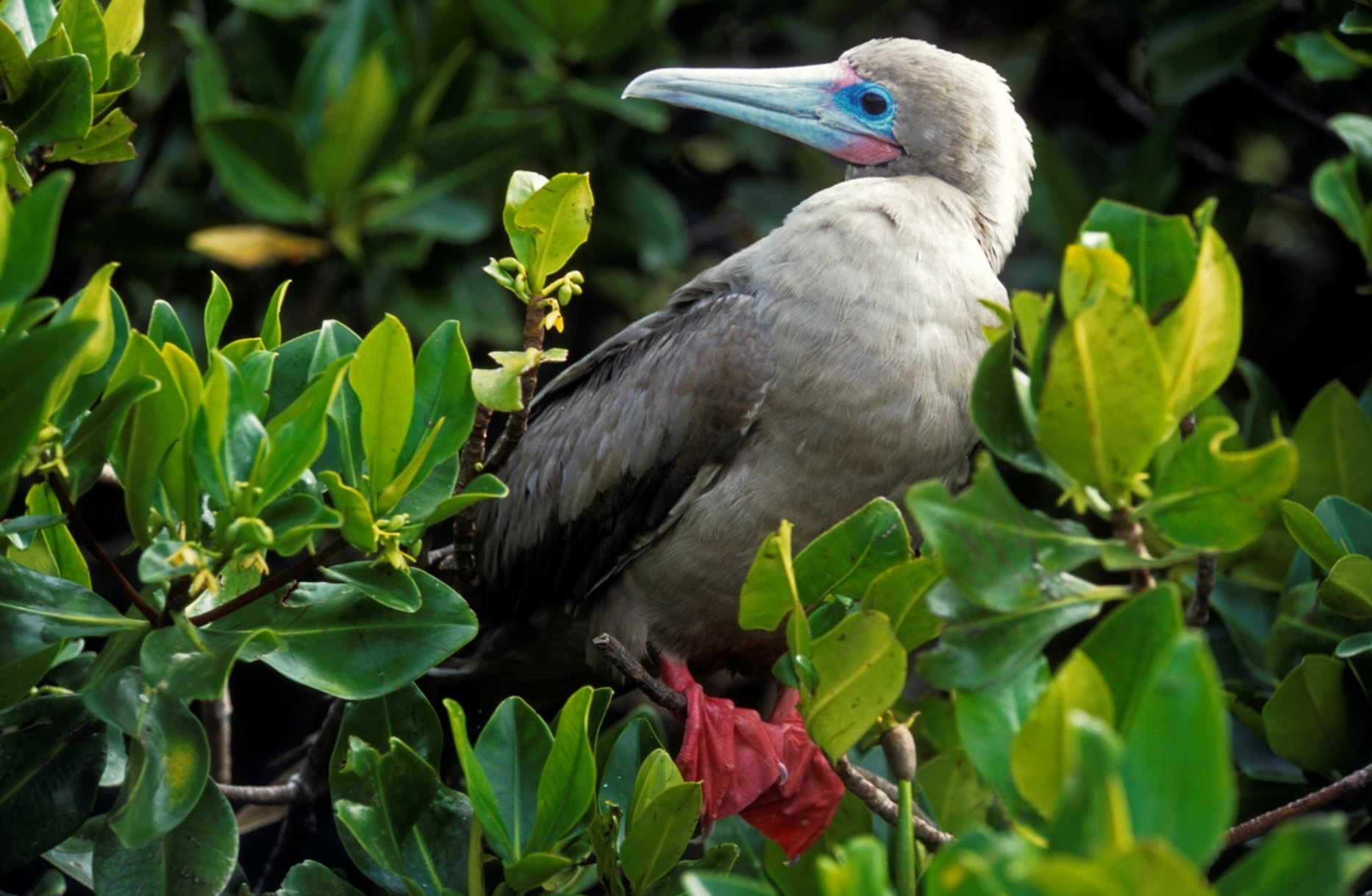
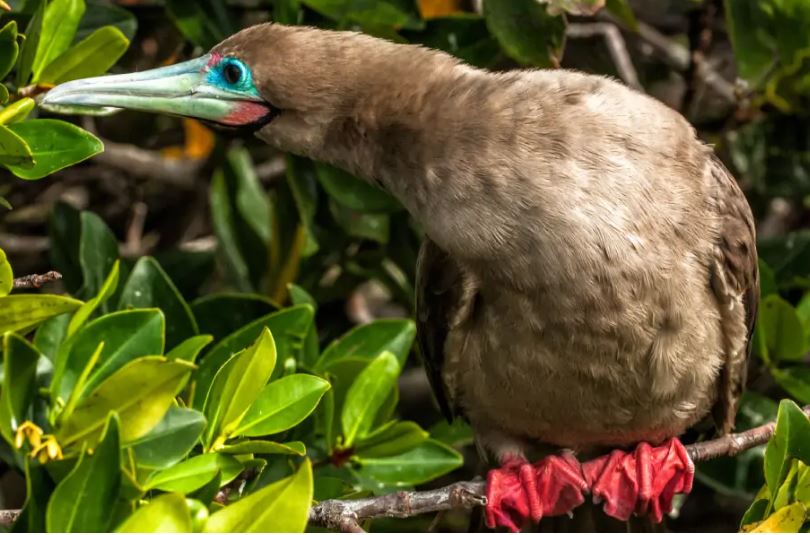
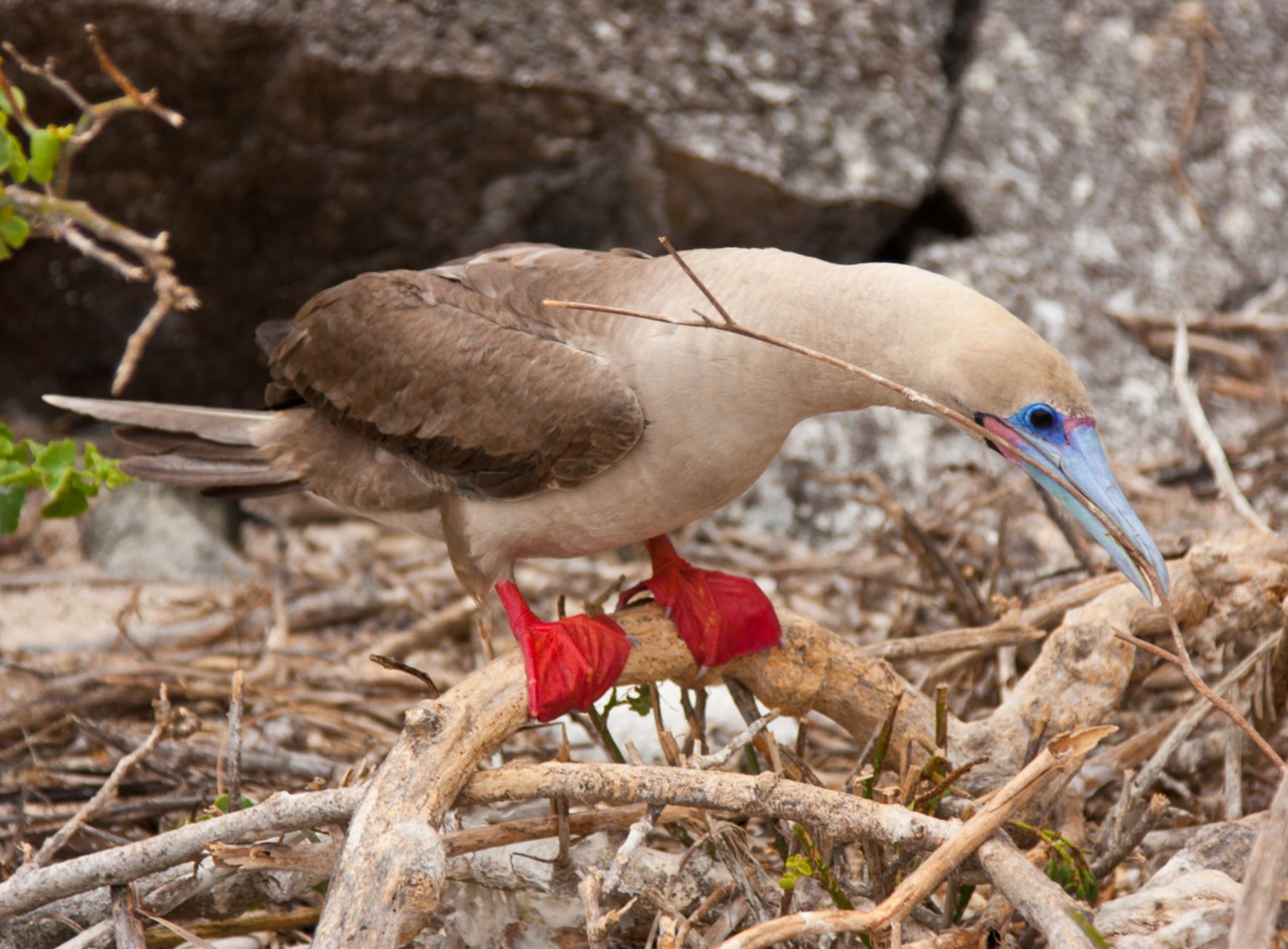
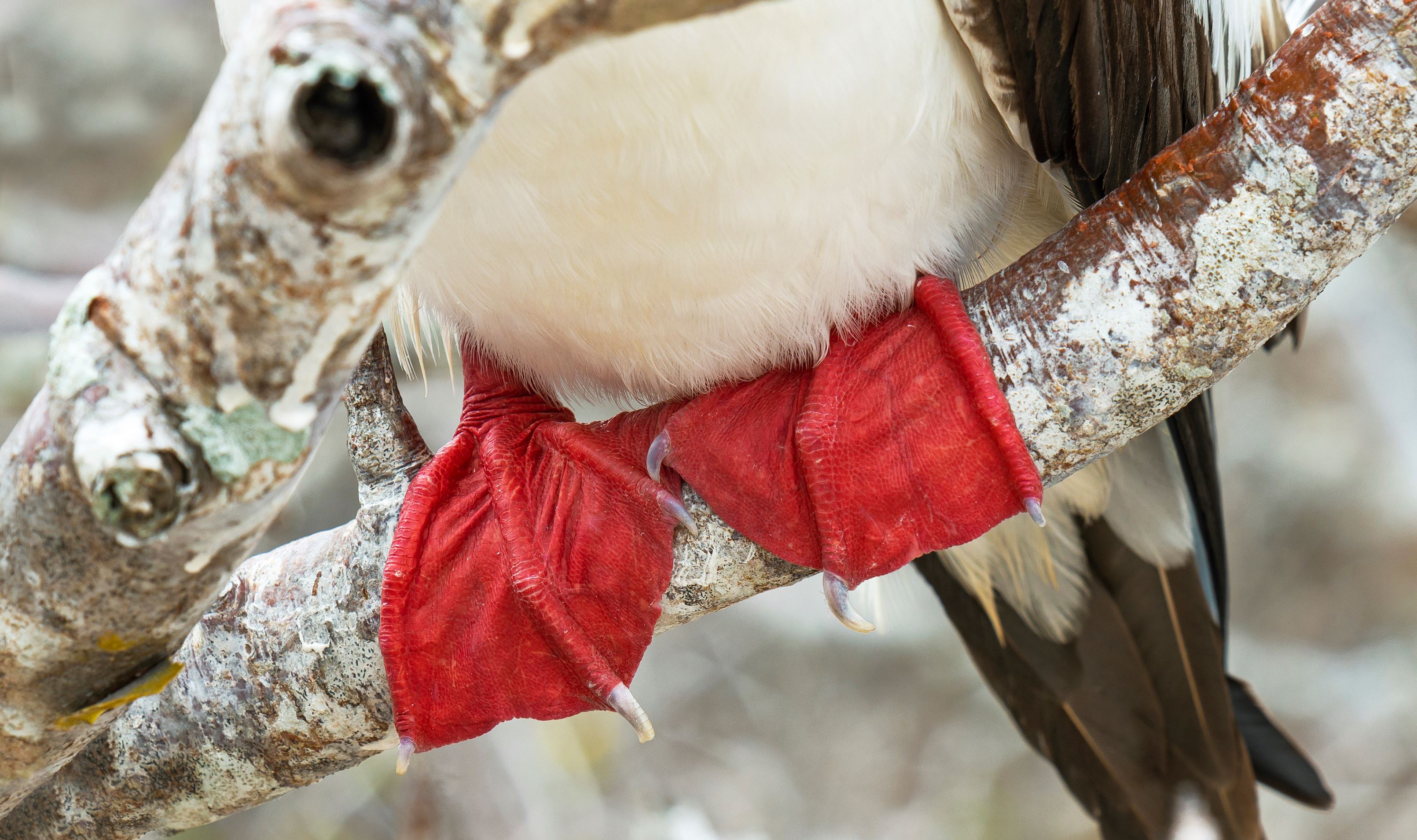
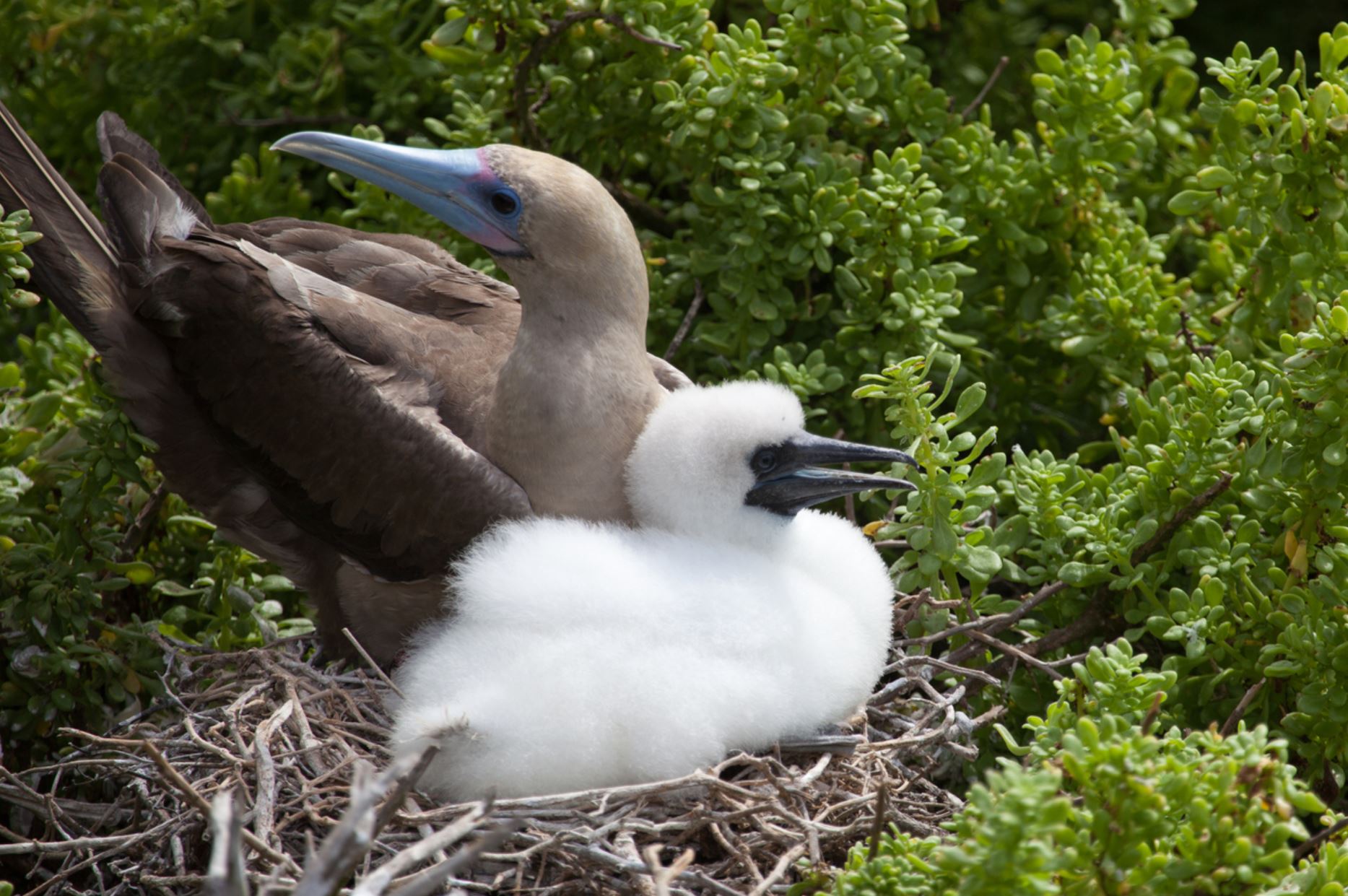
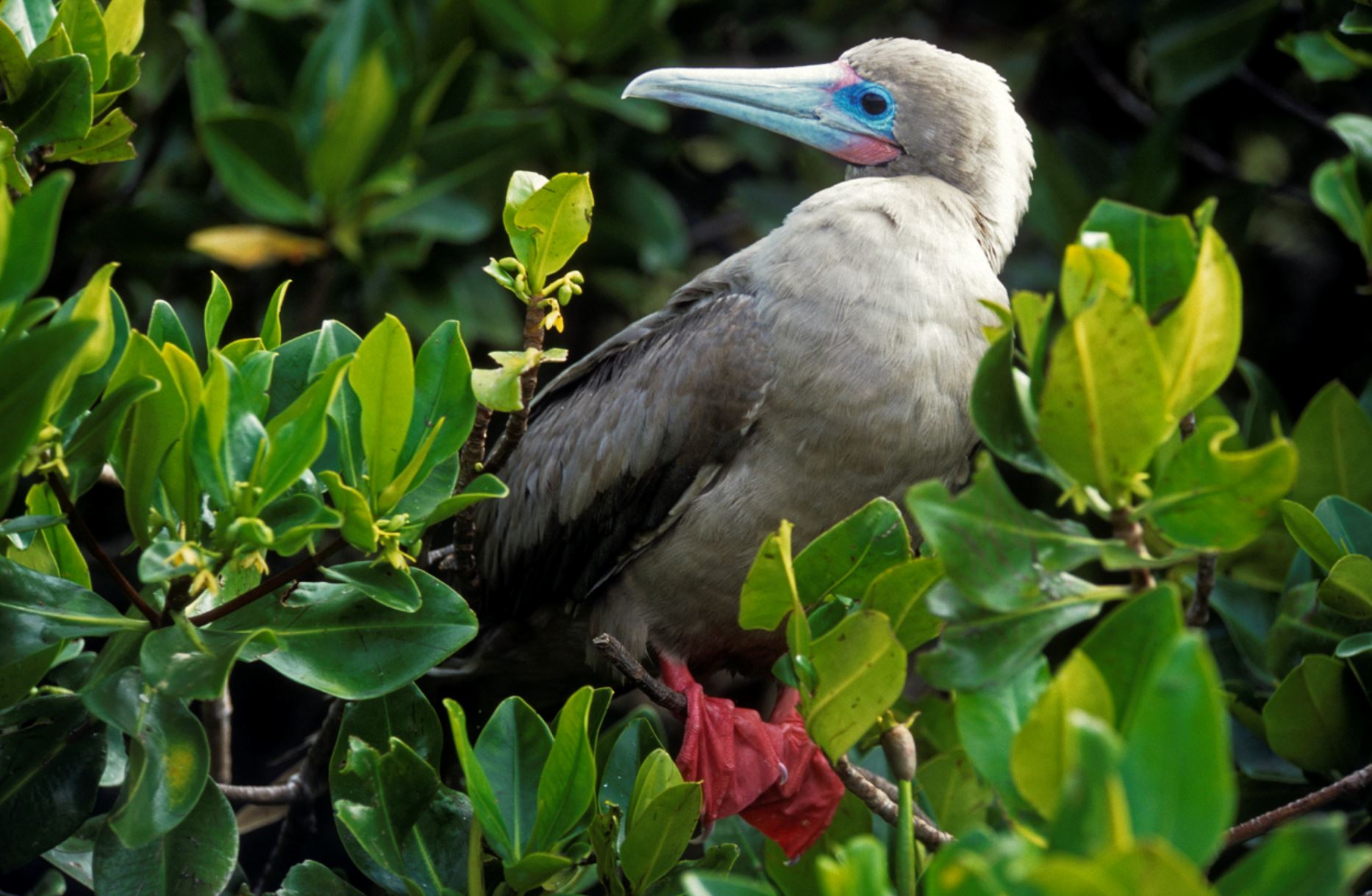
Red-footed Booby
In the Galapagos, the red-footed booby bird has two morphs colors of brown or white. Their pointy beaks and their fishing technique has given them the local name “piquero” that means lancer. The red color of its feet can only be seen when they are inland. There are about 30 thousand birds living in the archipelago.
They can plunge dive into the water at high speed since they have unique cushion air-sac bones in the head to protect the brain from the impact. The eyes and nostrils are also adapted to this way of fishing to avoid water from entering during the high-speed dive. They feed mainly on flying fish and squid, and they prefer hunting at dusk or dawn. They can dive down up to 30 meters in pursuit of their prey.
The red-footed booby has a particular requirement for nesting, as they do it only in trees and shrubs. One of the most important bushes for this bird is the Cryptocarpus, whose conservation is directly related to red-footed boobies preservation. Due that they are adapted to being on trees, they are clumsy on the ground and enjoy of extensive territories.
The courtship ritual involves lifting the head and showing their red feet to females, dancing in the nest, which is also an extreme balanced performance. Boobies are opportunistic breeders; they lay one egg that will hatch 45 days late, they are known to live for an estimated of 20 years. Both male and female take care of the offspring for longer than a year until it leaves the nest.
Animal Group: Seabirds
Scientific Name: Sula sula
Animal Average Size: 66 - 76 cm
Animal Average Weight: 1 kg
Places where you may see Red-Footed Bobbies in Galapagos:
Genovesa, Santa Cruz, San Cristobal
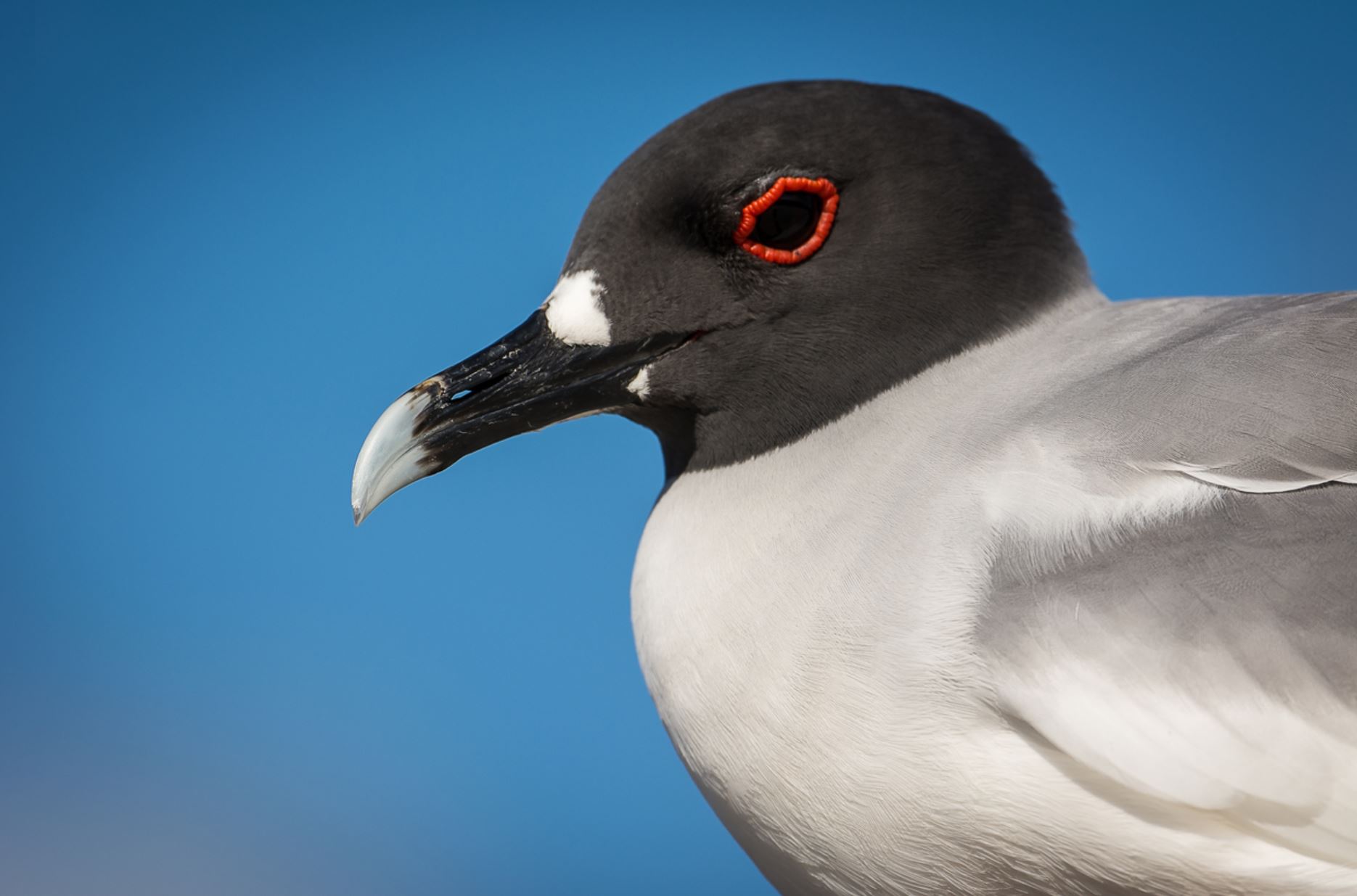
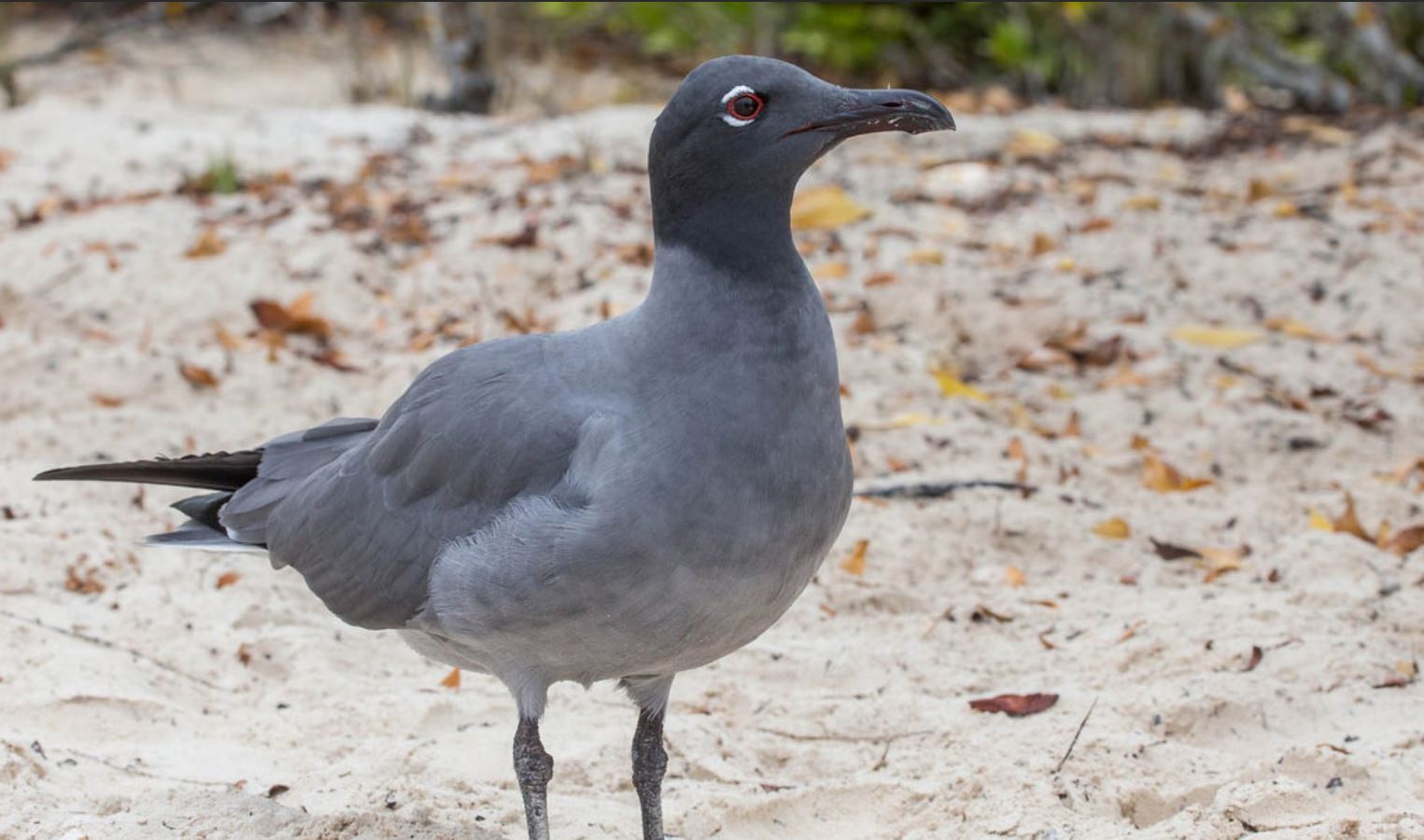
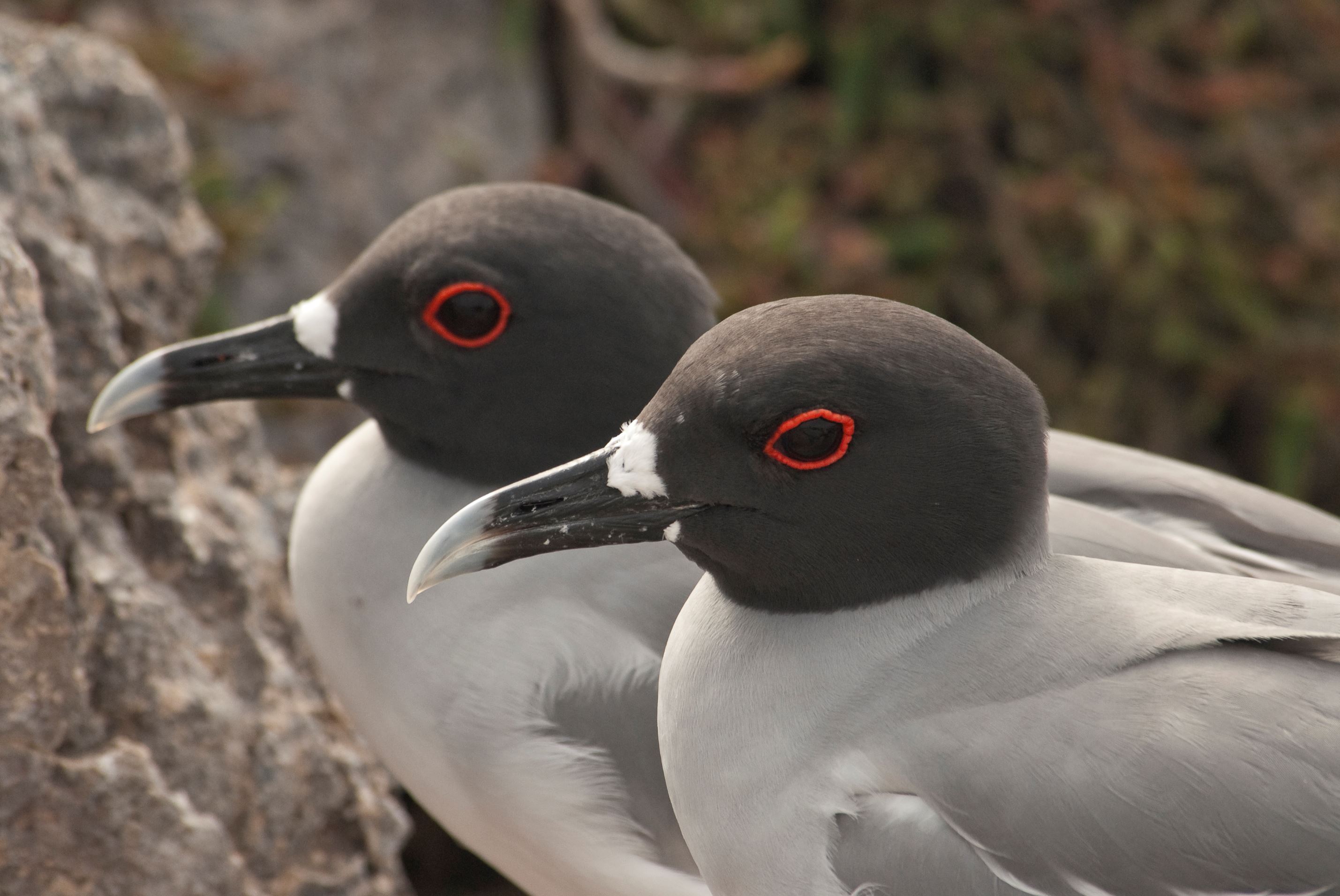
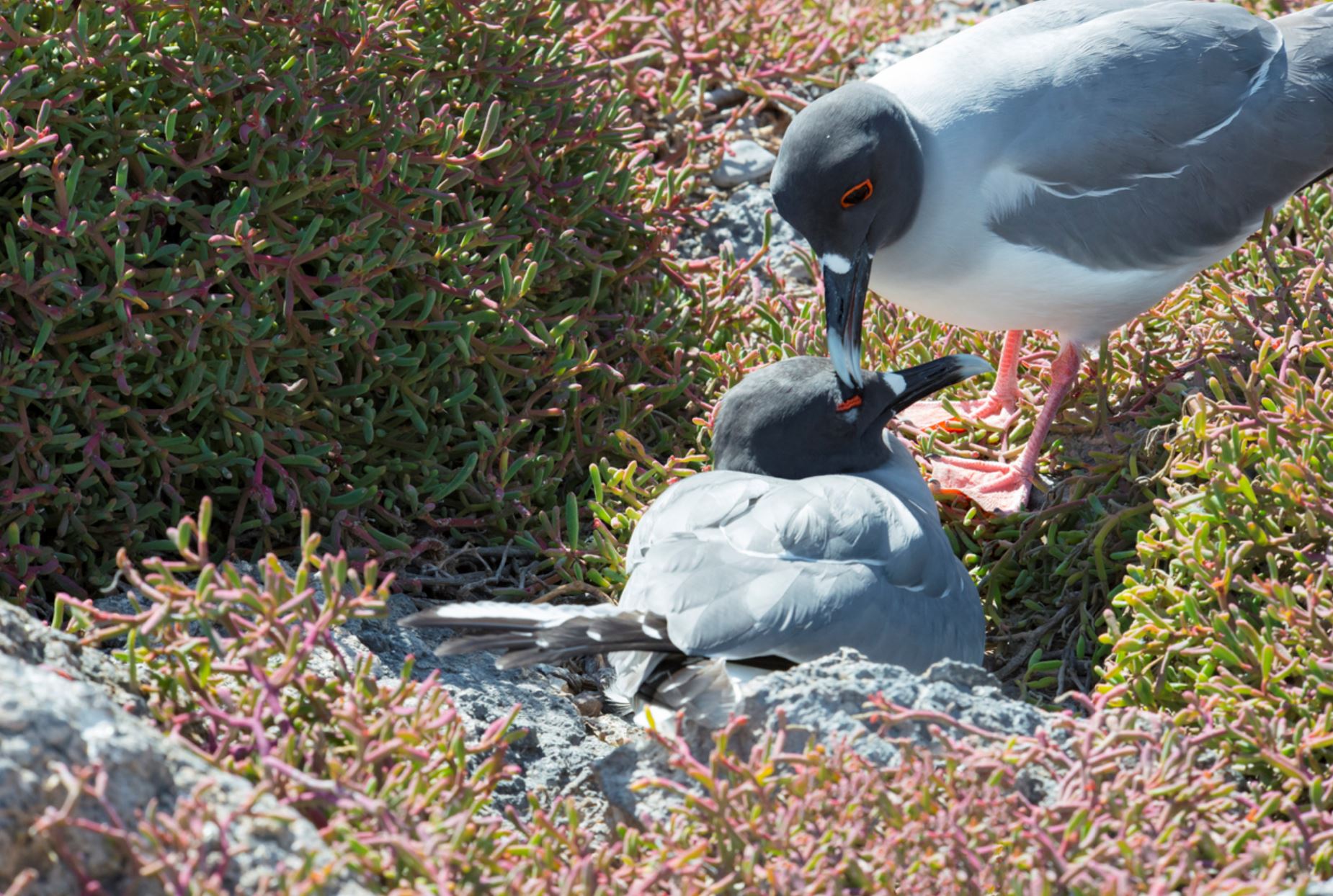
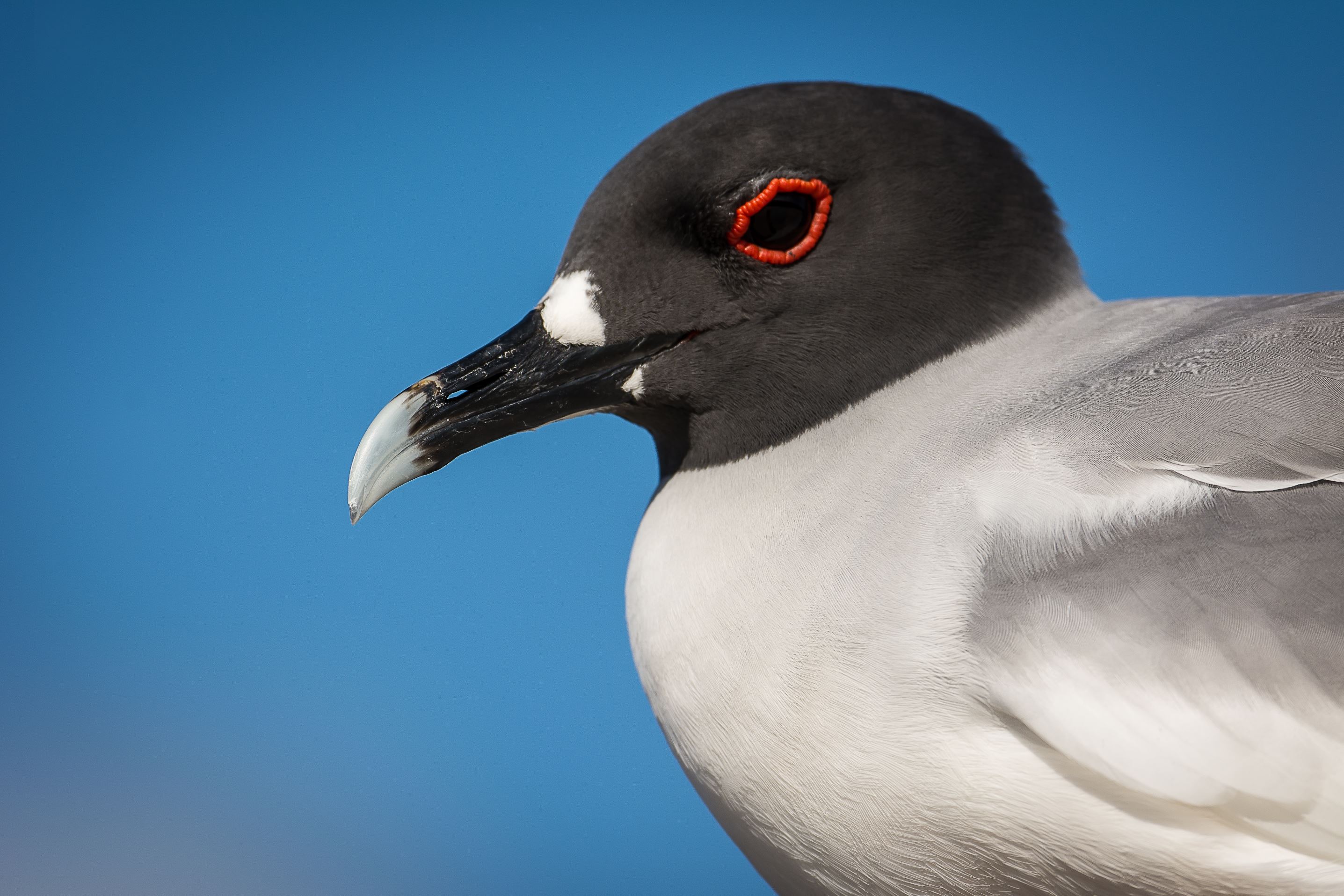
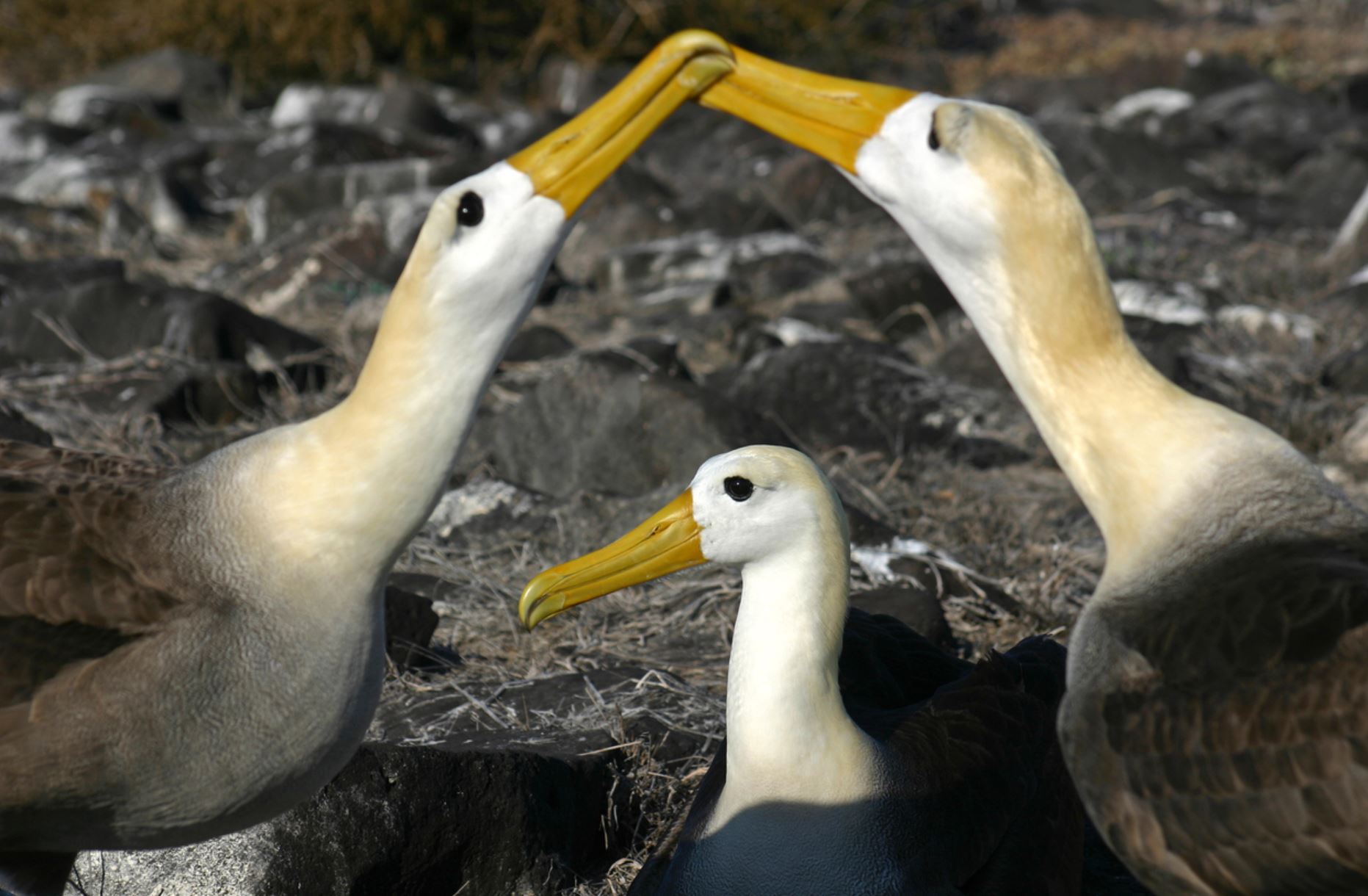
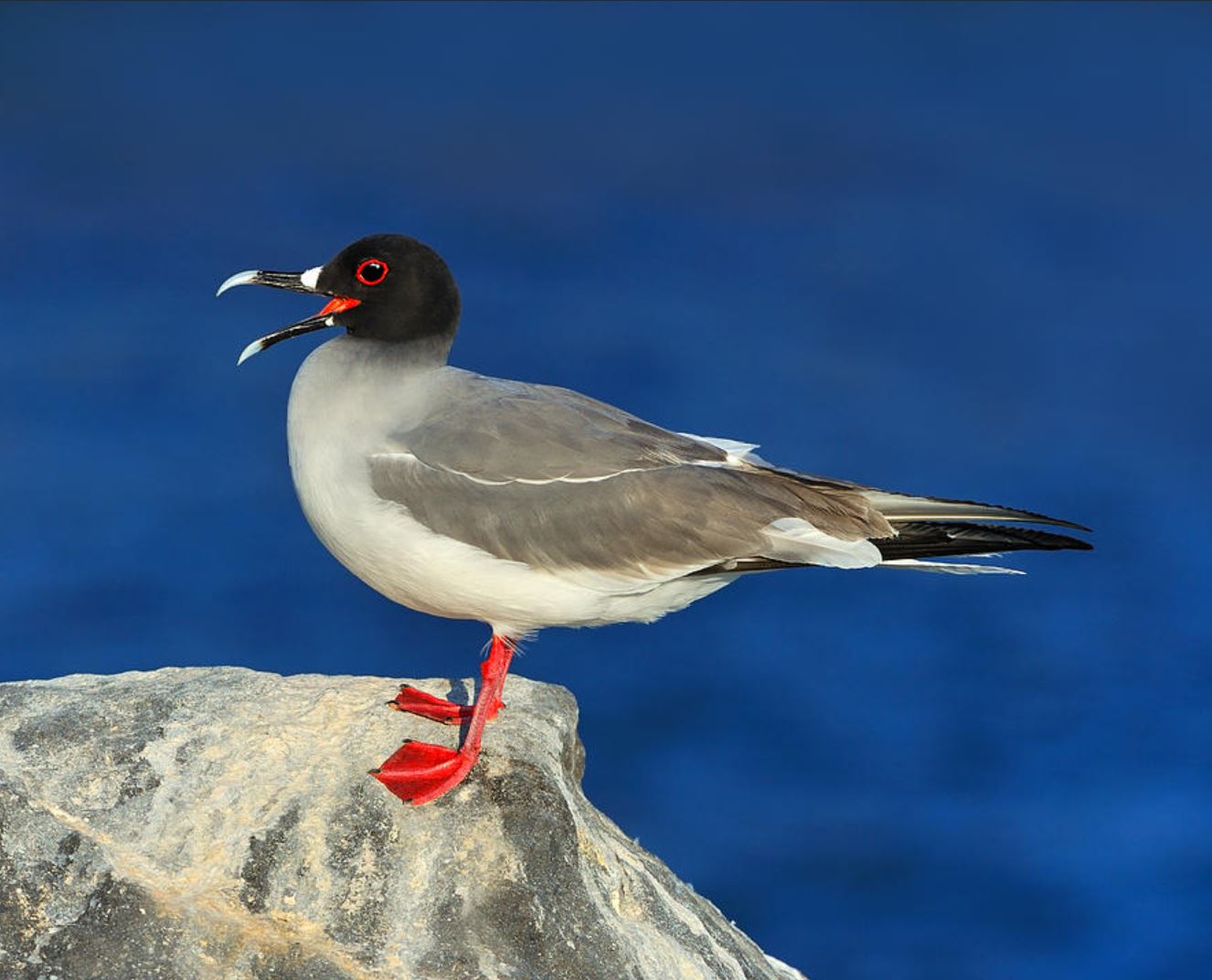
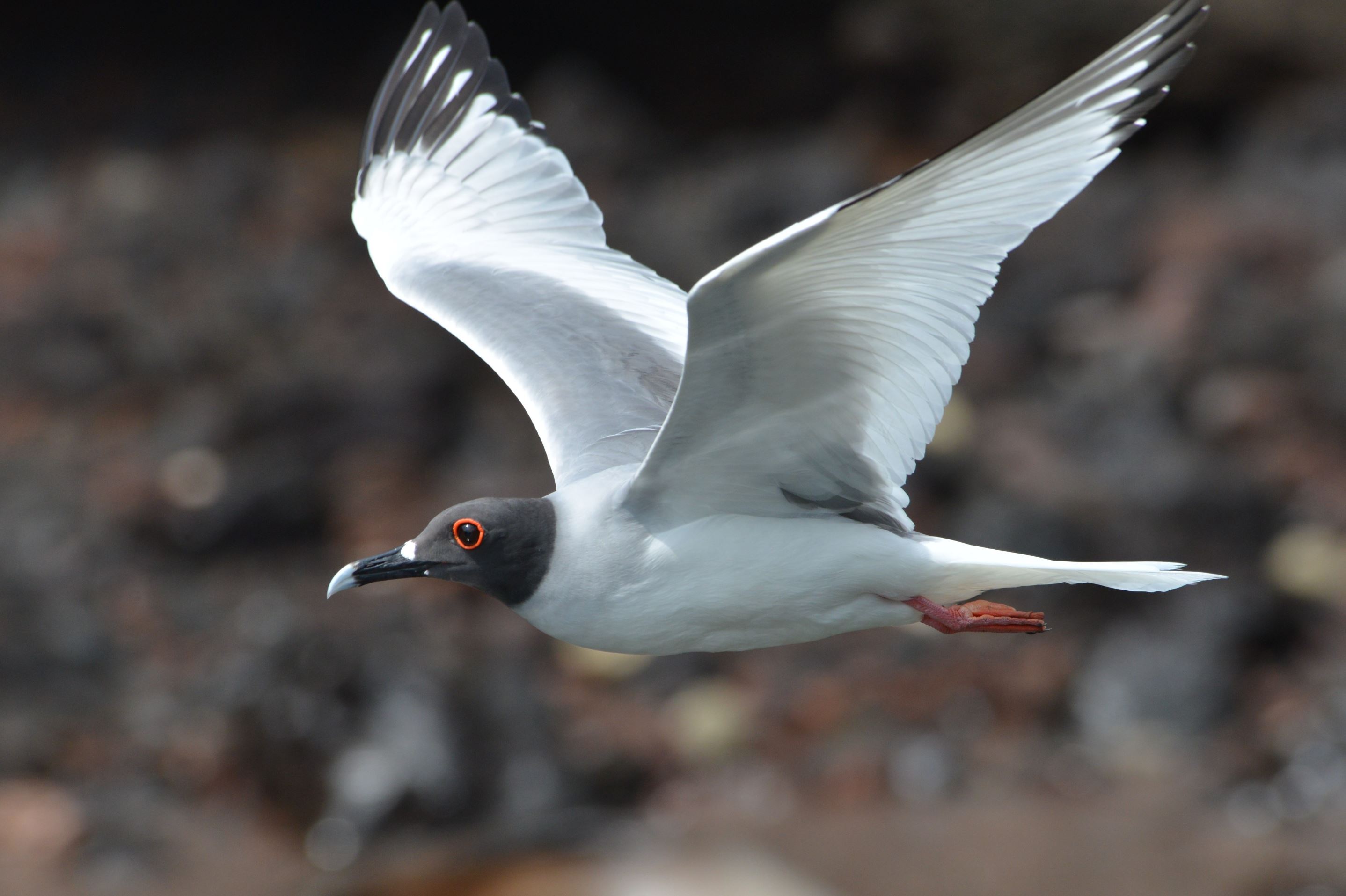
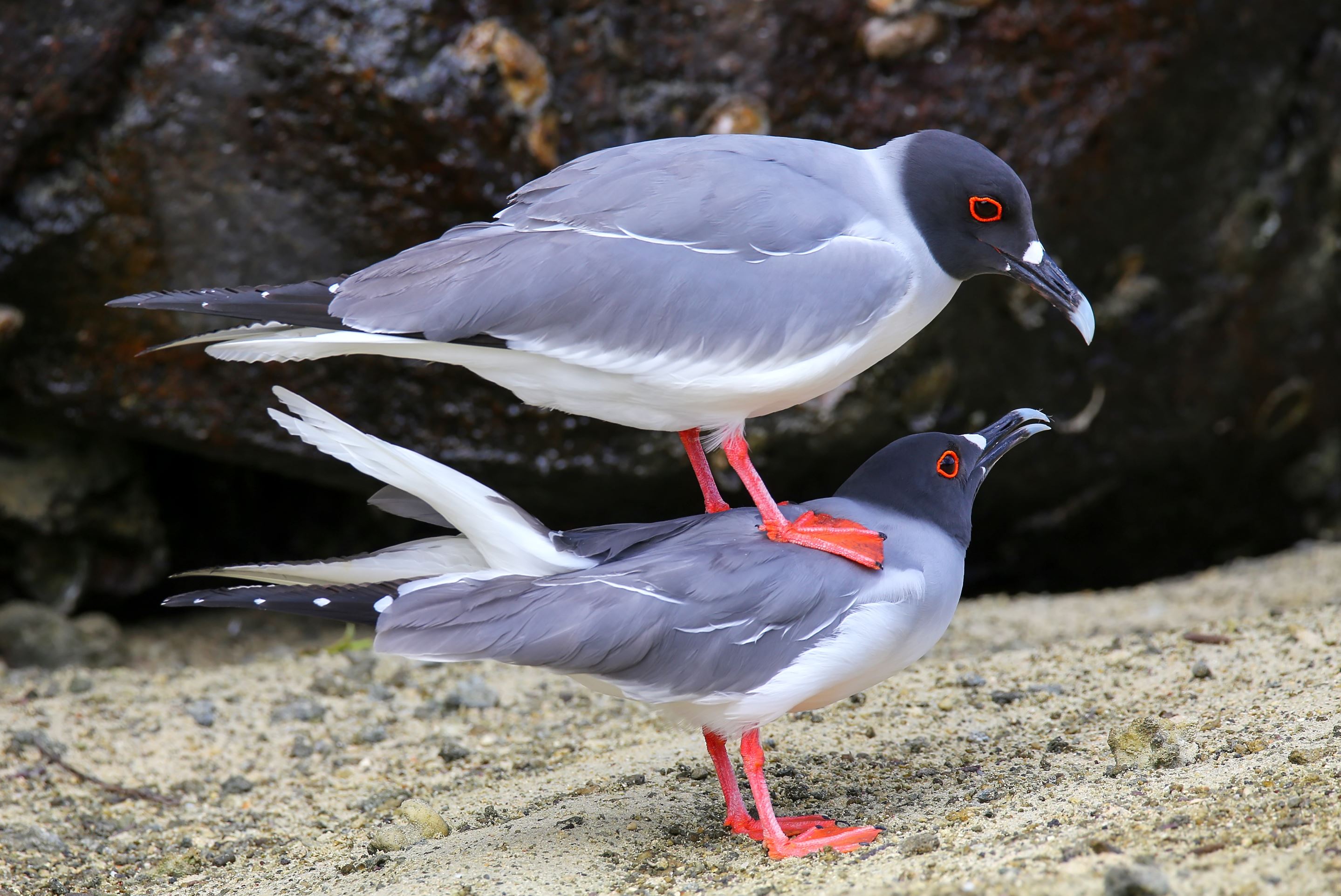
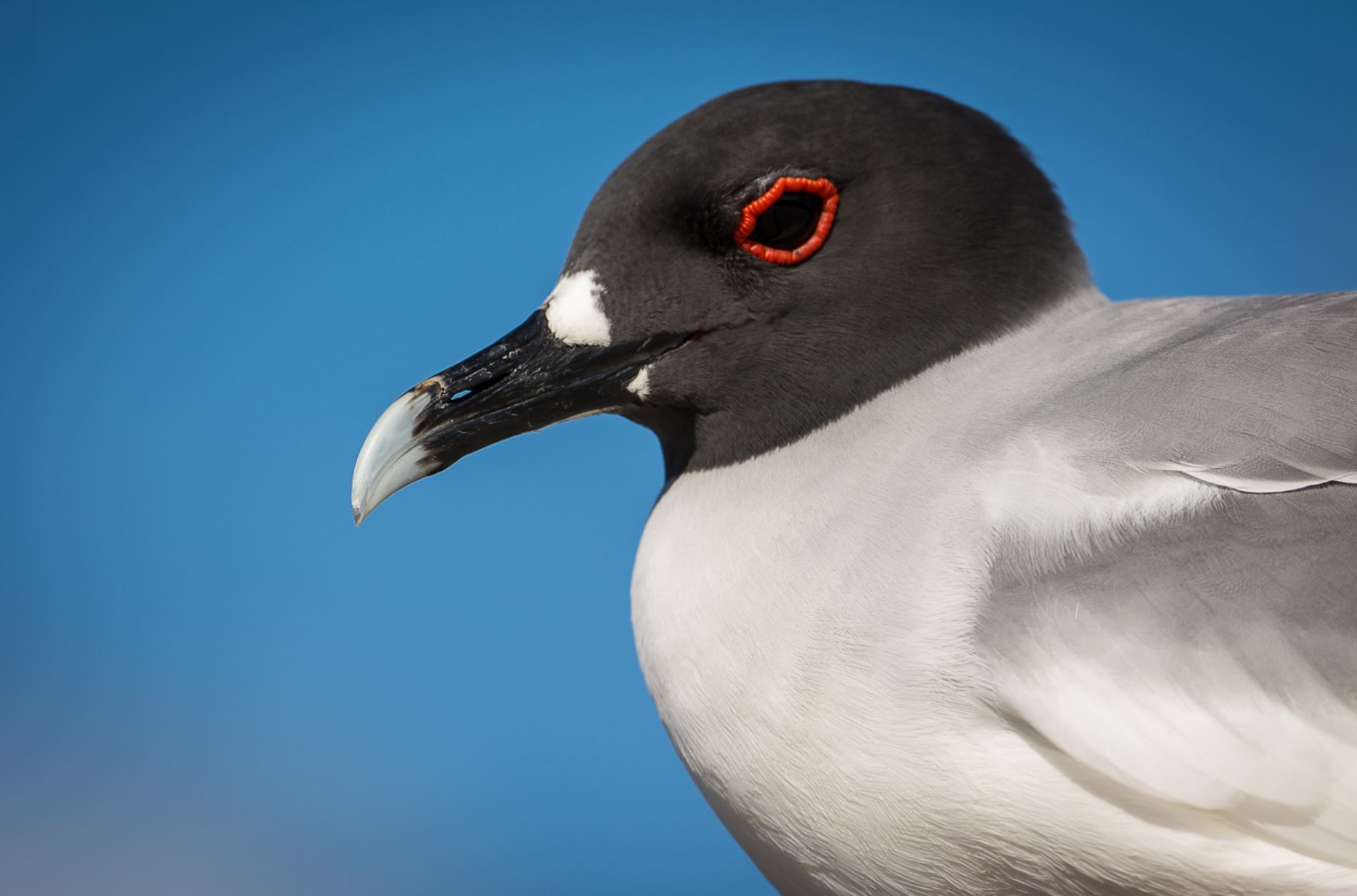
Swallow-Tailed Gull
The swallow-tailed gull is endemic to Galapagos. They prefer areas with warmer water in the eastern islands. When they are not breeding, they travel long distances and feed out of the sea as far as south Peru and Chile.
They feed mainly on squid and fish found in the surface on nocturnal shifts. Nocturnal fishing is unusual among gulls.
Their nests are located on the rocks, bare lava and cliff areas in the shoreline of most islands. Females lay 1 egg that hatches 35 days later. Chicks spend about 3 months with their parents before they are independent.
They make several vocalizations, most of which are to communicate with others in the colony. They can warn others individuals when intruders are near the nesting sites and by several aggressive postures towards intruders.
Animal Group: Seabirds
Scientific Name: Creagrus furcatus
Animal Average Size: 51 - 57 cm
Animal Average Weight: 0.61 - 0.78 kg
Places where you may see Sunfishes in Galapagos: Genovesa, South Plaza, Española
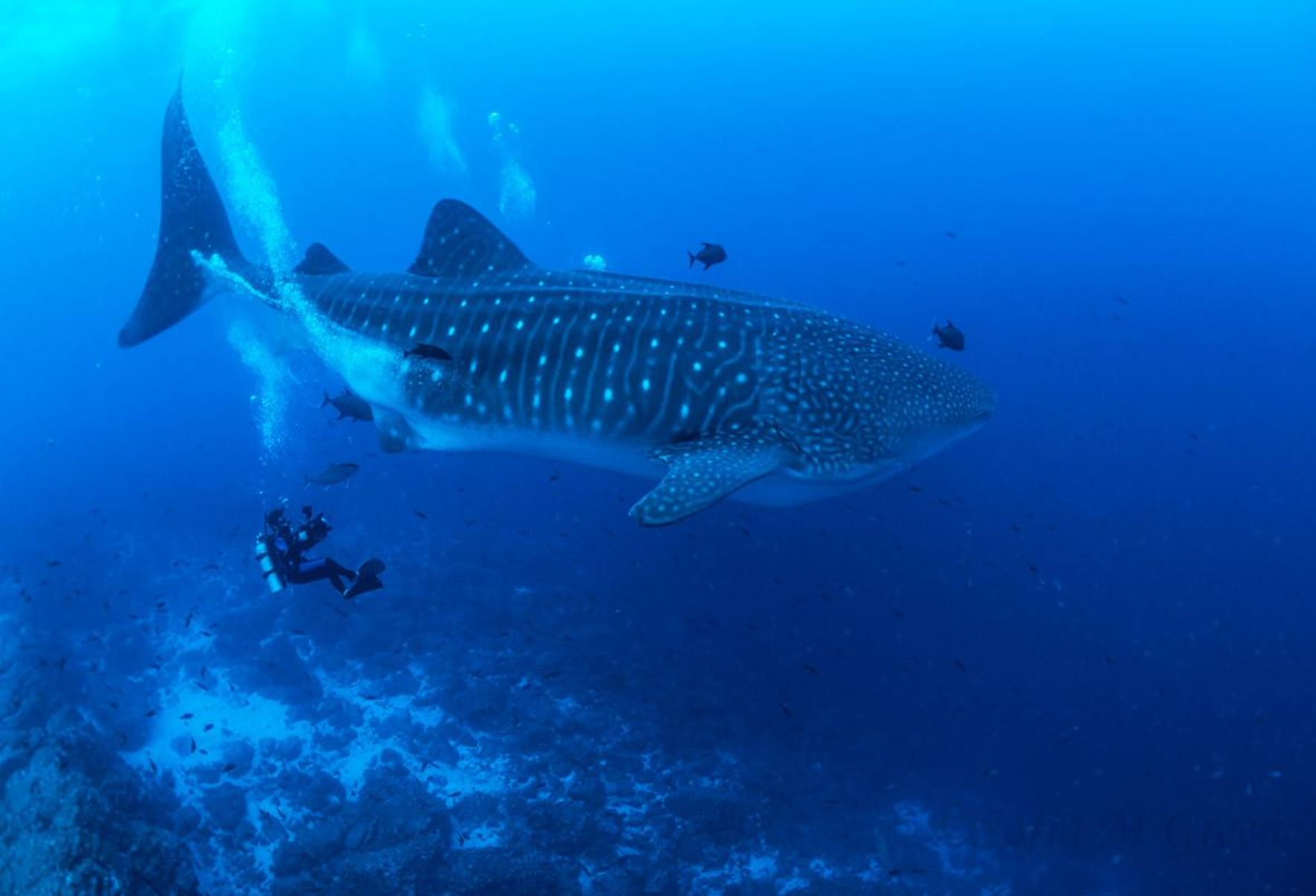
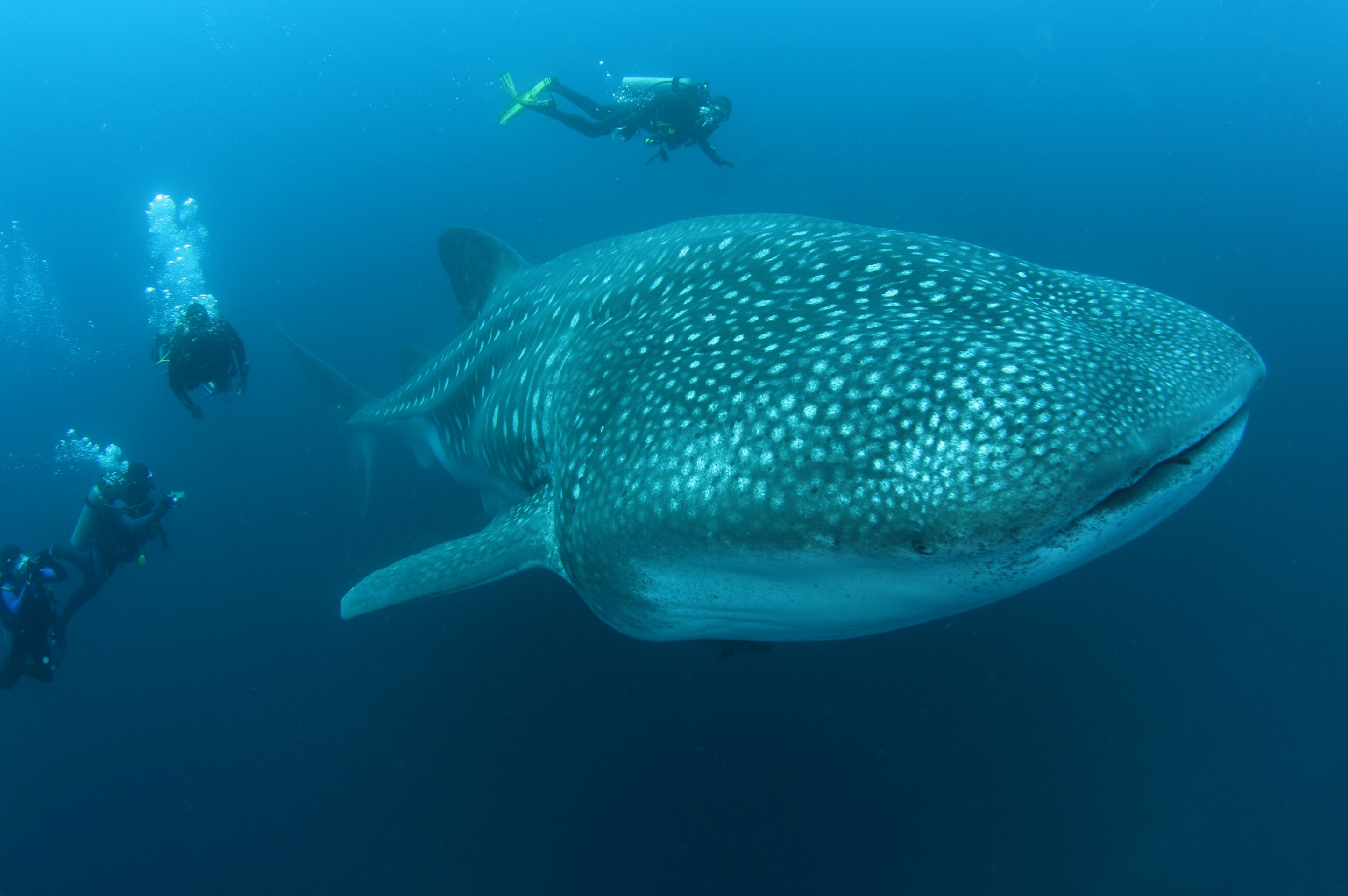
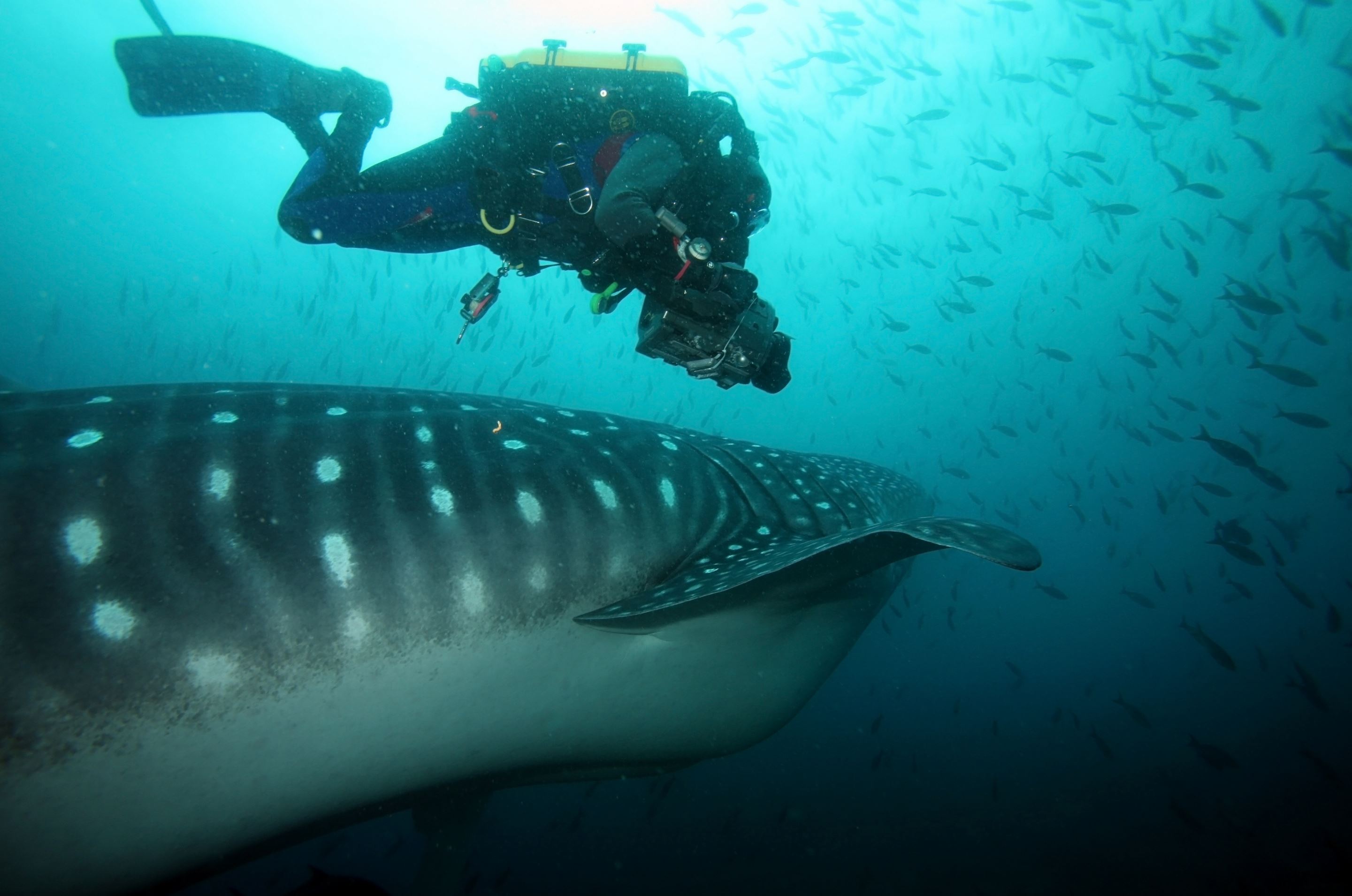
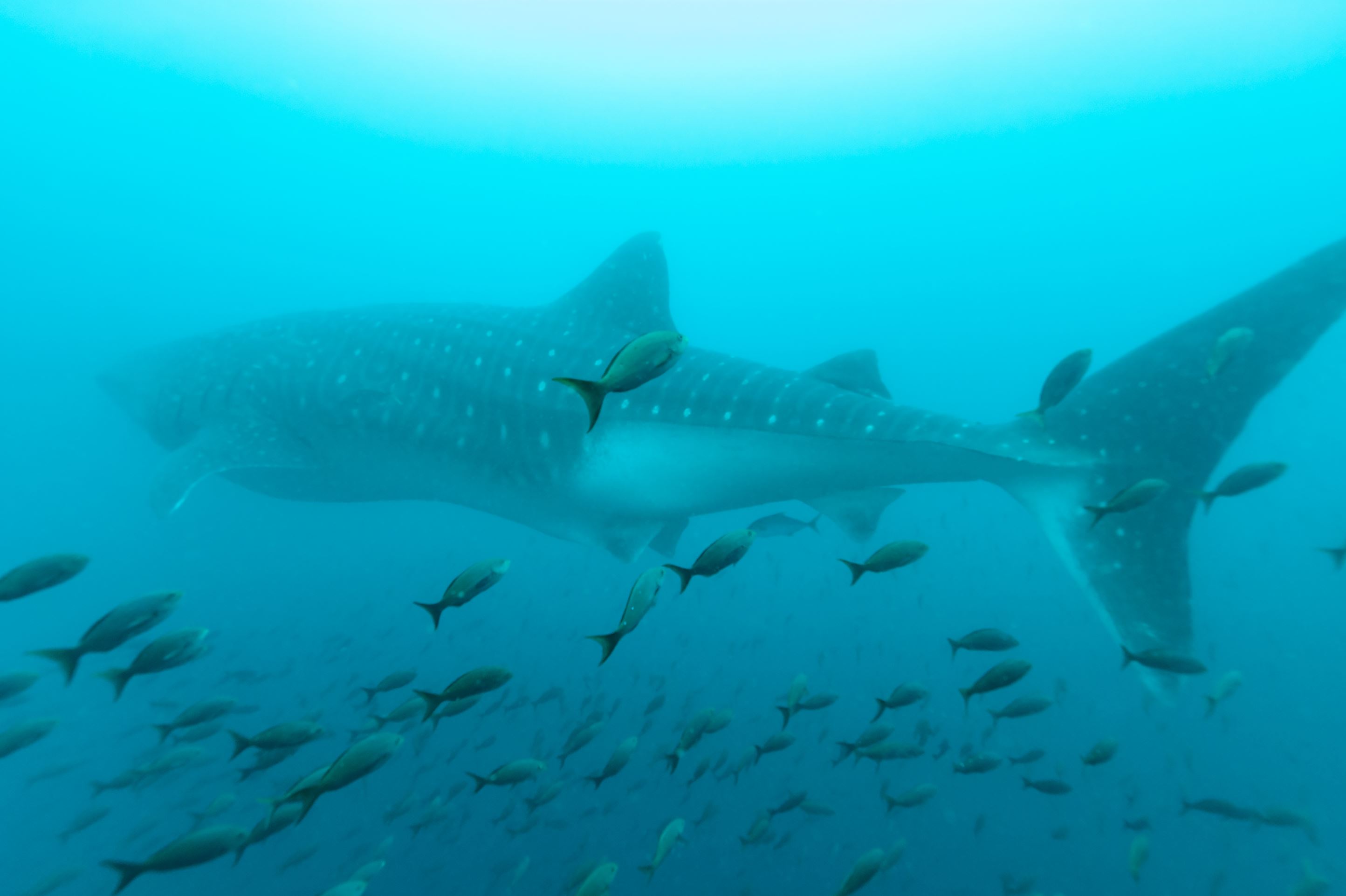
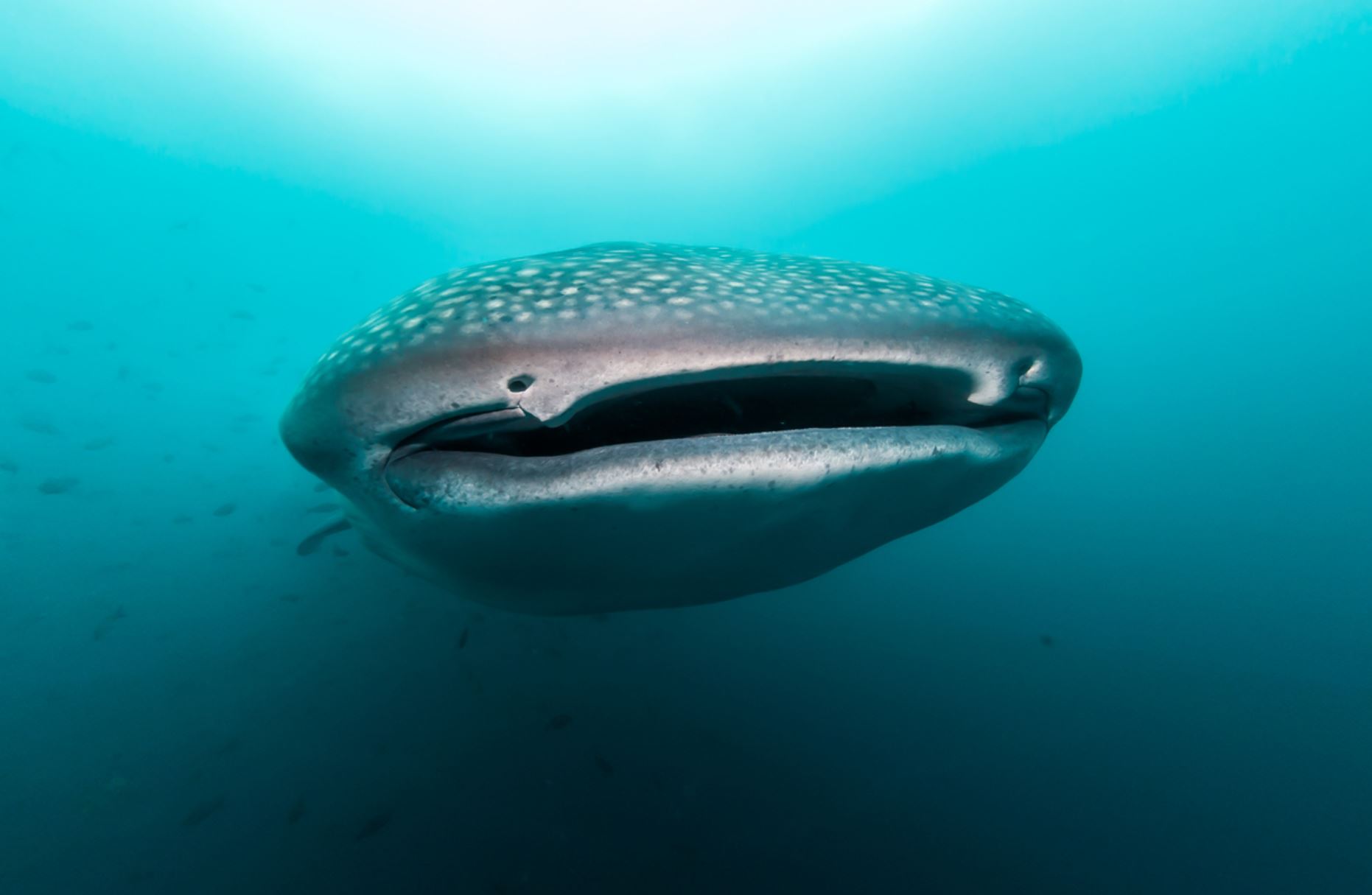
Whale Shark
The whale shark (Rhincodon typus), is a slow filter feeding (animals that feed by straining suspended matter and food particles from water) shark that is the largest living fish species, reaching up to 18 metres in length. Whale sharks are rare throughout Galapagos and mainly found in open water. They are grey-brown in colour fading to paler undersides and have a white spotted pattern.
As a filter feeder, it has a spacious mouth which can be up to 1.5 metres (4.9 feet) wide and can contain between 300 – 350 rows of tiny teeth. It has five large pairs of gills. Two small eyes are located towards the front of the sharks wide, flat head.
The Whale sharks skin can be up to 10 centimetres (3.9 inches) thick. The shark has a pair each of dorsal fins and pectoral fins. A juvenile whale sharks tail has a larger upper fin than lower fin while the adult tail becomes semi-lunate (or crescent-shaped). The whale sharks spiracles (mall openings on the surface of some animals that usually lead to respiratory systems) are just behind the eyes.
The whale shark is not an efficient swimmer since the entire body is used for swimming, which is unusual for fish and contributes to an average speed of only around 5 kilometres per hour (3.1 miles per hour).
The whale shark is believed to have originated about 60 million years ago. The name ‘whale shark’ comes from the fishes physiology; that is, a shark as large as a whale that shares a similar filter feeder eating mode.
The whale shark inhabits the world’s tropical and warm-temperate oceans. While thought to be primarily pelagic (open sea or ocean that is not near the coast), seasonal feeding aggregations of the sharks occur at several coastal sites such as Galapagos.
The whale shark is solitary and rarely seen in groups unless feeding at locations with an abundance of food. Males range over longer distances than females (which appear to favour specific locations).
- Animal Group: Marine life
- Scientific Name: Rhincodon typus
- Animal Average Size: 10 - 12 Meter
- Animal Average Weight: 15-30 Tonnen
Places where you may see Whale Sharks in Galapagos: Wolf, Darwin, Fernandina, Isabela, Santiago, Santa Cruz, Genovesa, Marchena, San Cristobal, Floreana, Española
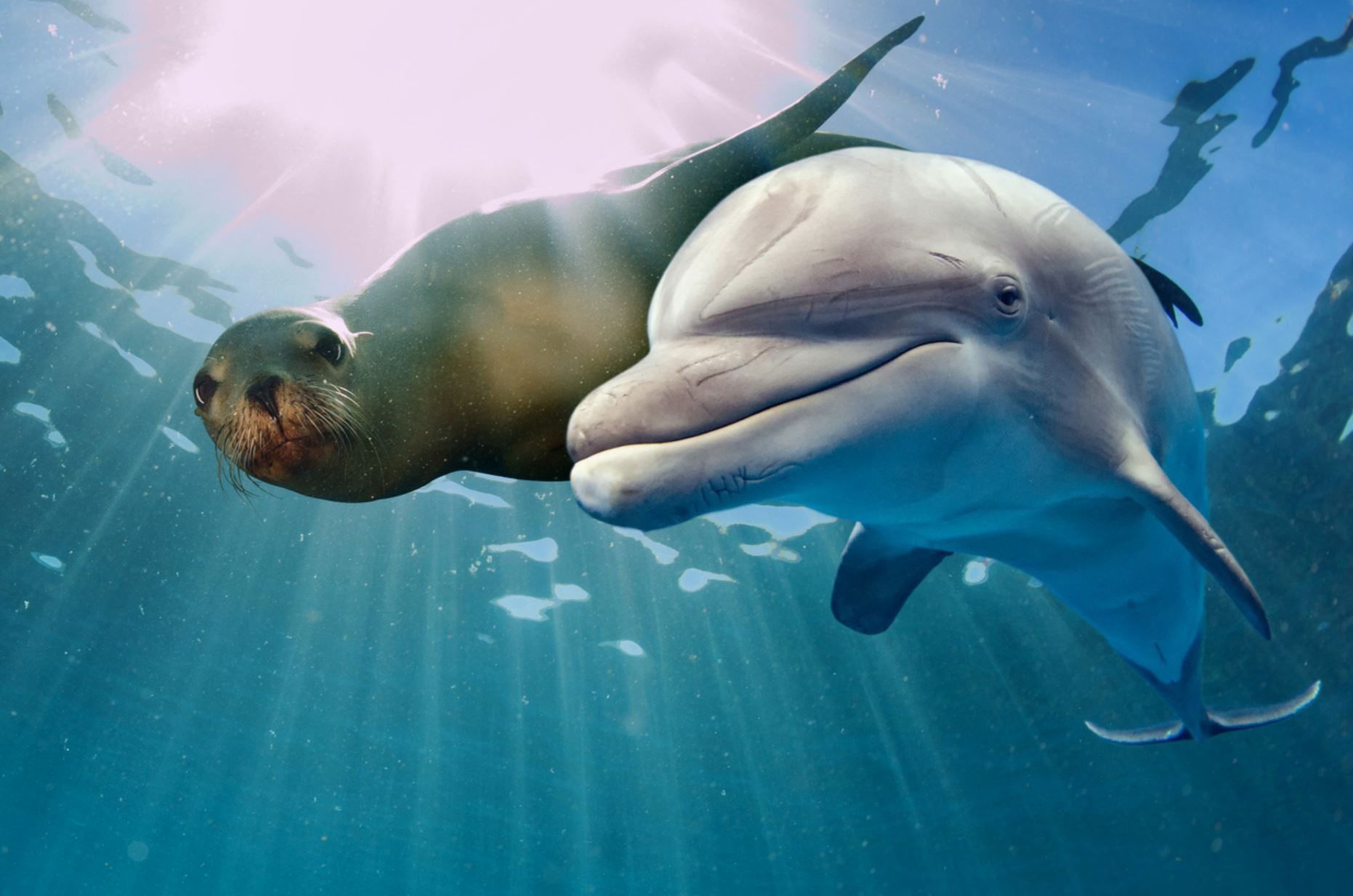
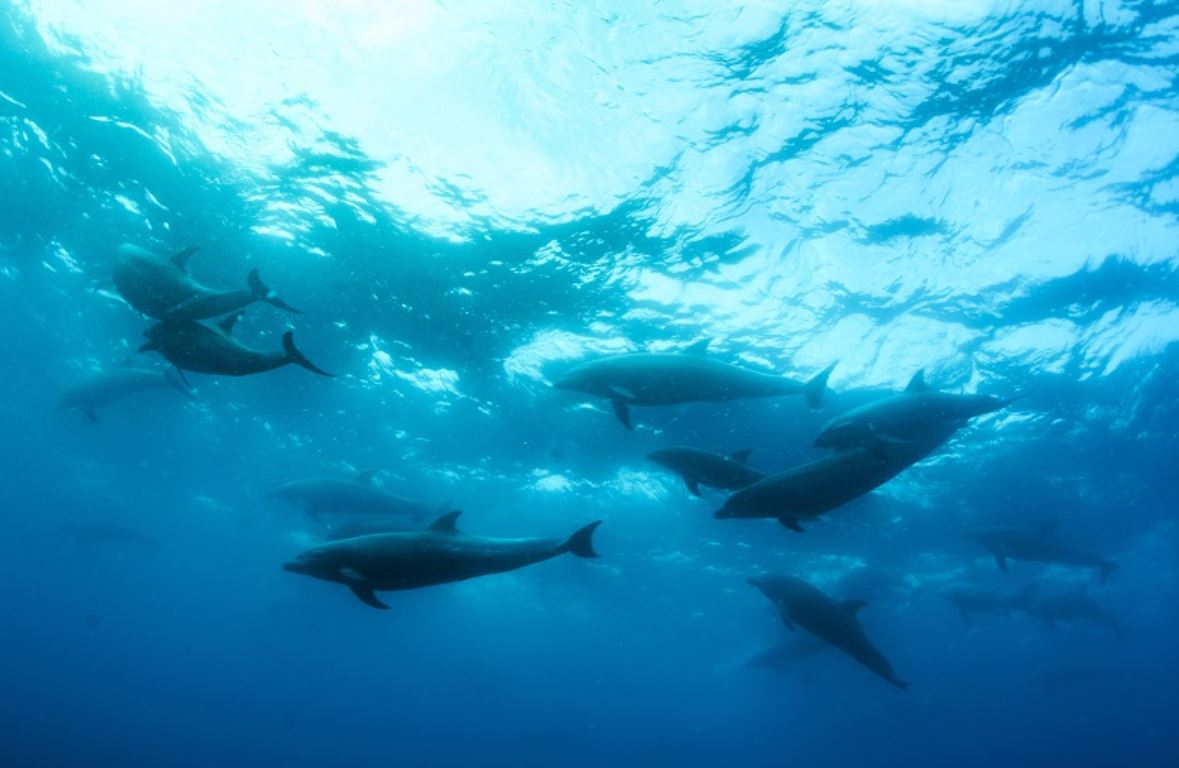
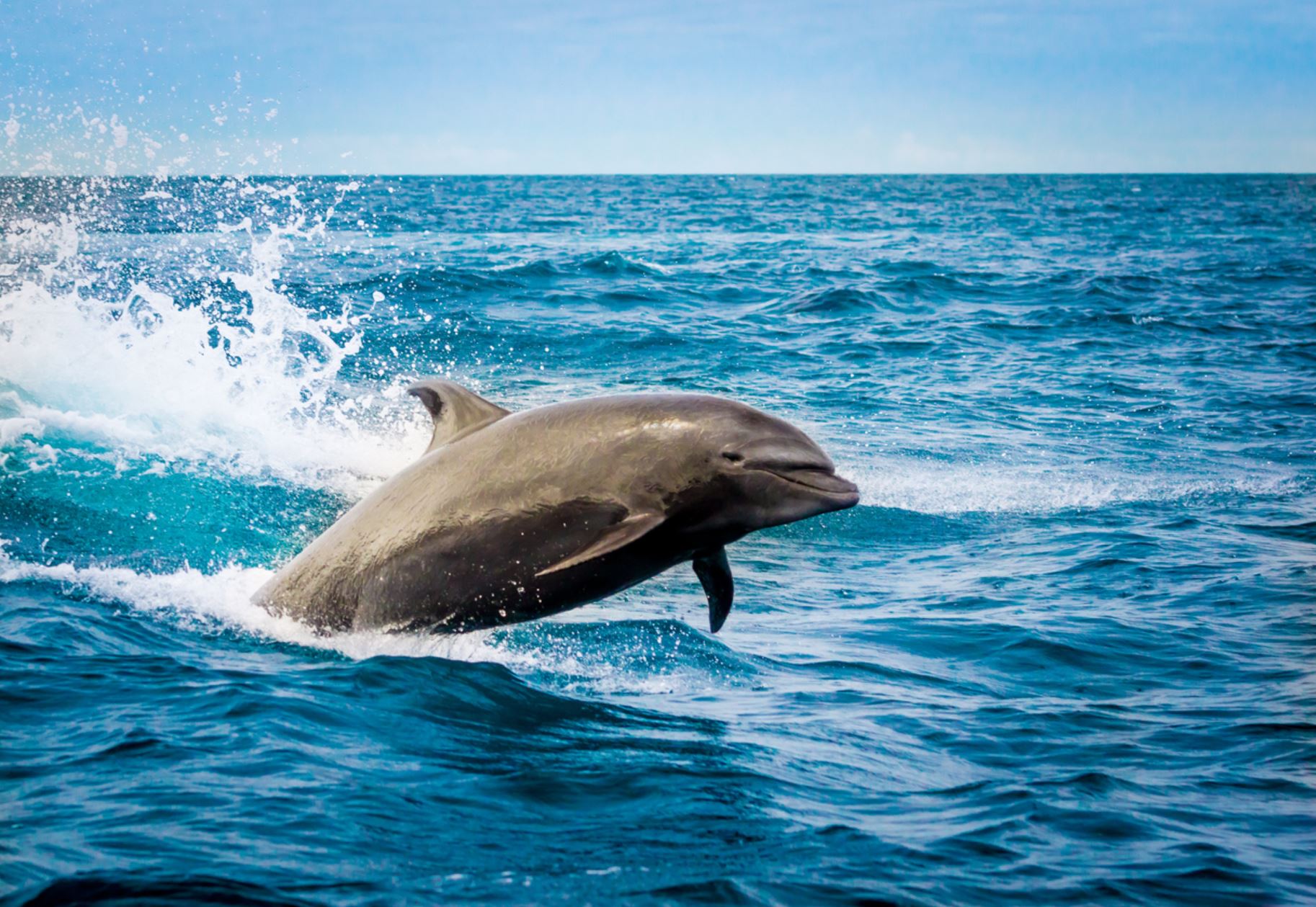
Dolphins
Bottlenose Dolphin
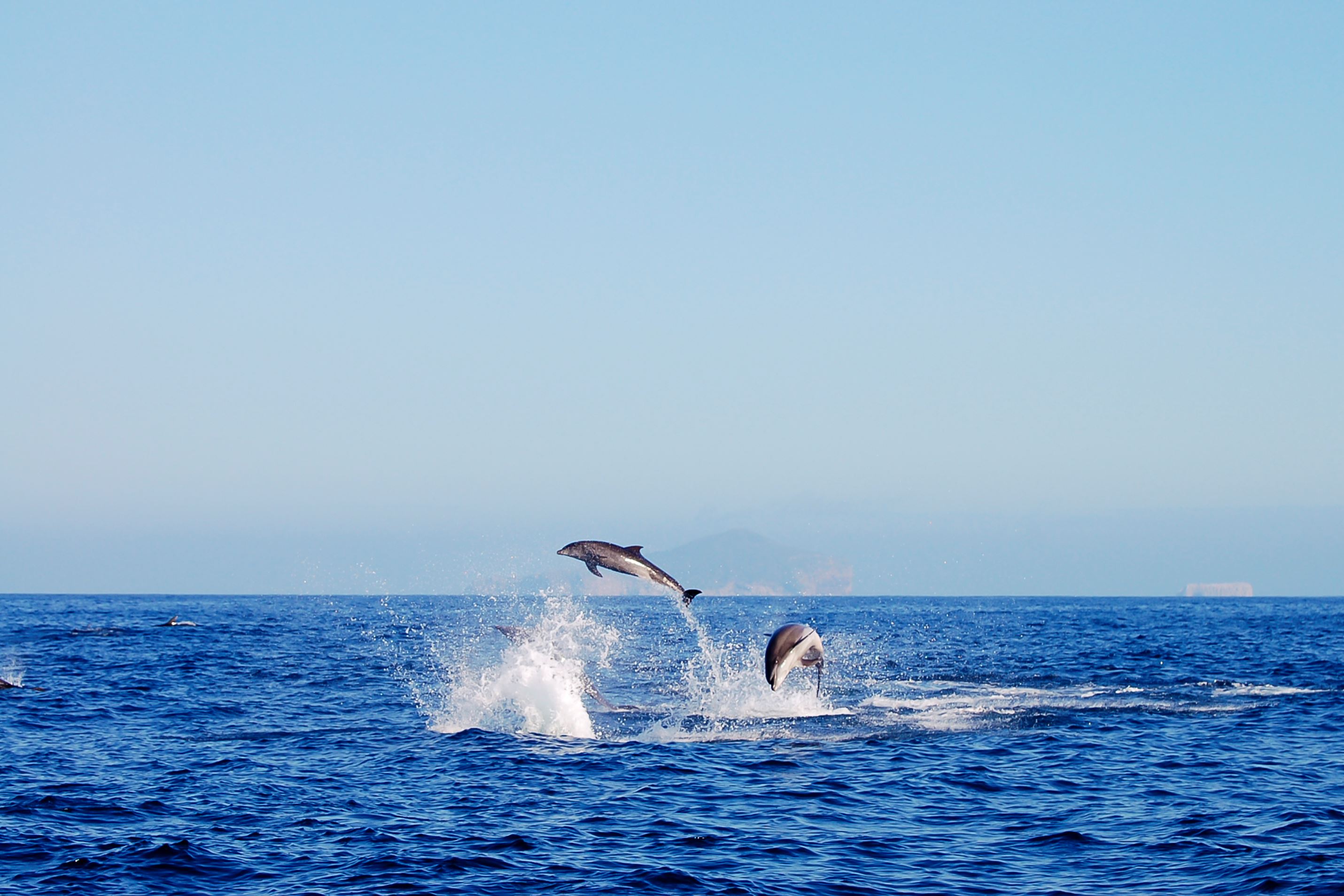
While not native to the Galapagos, the bottlenose dolphin is a frequent visitor to the islands and the most commonly seen cetacean in the Galapagos. They have short beaks and curved dorsal fins, and their backs and sides are dark gray or black, with paler skin underneath. They often travel in large pods and can sometimes be spotted playfully riding the bow waves of ships and yachts. They can appear any time our boat is moving and often put on whimsical shows that delight travelers. Their distance from the boat varies: some will frolic right alongside the vessel, others will dance near the bow, while still others will execute flips off on the horizon. If you spot them at night, the swimming dolphins cause the ocean to shimmer with bioluminescence as they churn up thousands of miniscule phosphorescent organisms that glow when disturbed. An encounter with these highly intelligent cetaceans is one of the highlights of any Galapagos adventure.
Common Dolphin
The common dolphin looks similar to the bottlenose but has a longer beak, gray flank markings, an upright dorsal fin and a dark stripe that runs from the flipper to the chin.
Striped Dolphin
This striking creature is seen less often than bottlenose or common dolphins because it rarely bow rides. It is smaller than the bottlenose and larger than the common dolphin and can be identified by its more rounded dorsal fin and distinctive color pattern consisting of bold, thin stripes.
Animal Group: Marine life
Scientific Name: Tursiops truncatus (Bottenlose Dolphin)
Animal Average Size: 13 feet
Animal Average Weight: 300 kg
Places where you may see Dolphins in Galapagos: Wolf, Darwin, Fernandina, Isabela, Santiago, Santa Cruz, Genovesa, Marchena, San Cristobal, Floreana, Española
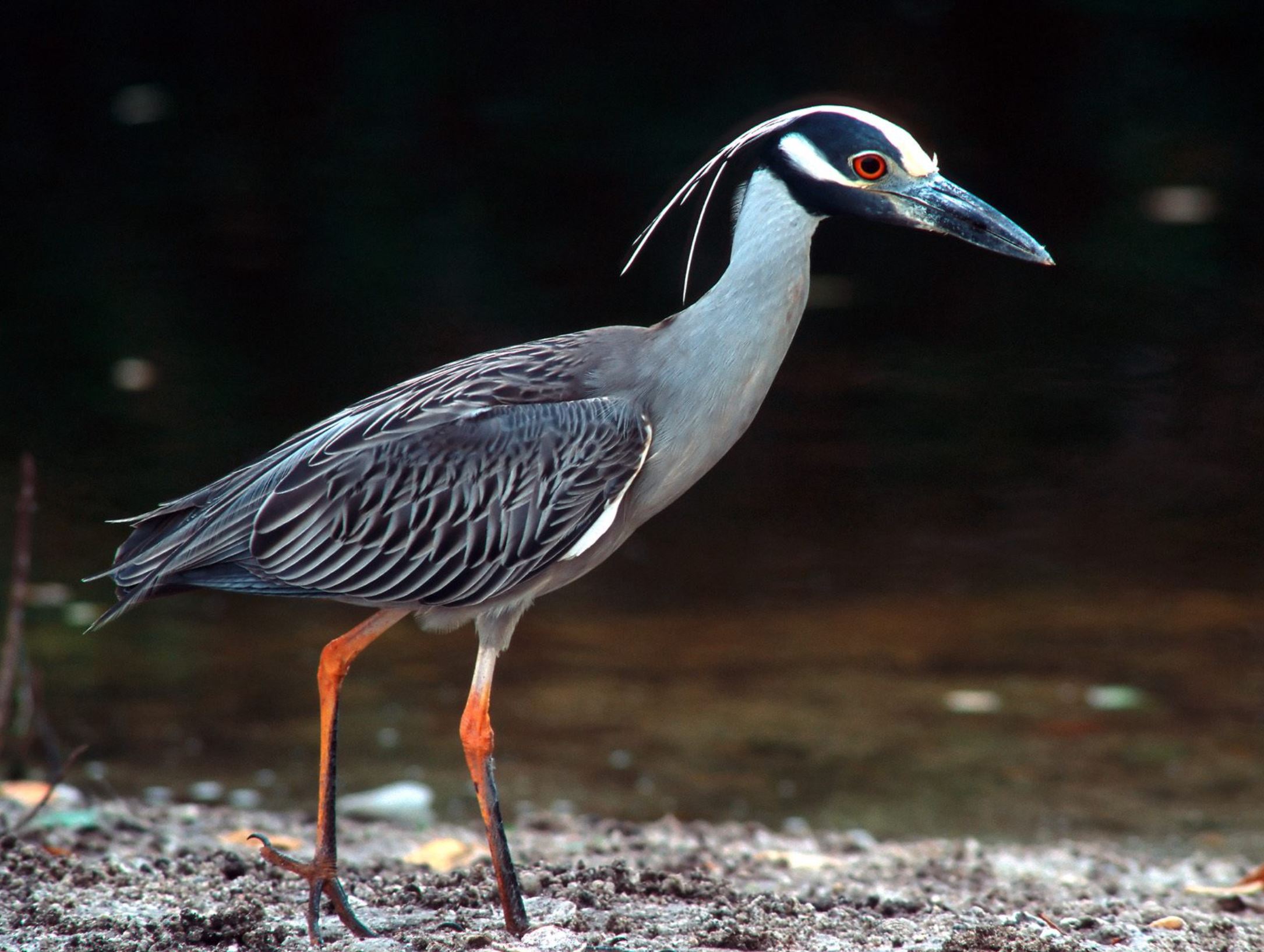
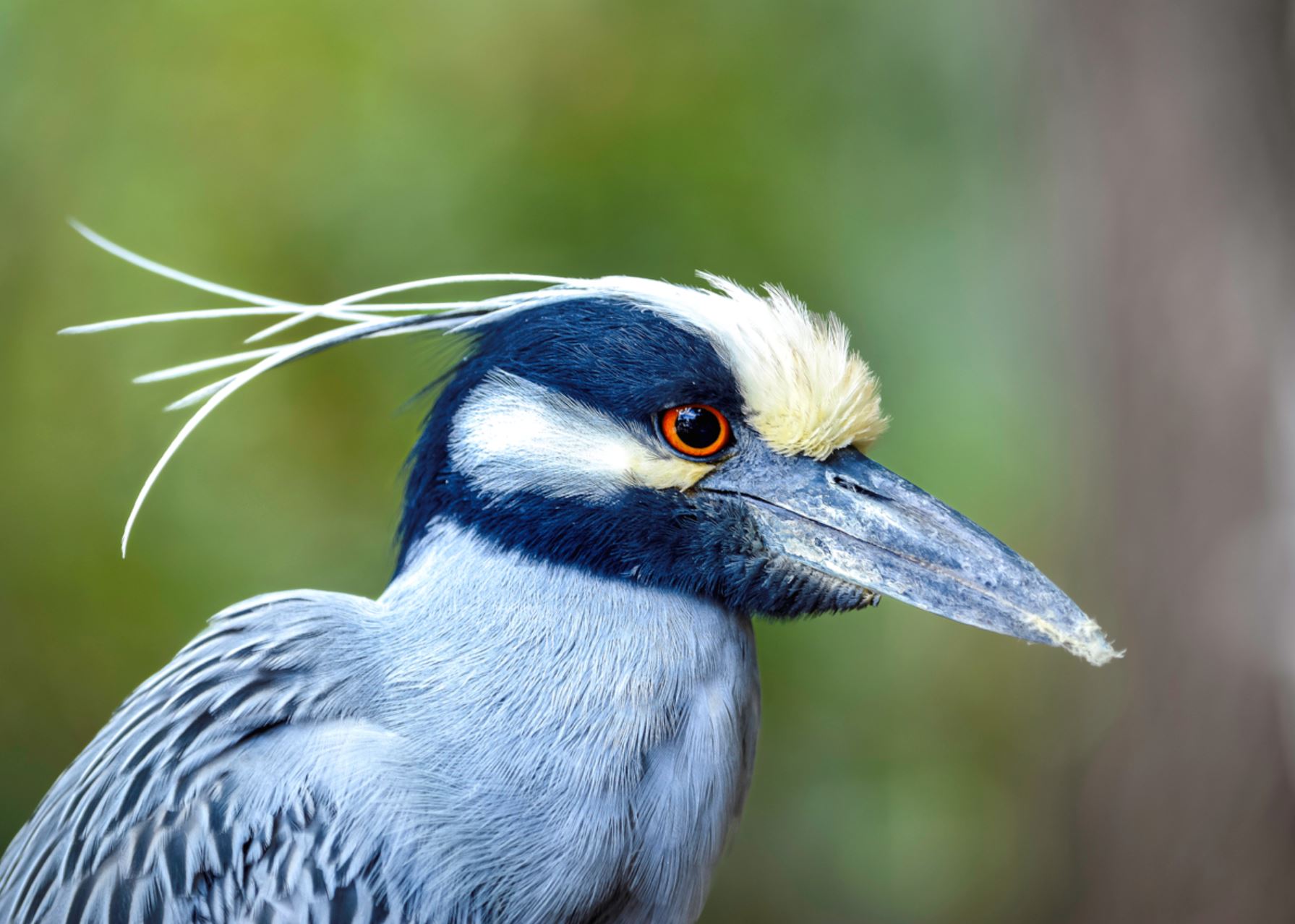
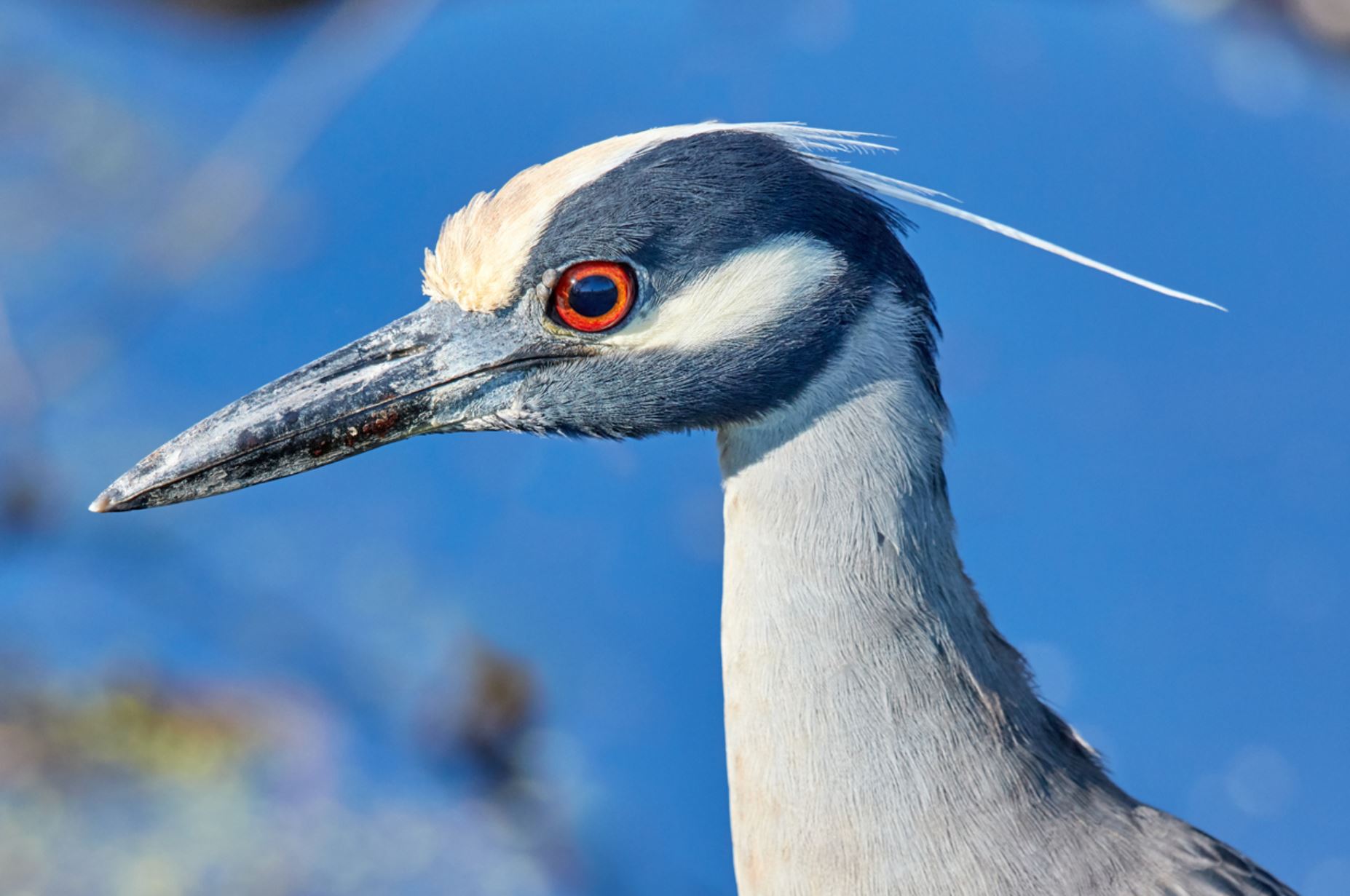
Yellow-crowned Night Heron
The Yellow Crested Night Heron, is a smaller heron, similar in appearance to the Black-crowned Night Heron. The Yellow Crested Night Heron grows to around 21 inches and has a wingspan of 44 inches. It is a fairly small, long legged, short necked Heron with a black bill. It is usually found around ponds, swamps and low-land forests. The Yellow Crested Night Heron is a stocky heron with a powder blue or grey body and brown-and-white mottled wings. Their face is black and white and their crowns/crests are pale yellow and sweeps back as a plume.
Yellow Crested Night Herons have eyes that are large and red and a heavy, black beak.
The Yellow Crested Night Heron is a very rare and elusive bird. To find this bird, like any bird, it is necessary to understand what its life is like.
When and where it will be is predictable, but sometimes it is just luck. The sun going down and coming up sets a timetable of activity. High tide and low tide can provide for many a time to eat or a time to build nests.
The Yellow Crested Night Heron is a difficult bird to see. It is called a Night Heron because of its nocturnal habits. It likes cool sleeping spots and nesting over still water. It seems to pick dark shade deep in the woods or caves at the edges of lagoons or in a gallery of trees that stand in water.
The Yellow Crested Night Heron lays pale blue-green eggs in a platform of sticks with a depression in the centre that islined with leaves . . . not easy to visit as it seems to prefer branches that protrude over water.
The Yellow Crested Night Heron feeds upon crayfish, mussels, frogs, snails and small snakes. Its yellowish green legs stand in the water about 2 or 3 inches deep to snatch small coral blue crabs. It throws them down its throat in a typical heron manner. Their common flight call is a high, squawking bark that sounds like ‘kowk’ or ‘kaow’.
- Animal Group: Birds
- Scientific Name: Nyctanassa violacea
- Animal Average Size: 21 in
- Animal Average Weight: 650 – 800 g
Places where you may see yellow-crowned Night Heron in Galapagos: Fernandina, Isabela, Santiago, Genovesa, Santa Cruz, Floreana, San Cristobal
Location
Mr. Frobeen can give you precise information about the ships.
Mr. Frobeen will be happy to advise you by phone at +49 (0)7633 9399360 or via email info@frobeen.de
If you want to book, what are the payment methods?
The reservation is gratis as an option.
If you want to make an fixed booking, there is to pay a deposit of 20%.
The remaining payment is due 4 weeks before departure. In individual cases, such as diving cruises, other rules apply. Information on request.
- Your payments are insured against bankruptcy!